Basic Skills Math SLOs
advertisement

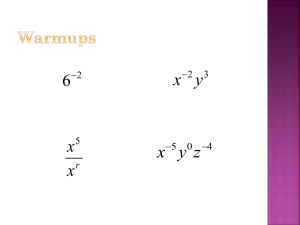
Math 50 Modern College Arithmetic and Pre-Algebra Math 50 Student Learning Outcomes 1. Demonstrate the ability to add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers, integers, fractions, mixed numbers, and decimals. 2. Solve Linear Equations by: a) Using the Addition/Subtraction property of equality, b) Using the Multiplication/Division property of equality. c) Using both the above properties together. 3. Translate English sentences to algebraic equations. 4. Simplify mathematical statements using the correct order of operations. 5. Calculate the perimeter and area of rectangles and triangles. Calculate the area and circumference of a circle. 6. Find equivalent forms of number (i.e. change fractions to decimals, change percents to fractions, change fractions to percents, change decimals to fractions, change decimals to percents, change percents to decimals, change mixed numbers to improper fractions, change improper fractions to mixed numbers). 7. Round whole numbers and decimals appropriately as directed. 8. Apply the concept of percent to real-world application such as sales tax, discount, and simple interest. Math A Elementary Algebra Math A Course Outcomes February 2004 1. Simplify algebraic expressions using the correct order of operations. 2. Solve formulas and linear equations for a specified variable. 3. Solve application problems by defining a variable, setting up and solving an equation and interpreting the result. 4. Perform algebraic operations on polynomials: factor, add, subtract, multiply, and divide by a monomial. 5. Given a linear equation, graph the line, identify, and interpret x and y intercepts and slope. 6. Write and graph linear equations given a) two points and b) one point and a slope. 7. Solve a system of two linear equations and interpret the solution graphically and algebraically. 8. Solve quadratic equations by factoring and the quadratic formula, including simplifying whole number square roots. 9. Simplify rational expressions with quadratic numerators and denominators. Objectives and Suggested Homework Assignments for Math BA using Introductory Algebra for College Students, 4th edition, by Robert Blitzer, (Prentice Hall, 2006). Please provide feedback and suggestions to Tom Greenwood, Donna Starr, or Rick Brantley so this list can be modified as needed. Thanks in advance for your help! Chapter 1 The Real Number System Section 1.1 Fractions Convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions. Write the prime factorization of a composite number. Reduce or simplify fractions. Multiply fractions. Divide fractions. Add and subtract fractions with identical denominators. Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators. Solve problems involving fractions. 1 – 89 odd, 95 – 105 odd, 117, 118 Section 1.2 The Real Numbers Define the sets that make up the real numbers. Graph numbers on a number line. Express rational numbers as decimals. Classify numbers as belonging to one or more sets of the real numbers. Understand and use inequality symbols. Find the absolute value of a real number. 1 – 33 odd, 45 – 89 odd Section 1.3 Ordered Pairs and Graphs Plot ordered pairs in the rectangular coordinate system. Find coordinates of points in the rectangular coordinate system. Interpret information given by line graphs. 1 – 59 odd, 65, 67 Section 1.4 Basic Rules of Algebra Evaluate algebraic expressions. Use commutative properties. Use associative properties. Use distributive properties. Combine like terms. Simplify algebraic expressions. 1 – 17 odd, 21 – 25 odd, 31 – 73 odd, 83 Section 1.5 Addition of Real Numbers Add numbers with a number line. Find sums using identity and inverse properties. Add numbers without a number line. Use addition rules to simplify algebraic expressions. 1 – 65 odd, 71 – 79 odd, 89 Section 1.6 Subtraction of Real Numbers Subtract real numbers. Simplify a series of additions and subtractions. Use the definition of subtraction to identify terms. Use the subtraction definition to simplify algebraic expressions. 1 – 85 odd, 89 – 95 odd, 101 – 105 odd, 113 Section 1.7 Multiplication and Division of Real Numbers Multiply real numbers. Multiply more than two real numbers. Find multiplicative inverses. Use the definition of division. Divide real numbers. Simplify algebraic expressions involving multiplication. 1 – 95 odd, 99, 105 – 109 odd, 119 Section 1.8 Exponents, Order of Operations, and Mathematical Models Evaluate exponential expressions. Simplify algebraic expressions with exponents. Use the order of operations agreement. Evaluate formulas. 1 – 51 odd, 53 – 87 eoo Chapter 2 Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable Section 2.1 The Addition Property of Equality Check whether a number is a solution to an equation. Use the addition property of equality to solve equations. 1 – 43 odd, 53, 55 Section 2.2 The Multiplication Property of Equality Use the multiplication property of equality to solve equations. Solve equations in the form x c . Use the addition and multiplication properties to solve equations. 1 – 53 odd, 63 – 67 odd, 73 Section 2.3 Solving Linear Equations Solve linear equations. Solve linear equations containing fractions. Identify equations with no solution or infinitely many solutions. 1 – 63 odd, 73 – 77 odd, 83, 84 Section 2.4 Formulas and Percents Solve a formula for a variable. Express a decimal as a percent. Express a percent as a decimal. Use the percent formula. Solve applied problems involving percent change. 1 – 59 odd, 71 – 75 odd, 81 – 85 odd Section 2.5 An Introduction to Problem Solving Translate English phrases into algebraic expressions. Solve algebraic word problems using linear equations. 1 – 33 odd Section 2.6 Solving Linear Inequalities Graph the solutions of an inequality on a number line. Use set-builder notation. Solve linear inequalities. Identify inequalities with no solution or infinitely many solutions. 1 – 57 odd Chapter 3 Problem Solving Section 3.2 Ratio and Proportion Find ratios. Solve proportions. Solve problems using proportions. 1 – 41 odd Chapter 4 Linear Equations and Inequalities in Two Variables Section 4.1 Graphing Equations in Two Variables Determine whether an ordered pair is a solution of an equation. Find solutions of an equation in two variables. Use point plotting to graph linear equations. Use point plotting to graph other kinds of equations. Use graphs of linear equations to solve problems. 1 – 49 odd Section 4.2 Graphing Linear Equations Using Intercepts Use a graph to identify intercepts. Graph a linear equation in tow variables using intercepts. Graph horizontal or vertical lines. 1 – 61 odd Section 4.3 Slope Compute a line’s slope. Use slope to show that lines are parallel. Calculate rate of change in applied situations. 1 – 25 odd, 35 – 45 odd Section 4.4 The Slope-Intercept Form of the Equation of a Line Find a line’s slope and y-intercept from its equation. Graph lines in slope-intercept form. Use slope and y-intercept to graph Ax + By = C. Use slope and y-intercept to model data. 1 – 59 odd Section 4.5 The Point-Slope Form of the Equation of a Line Use the point-slope form to write equations of a line. Write linear equations that model data and make predictions. 1 – 37 odd Section 4.6 Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Determine whether an ordered pair is a solution of an inequality. Graph a linear inequality in two variables. Solve applied problems involving linear inequalities in two variables. 1 – 35 odd Chapter 5 Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities Section 5.1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing Decide whether an ordered pair is a solution of a linear system. Solve systems of linear equations by graphing. Use graphing to identify systems with no solution or infinitely many solutions. 1 – 49 odd Section 5.2 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by the Substitution Method Solve linear systems by the substitution method. Use the substitutions method to identify systems with no solution or infinitely many solutions. Solve problems using the substitution method. 1 – 39 odd Section 5.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by the Addition Method Solve linear systems by the addition method. Use the addition method to identify systems with no solution or infinitely many solutions. Determine the most efficient method for solving a linear system. 1 – 63 odd Section 5.5 Systems of Linear Inequalities Graph the solutions of systems of linear inequalities. 1 – 43 odd Chapter 6 Exponents and Polynomials Section 6.1 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Understand the vocabulary used to describe polynomials. Add polynomials. Subtract polynomials. 1 – 35 odd, 39, 41, 47, 55 – 71 odd, 75 – 81 odd Section 6.2 Multiplying Polynomials Use the product rule for exponents. Use the power rule for exponents. Use the products-to-powers rule. Multiply monomials. Multiply polynomials when neither is a monomial. 1 – 63 odd, 67 – 73 odd, 79 – 83 odd, 101, 103 Section 6.3 Special Products Use FOIL in polynomial multiplication. Multiply the sum and difference of two terms. Find the square of a binomial sum. Find the square of a binomial difference. 1 – 33 odd, 45 – 55 odd, 63 – 73 odd, 83 – 87 odd Section 6.4 Polynomials in Several Variables Evaluate polynomials in several variables. Understand the vocabulary of polynomials in several variables. Add and subtract polynomials in several variables. Multiply polynomials in several variables. 1 – 45 odd, 77, 89 Section 6.5 Dividing Polynomials Use the quotient rule for exponents. Use the zero-exponent rule. Use the quotients-to-powers. Rule. Divide monomials. Check polynomial division Divide a polynomial by a monomial. 1 – 75 odd Section 6.7 Negative Exponents and Scientific Notation Use the negative exponent rule. Simplify exponential expressions. Convert from scientific notation to decimal notation. Convert from decimal notation to scientific notation. Compute with scientific notation. 1 – 109 eoo, 143 – 147 odd Chapter 7 Factoring Polynomials Section 7.1 The Greatest Common Factor and Factoring by Grouping Factor monomials. Find the greatest common factor. Factor out the greatest common factor of a polynomial. Factor by grouping. 7 – 83 odd, 95 Section 7.2 Factoring Trinomials Whose Leading Coefficient is One Factor trinomials with a leading coefficient of one. 1 – 65 odd, 77, 83, 85 Section 7.3 Factoring Trinomials Whose Leading Coefficient is Not One Factor trinomials by trial and error. Factor trinomials by grouping 1 – 85 odd Section 7.4 Factoring Special Forms Factor the difference of two squares. Factor perfect square trinomials Factor the sum and difference of two cubes. 1 – 87 odd, 107 Section 7.5 A General Factoring Strategy Recognize the appropriate method for factoring a polynomial. Use a general strategy for factoring polynomials. 1 – 91 odd, 109 Section 7.6 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring Use the zero-product principle. Solve quadratic equations by factoring. Solve problems using quadratic equations. 1 – 59 odd, 67, 69, 89 Chapter 8 Rational Expressions Section 8.1 Rational Expressions and Their Simplification Find numbers for which a rational expression is undefined. Simplify rational expressions. Solve applied problems involving rational expressions. 1 – 83 odd Section 8.2 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Multiply rational expressions. Divide rational expressions. 1 – 63 odd Section 8.3 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions with the Same Denominator Add rational expressions with the same denominator. Subtract rational expressions with the same denominator. Add and subtract rational expressions with opposite denominators. 1 – 63 odd Section 8.4 Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions with the Different Denominators Find the least common denominator. Add and subtract rational expressions with different denominators. 1 – 81 odd Section 8.5 Complex Rational Expressions Simplify complex rational expressions by dividing. Simplify complex rational expressions by multiplying by the LCD. 1 – 39 odd Section 8.6 Solving Rational Equations Solve rational equations. Solve problems involving formulas with rational expressions. 1 – 43 odd Section 8.7 Applications Using Rational Equations and Variation Solve problems involving motion. Solve problems involving work. Solve problems involving similar triangles. 1 – 23 odd Chapter 9 Roots and Radicals Section 9.1 Finding Roots Find square roots. Use a calculator to find decimal approximations for irrational square roots. 1 – 25 odd, 31 – 45 odd Section 9.2 Multiplying and Dividing Radicals Multiply square roots. Simplify square roots. 1 – 91 eoo Section 9.3 Operations with Radicals Add and subtract radicals 1 – 49 odd Section 9.4 Rationalizing the Denominator Rationalize denominators containing one term. 1 – 23 odd Chapter 10 Quadratic Equations and Functions Section 10.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by the Square Root Property Solve quadratic equations using the square root property. Solve problems using the Pythagorean Theorem. Find the distance between two points. 1 – 39 odd Section 10.3 The Quadratic Formula Solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. Determine the most efficient method to use when solving a quadratic equation. 1 – 51 odd