To find the focal length of a Concave Mirror
advertisement

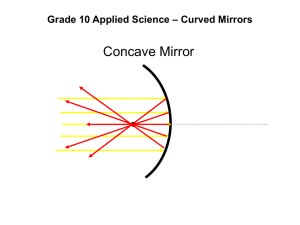
Objective of the Experiment: To measure the focal length of a concave mirror. Introduction The following experiment will define the method to find out the focal length of a Concave Mirror using a formula or a graph. The distance from the focal point to the pole is called the Focal length of a mirror. Concave mirrors have the shape as shown in below figures. The formula states that “The distance of the image from the concave mirror changes as the distance of the object changes and these distances are only the same when the object is at the center of the curvature. For a concave mirror: If the image is real 1 1 1 f u v If the image is virtual 1 1 1 u v f Where: f is the focal length. u is the distance from the object (cross threads) to the mirror v is the distance from the image (screen) to the mirror. Equipment Used: Concave mirror and a stand Ray box, Illuminated cross-threads to be used as an object White sheet of paper to be used as screen Metre stick. Method 1) Place the concave mirror on a stand and find the approximate value of the focal length of the concave mirror by focusing an image of a distant object onto the screen. Measure and record the distance from the image to the mirror. This is the approximate focal length of the concave mirror. 2) Set up the equipment as shown in the figure below by placing an illuminated cross-thread fixed on a cardboard as an object in front of the concave mirror and the ray box behind the object. 3) Switch on the ray box for the light beam to fall on the mirror. 4) Locate the image of the cross-threads on the screen and adjust the position of the screen until the image of the cross-threads are in focus. 5) Using a metre stick, measure and record the distance from the object (cross threads) to the mirror (u) 6) Using a metre stick, measure and record the distance from the screen to the mirror. (v) 7) Repeat this method and record the results u and v by placing the object at different distances from the concave mirror. u (in cm) v( in cm) 15 20 25 30 35 40 44 37 26 25 24.5 24 8) The focal length of the mirror can then be calculated by using the formula 1 1 1 f u v and the results are given in below table. Results 1 u 1 v f 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.035 0.028 0.025 0.023 0.027 0.038 0.04 0.041 0.042 12.0 13.3 14.5 12.9 12.8 14.9 Common Mistakes: Error in measuring an approximate value for focal length f. To do this, focus light from a distant object (e.g. a window) onto a sheet of paper using the concave mirror. Measure the distance from the paper to the mirror using a ruler – this is an approximate value for f. Not ensuring the image of the cross-threads on the screen is in definite focus The object must not be placed inside the focus. Not telling the examiner how to measure U and V Not using the correct formula when calculating f , the focal length 1∕u + 1∕v = 1∕f When getting the value of f from a graph: - not plotting 1∕u and 1∕v - trying to find the slope of the line – NO SLOPE! The line does not go through the origin (0,0) The focal length is found by intersecting points from the graph. As this is a straight line graph, the line cuts the x-axis when y=0 (co-ordinate geometry) Similarly, the line 1 ∕ u + 1 ∕ v = 1 ∕ f cuts the 1 ∕ u axis when 1∕ v = 0 Therefore, 1 ∕ u + 0 = 1 ∕ f => 1 ∕ u = 1 / f Likewise, 1 / v = 1 / f Draw graph approximately 2/3 of the page to allow for plotting off the graph. Method II The focal length from the graph can be calculated by using the formula and 1 taking the values from the graph where the line cuts the x-axis ( ) and the y-axis v 1 ( ). u 1 1 1 f u v 1 1 1 f u v → (0, 0.085) where u is equal to 0(from the graph) and v is equal to 0.065 1 1 1 1 f 11.8cm = f v 0.085 f → (0.068,0) where u is equal to 0.068 and v is equal to 0. Average focal length = 1 1 1 f 14.7cm f u 0.068 26.5 13.3cm 2 Conclusion From the above results, we can calculate the average focal length of a concave mirror: Average Focal Length of Concave mirror = 13.3cm Precautions: Errors can be made while: 1) deciding when the image is in sharp focus 2) Measuring the distances of u and v with metre stick. Common Mistakes: Error in measuring an approximate value for focal length f. To do this, focus light from a distant object (e.g. a window) onto a sheet of paper using the concave mirror. Measure the distance from the paper to the mirror using a ruler – this is an approximate value for f. Not ensuring the image of the cross-threads on the screen is in definite focus The object must not be placed inside the focus. Not telling the examiner how to measure U and V Not using the correct formula when calculating f , the focal length 1∕u + 1∕v = 1∕f When getting the value of f from a graph: - not plotting 1∕u and 1∕v - trying to find the slope of the line – NO SLOPE! The line does not go through the origin (0,0) The focal length is found by intersecting points from the graph. As this is a straight line graph, the line cuts the x-axis when y=0 (co-ordinate geometry) Similarly, the line 1 ∕ u + 1 ∕ v = 1 ∕ f cuts the 1 ∕ u axis when 1∕ v = 0 Therefore, 1 ∕ u + 0 = 1 ∕ f => 1 ∕ u = 1 / f Likewise, 1 / v = 1 / f Draw graph approximately 2/3 of the page to allow for plotting off the graph. Sample Leaving Certificate Questions: •Year 2007 Section A Question 3(Higher Level) 3. In an experiment to measure the focal length of a concave mirror, an approximate value for the focal length was found. The image distance v was then found for a range of values of the object distance u. The following data was recorded. u/cm 15.0 20.0 25.0 30.0 35.0 40.0 v/cm 60.5 30.0 23.0 20.5 18.0 16.5 How was an approximate value for the focal length found? What was the advantage of finding the approximate value for the focal length? (10) For a concave mirror 1 1 1 f u v 1 1 1 0 If u is very much greater than the focal length, then u ,therefore f v and f=v Using the concave mirror, focus a distant object, e.g. a tree, on a sheet of paper. The distance from the mirror to the paper is approximately equal to the focal length of the mirror. This method is useful as it gives some idea of the focal length of the concave mirror and the actual value can be measured by using a more accurate method. Describe, with the aid of a labeled diagram, how the position of the image was found. (12) Set up the equipment as shown in the figure below by placing an illuminated cross-thread fixed on a cardboard as an object in front of the concave mirror and the ray box behind the object. Switch on the ray box for the light beam to fall on the mirror. Locate the image of the cross-threads on the screen and adjust the position of the screen until the image of the cross-threads are in focus. Calculate the focal length of the concave mirror by drawing a suitable graph based on the recorded data. (18) 1 (in cm) u 1 (in cm) v f(in cm) 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.028 0.025 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.06 12.5 12.5 12.5 12.5 11.4 11.8 Average Focal Length: 12.2cm The focal length from the graph: 1 1 1 f u v (0, 0.08) where u = 0 and v = 0.08 1 1 1 f 12.5cm f v 0.08 1 1 1 f u v (0.082,0) where u = 0.082 and v = 0 1 1 1 f 12.19cm f u 0.082 Average focal length: 24.69 12.3cm 2 •Year 2002 Section A Question 3(Ordinary Level) 3. A student carried out an experiment to measure the focal length of a concave mirror. The student placed an object at different positions in front of the mirror so that a real image was formed in each case. The table shows the measurements recorded by the student for the object distance u and the image distance v. u/cm 20 30 40 50 v/cm 64 43 41 35 Draw a labeled diagram showing how the apparatus was arranged. (9) Describe how the student found the position of the image. (7) Set up the equipment as shown in the figure below by placing an illuminated cross-thread fixed on a cardboard as an object in front of the concave mirror and the ray box behind the object. Switch on the ray box for the light beam to fall on the mirror. Locate the image of the cross-threads on the screen and adjust the position of the screen until the image of the cross-threads is in focus. Show on your diagram the object distance u and the image distance v. (6) Shown above Using the formula 1/ f =1/ u +1/ v or otherwise and the above data, find an average value for the focal length f of the mirror. (18) 0.05 0.03 0.025 0.02 1 (in cm) u 0.016 0.023 0.024 0.029 1 (in cm) v f 15.15 18.87 20.4 20.40 Average Focal Length: 18.79cm •Year1998 Section B Question 6(Ordinary Level) 6. In an experiment to determine the focal length of a concave mirror an object was placed at different positions in front of the mirror so that a real image was produced in each case. The following values for the object distance and the image distance were obtained: Object Distance, u/cm Image Distance, v/cm 15 28.9 25 16.6 35 14.2 Sketch a diagram to show how the apparatus might have been arranged in this experiment. (9) Explain how the position of the image might have been found. (12) Set up the equipment as shown in the figure by placing an illuminated crossthread fixed on a cardboard as an object in front of the concave mirror and the ray box behind the object. Switch on the ray box for the light beam to fall on the mirror. Locate the image of the cross-threads on the screen and adjust the position of the screen until the image of the cross-threads is in focus. Using the formula, 1/f = 1/u + 1/v, or otherwise, use the above data to find the average focal length, f, of the mirror. (18) 1 (in cm) u 1 (in cm) v f(in cm) 0.066 0.04 0.029 0.035 0.06 0.07 9.9 10 10.10 Average Focal Length: 10cm