Answers to Venn diagram problems

Answers to Venn diagram problems
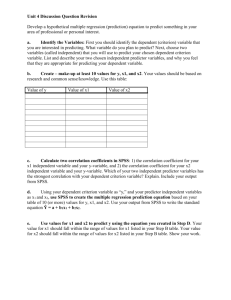
1. a.
40% b.
8% c.
Forward method.
Step 1: SPSS will select X2 and test the contribution of this variable. It’s contribution of 17% is significant.
Step 2: Out of the remaining variables SPSS will select the predictor that has provides the largest unique contribution, above and beyond what X2 provides. X1 provides the largest unique contribution. SPSS finds that this unique contribution of 15% is significant.
Step 3: SPSS now tests the unique contribution of the one remaining predictor, X3, to see if it contributes a significant amount of variability to the regression model. X3’s contribution of 8% is significant, so it is also added to the model.
The final model is that all three predictor are used to predict scores for variable Y.
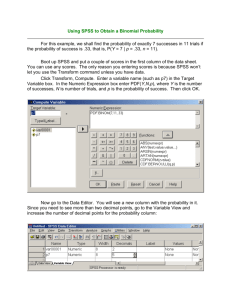
2. a.
30% b.
6% c.
Forward Method:
Step 1: Variable X2 has the largest squared correlation with variable Y so it is considered first for inclusion in the regression equation. X2’s contribution of 22% is significant so it is added to the model.
Step 2: Out of the remaining predictor variables SPSS selects the predictor variables that provides the largest unique contribution to the regression model. Variable X3 is considered second because it provides a unique contribution of 6%. This unique contribution is significant so X3 is added to the repression equation.
Step 3: SPSS will now evaluate the unique contribution of the one remaining predictor variable, X1. The unique contribution of X1 (2%) is not significant so it is not added to the model.
The final model obtained from the forward method is that predictor variables X2 and X3 are included in the regression equation. d.
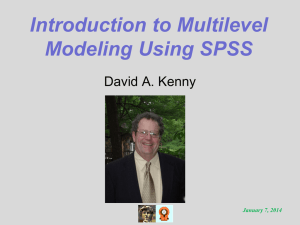
Backward Method
SPSS generates a regression using all of the predictor variables.
In the next step, SPSS will identifies the variable that makes the smallest unique contribution to the model. In this case, that could be X1 because its unique contribution is 2%.
SPSS tests the unique contribution of X1 of 2% and tests it to see if it is significant. It’s not, so it removes X1 from the equation.
Of the remaining two predictor variables (X2 and X3) SPSS will identify the predictor that makes the smallest unique contribution. X2 makes a unique contribution of 11% and X3 makes a unique contribution of 6%.
SPSS tests the unique contribution of X3 to see if it is significant. It is so
SPSS will keep variables X2 and X3 as predictor variables.