fem3002_1328514193. DR. ROZUMAH
advertisement

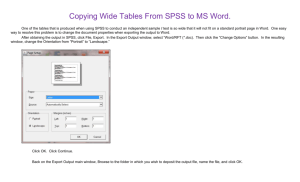
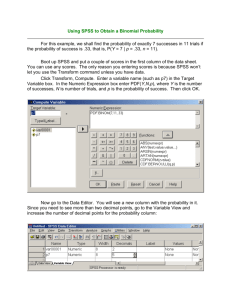
Name of Course: Research Methodology Course Code: Credit Hour: FEM 3002 3 (2+1) This course comprises 2 hours of lecture and 3 hours of laboratory work per week. To fulfill the requirement for the laboratory work will complete 2 assignments, which are: 1) Research proposal, and 2) Managing and analyzing data using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). Professor Dr. Rozumah Baharudin Professor in Family and Parenting Ecology Tel: 03-89467082 Faks: 03-89467093 email: rozumah@yahoo.com Alamat: Department of Human Development & Family Studies Fakulti Ekologi Manusia, UPM 43400 UPM, Serdang, Selangor Course synopsis Introduction to research design and analysis in Human Development. Meaning of science, scientific research and its application in Human Development. Research planning process, data analysis and interpretation, report writing and presentation of research findings. (Pengenalan kepada rekabentuk dan analisis penyelidikan di dalam Pembangunan Manusia. Pengertian Sains, penyelidikan saintifik dan penggunaannya di dalam Pembangunan Manusia. Perancangan dan proses penyelidikan, analisis dan interpretasi data, penulisan dan penyampaian hasil penyelidikan). Module Objectives FEM 3002 is a compulsory course for the Bachelor Science (Human Development) program. At the end of this module students will be able to: • discuss the philosophy of research, and the concepts of science and the scientific methods. • describe the research design in human development • describe the steps in preparing and conducting a research project • analyze and interpret research data and prepare a research report. This course will require 28 hours of lecture ( 2 x 14 weeks) and at least 42 hours of laboratory work (3 x 14 weeks). Given that this is a long distance education course students will not have the opportunity to attend a hands-on laboratory work; however, the assignments and exercises in the module will allow students to apply the “learn by doing” approach on their own. This module is divided into 9 units that cover the various main topics. Table 1 presents the weekly division of topics that students should follow closely in order to study the materials in this module. Table 2 provides a detail content of each unit in the module. Unit Title Week 1. Philosophy of Research 1 2. Research Process 2 3. Research Design 3-4 4. Writing Research Proposal 5-6 5. Measurement 6. Sampling 7. Data Collection 10-11 8. Data Analysis: 12-13 7 8-9 Descriptive and Inferential Statistics 9. Writing Research Report 14 Unit 1. Title Philosophy of Research Research Concept Research Objective Research and the Scientific Method Types of Research 1. Summary Research Processes Identifying Problems Developing Hypothesis Data Collection Data Analysis Writing Report 1. Summary Research Design Meaning and Objective of Research Design Non-Experimental Experimental dan Experimental Quasi 1. Summary Preparing Research Proposal Proposal Format Proposal Checklist f. Lab Work/Assignment To fulfill 42 hours of lab work, students need to complete the following assignments: •Lab/Assignment I: Write a research proposal •Lab/Assignment II: SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) on-line tutorial report) The lab work will be explained further during the class meeting at UPM. Please take note that the laboratory contents and exercises may change from one semester to another, and students will be informed of the changes during each class meeting. Assignment I: Research Proposal (10 pages) For this assignment you will write a research proposal on a topic that is related to your interest and program of study. Before writing, you need to understand the whole topics related to research methodology. Please use the proposal outline/guideline given to you in Unit 4. Failing to abide by the guidelines given will have negative influence on your marks. Assignment II: On-line SPSS Tutorial Exercise (30 pages) • • • • • • • • For this assignment you are required to study and work through the online SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) tutorial at the following sites: http://www.psych.utoronto.ca/courses/c1/spss/page5.htm. http://www.mhhe.com/socscience/psychology/runyon/spss/spss.html http://www.asu.edu/spss/v12/index.html From the above online tutorials, learned everything about the basics of SPSS for use in data analyses. Write a report on what you have learned and provide examples where necessary. In the report be sure you include aspects related to the following topics: Data entry Descriptive statistics Inferential statistics (such as Chi-square, T-tests, Correlations, Regression, · Oneway ANOVA and Factorial ANOVA) Your marks will be determined by well you can explained what SPSS is, how we can utilized it for data analyses, and the steps and meaning of descriptive and inferential statistics. Course Evaluation • The course evaluation is conducted in 2 ways: 1) Course work comprising the lab-work/assignments (2 reports = 35%), and Mid-semester test (which covers Unit 1 to 4 = 15%), and 2) Final examination (which covers all topics - Unit 1-9 = 40%). • Assignment 1 (15%) • Assignment 2 (20%) • Mid-semester Test (25%) • Final examination (40%) • 100% Mid-semester Test Students are required to sit for the midsemester test. Questions in the test will be in both objective and subjective formats. The test will cover Unit 1 to 4, and aspects related to Assignment 1. This test carries 35% of the total marks. Final Examination • The final exam is comprehensive. This means that questions will be developed based on all the units in this module. Students need to prepare to be tested on materials learned from Unit 1 to 9 and aspects related to Assignments 1 and 2. The questions will be in the objective and subjective format. UNIT I PHILOSOPHY OF RESEARCH PHILOSOPHY OF RESEARCH The term philosophy derives from a combination of the Greek words philos = love sophia = wisdom Nature of knowledge and belief. In research the concerned is on the investigation of what distinguishes mere belief from knowledge. Research often makes use of all four of these ways of knowing: 1. INTUITIVE (when coming up with an initial idea for research) 2. AUTHORITATIVE (when reviewing the professional literature) 3. LOGICAL (when reasoning from findings to conclusions) 4. EMPIRICAL (when engaging in procedures that lead to these findings) The empirical knowledge, is what most modern research acquisition aims at establishing, which is known as empirical research. • Research is an activity that search answers for questions and/or finding solutions to problem(s). • Research must be done systematically and scientifically. • In the inductive reasoning, research is designed to identify components that eventually lead to a conclusion or generalization. • In the deductive reasoning, the conclusion is stated first before the research is done. • Research can be divided based on its purpose, design and approach. • Research can be divided according to types and categories based on its objective, application and design. • Research must be conducted according a certain processes. • Five research processes have been described in this Unit, beginning from identifying problem, developing hypothesis, data collection, data analysis and report writing. • Research design refers to the detail plan of a research. • Research design can be categorized into nonexperimental and experimental • Non-experiemental research can be divided into 4 types, which are historical research, descriptive, developmental and correlation. • Experimental research can be classified according to two types, which are true experiment and quasi experiment. • Preparing a research proposal is an important step in research as an effort to gain approval from your research assessor or committee. It is also an important document for you to submit in applying for research funding. • There are several important elements in a research proposal including the title, introduction, and statement of problem, significance of study, objective of study, hypothesis, and methodology (location, sampling, data collection, & data analysis). Students must follow the research proposal guideline provided by their academic discipline or faculty underwhich they pursue their degree. • A well-prepared proposal is important in guiding to complete a successful research. Please see detail notes of Unit 1 to 4 in the FEM3002 Module