Determining Sample Sizes for the Purpose of Mean Estimation
advertisement

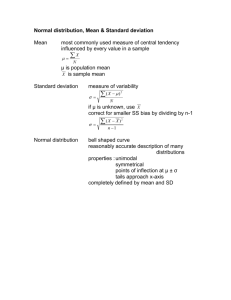
Determining Sample Sizes for the Purpose of Estimation Survey Sampling Examples 1-2 were designed to challenge your ability to estimate means within 95% confidence. The current exercise was developed to challenge your ability to determine what the sample size would be in both examples given a bound and estimate of population variance. Mean Estimation for a Simple Random Sample Example 1: N = 1,850, a 5 point Likert item is used. Problem 1 Assume that a population variance of .2 has been obtained, and that the board members want a bound of + .10. Problem 2 Assume that the board members want a bound of + .05, and that you have no estimate of population variance (use Tchebysheff's theorem for a 5 point Likert item). Problem 3 Assume that a population standard deviation of .4 has been obtained, and that the board members want a bound of + .07. Example 2: N = 20,000, a 10-item questionnaire is used (each item scaled 1 to 5) for the purpose of producing satisfaction scores ranging from 10 to 50. Problem 4 Assume that a population standard deviation of 8 has been obtained, and that the financial aid department wants a bound of + 5 points. Problem 5 Assume that financial aid department wants a bound of + 2 points around the mean score, and that you have no estimate of population variance (use Tchebysheff's theorem). Problem 6 Assume that a population variance of 49 has been obtained, and that the financial aid department wants to assume a standard error of 2.0. Further assume that financial aid department wants to be roughly 95% confident in its estimate. Proportion Estimation for a Simple Random Sample Example 3: A University president wants to conduct a simple random sample of college students to determine the proportion of students in favor of converting the semester system to the quarter system. How many students should she have interviewed? (Assume N = 2000 and a desired bound of .02). Use the maximum variance possible for a proportion in the population. Mean Estimation for a Stratified Random Sample Example 4: A school desires to estimate the average score that may be obtained on a reading comprehension exam for students in the sixth grade. The school’s students are grouped into three tracks, with the fast learners in track I and slow learners in track III. The school decides to stratify on tracks since this method would reduce the variability of test scores. The sixth grade contains 55 students in track I, 80 students in track II, and 65 students in track III. A stratified random sample of students, proportionately allocated, is desired. Assuming a bound of .05 and prior evidence that the scores have a variance of 10, determine what sample size is needed.