Parameter - Penn State Department of Statistics
advertisement
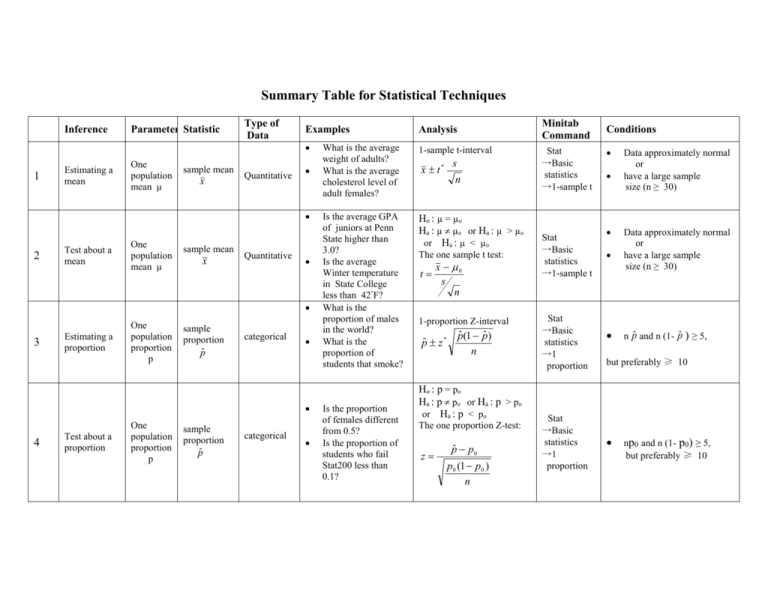
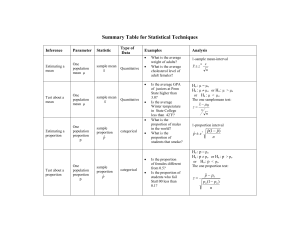
Summary Table for Statistical Techniques Inference 1 Estimating a mean Parameter Statistic One population mean µ sample mean x Type of Data Quantitative Analysis What is the average weight of adults? What is the average cholesterol level of adult females? 1-sample t-interval Is the average GPA of juniors at Penn State higher than 3.0? Is the average Winter temperature in State College less than 42ْ F? What is the proportion of males in the world? What is the proportion of students that smoke? Ho : µ = µo Ha : µ µo or Ha : µ > µo or Ha : µ < µo 2 Test about a mean One population mean µ sample mean x Quantitative 3 Estimating a proportion One population proportion p sample proportion categorical p̂ 4 Test about a proportion One population proportion p sample proportion p̂ categorical Minitab Command Examples Is the proportion of females different from 0.5? Is the proportion of students who fail Stat200 less than 0.1? x t * s n The one sample t test: x 0 t s n 1-proportion Z-interval pˆ z * pˆ (1 pˆ ) n Ho : p = po Ha : p po or Ha : p > po or Ha : p < po The one proportion Z-test: z pˆ p0 p0 (1 p0 ) n Stat →Basic statistics →1-sample t Stat →Basic statistics →1-sample t Stat →Basic statistics →1 proportion Stat →Basic statistics →1 proportion Conditions Data approximately normal or have a large sample size (n ≥ 30) Data approximately normal or have a large sample size (n ≥ 30) n p̂ and n (1- p̂ ) ≥ 5, but preferably ≥ 10 np0 and n (1- p0) ≥ 5, but preferably ≥ 10 Inference Parameter Statistic Type of Data Examples 5 Estimating the difference of two means difference in two population means µ1-µ2 difference in two sample means Quantitative x1 x 2 6 Test to compare two means difference in two population means µ1-µ2 difference in two sample means Quantitative x1 x 2 7 Estimating a mean with paired data mean of paired difference µD sample mean of difference Quantitative d 8 Test about a mean with paired data mean of paired difference µD sample mean of difference d Quantitative How different are the mean GPAs of males and females? How many fewer colds do vitamin C takers get, on average, than non vitamin C takers? Do the mean pulse rates of exercisers and non-exercisers differ? Is the mean EDS score for dropouts greater than the mean EDS score for graduates? What is the difference in pulse rates, on the average, before and after exercise? Is the difference in IQ of pairs of twins zero? Are the pulse rates of people higher after exercise? Minitab Command Analysis two-sample t-interval ( x1 x 2 ) t * s1 2 s 2 2 n1 n2 Ho : µ1 = µ2 Ha : µ1 µ2 or Ha : µ1 > µ2 or Ha : µ1 < µ2 The two sample t test: t ( x1 x 2 ) 0 s1 2 s 2 2 n1 n 2 paired t-interval d t* sd n Ho : µD = 0 Ha : µD 0 or Ha : µD > 0 or Ha : µD < 0 d 0 t sd n Stat →Basic statistics →2-sample t Conditions Stat →Basic statistics →2-sample t Stat →Basic statistics →Paired t Stat →Basic statistics →Paired t Independent samples from the two populations data in each sample are about normal or large samples (ni ≥ 30) independent samples from the two populations data in each sample are about normal or large samples (ni ≥ 30) differences approximately normal or have a large number of pairs (n ≥ 30) differences approximately normal or have a large number of pairs (n ≥ 30) 9 10 Inference Parameter Statistic Estimating the difference of two proportions difference in difference in two population two sample proportions proportions p1-p2 pˆ 1 pˆ 2 Test to compare two proportions Relationship 11 in a contingency table 12 Regression Test the slope difference in difference in two two sample population proportions proportions pˆ 1 pˆ 2 p1-p2 relationship between two categorical variables or difference in two or more population proportions Type of Data Examples How different are the percentages of male and female categorical smokers? How different are the percentages of upper- and lowerclass binge drinkers? Is the percentage of males with lung cancer higher than the Percentage of females categorical with lung cancer? Are the percentages of upper- and lower-class binge drinkers different? Analysis Minitab Command Conditions two-proportions Z-interval ( pˆ 1 pˆ 2 ) z * pˆ 1(1 pˆ 1) pˆ 2(1 pˆ 2) n1 n2 Ho : p1 = p2 Ha : p1 p2 or Ha : p1 > p2 or Ha : p1 < p2 The two proportion z test: z pˆ 1 pˆ 2 pˆ (1 pˆ ) pˆ (1 pˆ ) n1 n2 Stat→Basic statistics →2 proportions independent samples from the two populations n1 p̂1 , n1(1- p̂1 ), n2 p̂ 2 and n2(1- p̂ 2 )≥ 5, preferably 10 Stat→Basic statistics →2 proportions independent samples from the two populations n1 p̂1 , n1(1- p̂1 ), n2 p̂ 2 and p̂ 2 )≥ 5, preferably 10 Ho : The two variables are the observed counts in a contingency table Relationship between two Estimated Quantitative Slope b1 Data Is there a relationship between smoking and lung cancer? categorical Do the proportions of students in each class who smoke differ? not related Ha : The two variables are related The chi-square statistic: 2 all cells Stat →Tables →CrossTabulation And Chi-Square Stat →Regression →Regression Linearity No extreme outliers Constant Var. and Normality (Observed Expected) 2 Expected Ho: β1=0 is there a linear relation Ha: β1≠ 0 Quantitative Between father’s height Know how to find the test And son’s height? Statistic from Minitab output all expected counts should be greater than 1 at least 80% of the cells should have an expected count greater than 5