Measurement
advertisement

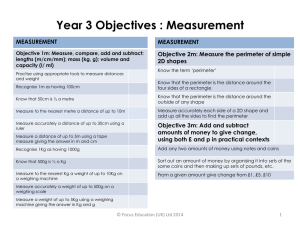
Kindergarten Grade 1 use simple measurement terms correctly (e.g., tall/short, big/small, empty/full, heavy/light, tomorrow/yesterday); order two or more objects according to size or mass (e.g., the Three Bears); use non-standard measuring device appropriately (e.g., string, scoops, sugar cubes, sand timer); use some standard measuring device appropriately (e.g., tape measure, balance scale, thermometer, clock); identify the values of some coins. UNITS OF MEASURE compare two objects and identify similarities and differences (e.g., compare the length and width of two pencils); represent the results of measurement activities using concrete materials and drawings; demonstrate that a non-standard unit is used repeatedly to measure (e.g., count the number of floor tiles to measure the length of the classroom); use mathematical language to describe dimensions (e.g., height, length); select an appropriate non-standard unit to measure length; estimate, measure, and record the linear dimensions (e.g., length, height) of objects using non-standard units, and compare and order objects by their linear dimensions; order sequences of events orally and with pictures; demonstrate an understanding of the passage of time by comparing the duration of various activities (e.g., walking home will take as long as watching one television show); name the days of the week in order, and the seasons; estimate and measure the passage of time using nonstandard units; read analog clocks, and tell and write time to the hour and half-hour; relate temperature to their daily activities; demonstrate an understanding of the value of some coins (1¢, 5¢, 10¢); represent a given value of coins up to 10¢ using concrete materials or drawings; name coins up to $2 and state the value of pennies, nickels, and dimes; use appropriate language to describe relative times, sizes, temperatures, amounts of money, areas, masses, and capacities (e.g., tallest, warmer); use non-standard units to solve oral measurement problems related to everyday issues; PERIMETER AND AREA demonstrate an understanding of the relationship between the tiling of a surface and the number of units needed to cover the surface; estimate and count the number of uniform and non uniform shapes that will cover a surface; CAPACITY, VOLUME, AND MASS estimate, measure, and record the capacity of containers using non-standard units, and compare the measures; estimate, measure, and record the mass of objects using non-standard units, and compare the measures. Measurement Grade 2 UNITS OF MEASURE demonstrate an understanding that the measure of one object can be used to describe a similar attribute of another object (e.g., the mass of a box can be used to measure the mass of a larger box); record the results of measurement activities in a variety of ways (e.g., in graphs, stories); demonstrate an understanding that a standard unit of measure is used to describe the measure of an object (e.g., a metre length is used repeatedly to describe the length of a room); demonstrate an understanding of some standard units of measure: for length and distance (centimetre, metre) and time (second, minute, hour, day); use the terms centimetre and metre in measurement and describe the relationship between the two linear measures; select an appropriate non-standard unit and an appropriate standard unit to measure length; demonstrate an understanding of the relationship between days and weeks, months and years, minutes and hours, hours and days; name the months of the year in order and read the date on a calendar; estimate and measure the passage of time using minutes and hours; read digital and analog clocks, and tell and write time to the quarter-hour; relate changes in temperature to their own experiences (e.g., how changes in temperature during the day affect their activities); use a thermometer to determine whether temperature is rising or falling; name and state the value of all coins and demonstrate an understanding of their value; estimate and count money amounts to $1 and record money amounts using the cent symbol; create equivalent sets of coins up to $1 in value; use mathematical language to describe relative times, sizes, temperatures, amounts of money, areas, masses, and capacities (e.g., higher tower, fewer cups); use non-standard and standard units to solve measurement problems relating to themselves and their environment; PERIMETER AND AREA estimate, measure, and record the linear dimensions of objects using non-standard and standard units (centimetre, metre), and compare and order objects by their linear dimensions; measure and record the distance around objects using non-standard units, and compare the distances; estimate and measure specified areas using uniform non-standard units, and record the measures (e.g., the area of the page is four pencil cases); CAPACITY, VOLUME, AND MASS estimate, measure, and record the capacity of containers using non-standard units, compare the measures, and order a collection of containers by capacity; estimate, measure, and record the mass of objects using non-standard units, compare the measures, and order a collection of objects by mass. Grade 3 Grade 4 UNITS OF MEASURE explain the use of standard units of measurement and the relationships between linear measures (e.g., millimetres are smaller than metres); select the most appropriate unit of measure to measure length (centimetre, metre, kilometre); estimate, measure, and record linear dimensions of objects (using centimetre, metre, kilometre); compare and order objects by their linear dimensions; demonstrate an understanding of the relationship between days and years, weeks and years; estimate and measure the passage of time in five minute intervals, and in days, weeks, months, and years; tell and write time to the nearest minute in 12-hour notation using digital clocks; read and write time to the nearest five minutes using analog clocks; estimate, read, and record temperature to the nearest degree Celsius; demonstrate the relationship between all coins and bills up to $100; make purchases and change for money amounts up to $10, and estimate, count, and record the value up to $10 of a collection of coins and bills; read and write money amounts using two forms of notation (89¢ and $0.89); PERIMETER AND AREA measure the perimeter of two-dimensional shapes using standard units (centimetre and metre), and compare the perimeters; estimate and measure the area of shapes using uniform non-standard units, and compare and order the shapes by area; CAPACITY, VOLUME, AND MASS estimate, measure, and record the capacity of containers using standard units (millilitre, litre), and compare the measures; estimate, measure, and record the mass of familiar objects using standard units (gram, kilogram). UNITS OF MEASURE describe the relationship between millimetres, centimetres, decimetres, metres, and kilometres; draw items given specific lengths (e.g., a pencil 5 cm long); select the most appropriate standard unit (millimetre, centimetre, decimetre, metre, or kilometre) to measure linear dimensions and the perimeter of regular polygons; estimate lengths in millimetres, centimetres, metres, and kilometres; distinguish between estimated and precise measurements and know when each kind is required; relate years to decades, decades to centuries, centuries to millenniums; estimate and measure time intervals to the nearest minute; make purchases of and change for items up to $50; read and write money values to $50; estimate the amount of money in collections of coins and bills to $50 and count to determine the total value; PERIMETER AND AREA select the most appropriate standard unit (square centimetre or square metre) to measure the area of polygons of different sizes; use linear dimensions and perimeter and area measures with precision to measure length, perimeter, and area; estimate the area of regular polygons and measure the area in square centimetres using grid paper; understand that different two-dimensional shapes can have the same perimeter or the same area; explain the meaning of linear dimension, perimeter, and area; relate measures of area and perimeter to the linear dimensions of parts of rectangles or squares; explain the difference between perimeter and area and indicate when each measure should be used; CAPACITY, VOLUME, AND MASS select the most appropriate standard unit (e.g., millilitre, litre) to measure the capacity of containers; model three-dimensional figures of specific volumes using blocks; estimate, measure, and record the mass of objects using standard units (gram, kilogram), compare the measures, and order objects by mass; select the most appropriate standard unit to measure mass (e.g., milligram or gram); describe the relationship between grams and kilograms and millilitres and litres. Measurement Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 UNITS OF MEASURE use prefixes in the metric system correctly; draw items using a wide variety of SI units of length (e.g., a triangle with 9-dm sides); select the most appropriate standard unit (millimetre, centimetre, decimetre, metre, or kilometre) to measure linear dimensions and the perimeter of irregular polygons; determine the relationship between linear units (e.g., centimetre to metre); estimate long lengths using non-standard units (e.g., a tall building is about 15 car lengths); investigate measures of circumference using concrete materials (e.g., use string to measure the circumference of cans or bottles); estimate and measure time intervals to the nearest second; read and write dates and times using SI notation (e.g., June 30, 1998, is written 1998 06 30); read an analog clock to the nearest second and write the time to the nearest minute; estimate the amount of money in collections of coins and bills to $1000 and count to determine the total value; read and write money values to $1000; make purchases of and change for items up to $100; identify the relationship between the movement of objects and speed (e.g., how long will it take a bowling ball to travel the length of a bowling lane?); PERIMETER AND AREA develop rules for calculating the perimeter and area of rectangles, generalize rules, and develop formulas; estimate and calculate the perimeter and area of rectangles and squares; explain the rules used in calculating the perimeter and area of rectangles and squares; estimate the area of irregular polygons and measure the area by dividing the polygons into parts, using grid paper; develop methods of using grid paper to track and measure the perimeter and area of polygons and irregular two-dimensional shapes; CAPACITY, VOLUME, AND MASS measure containers by volume using standard units: cubic centimetres; determine the relationship between capacity and volume (e.g., millilitre and cubic centimetre) by measuring the volume of various objects and by determining the displacement of liquid by each object; relate the volume of an irregular three-dimensional figure to its capacity (e.g., through displacement of a liquid); describe the relationship between millilitres and cubic centimetres; determine the relationship between kilograms and metric tonnes; select the most appropriate standard unit to measure mass (e.g., kilogram or tonne). UNITS OF MEASURE use prefixes in the metric system correctly; select the most appropriate standard unit (millimetre, centimetre, decimetre, metre, or kilometre) to measure linear dimensions and the perimeter of irregular polygons; determine the relationship between linear, square, and cubic units (e.g., compare cubic centimetres and cubic metres by constructing a cubic metre with rolled newspaper); describe the relationship between a 12-hour clock and a 24-hour clock; represent amounts of money under $100 using the smallest possible number of coins and bills; read and write money values to $10 000; estimate and count amounts of money to $10 000, using a calculator for most calculations; make simple conversions between metric units (e.g., metres to kilometres, grams to kilograms); select among commonly used SI units of length, mass, capacity, area, and volume in solving problems; relate time and distance and speed: kilometres per hour; PERIMETER AND AREA relate dimensions of rectangles and area to factors and products (e.g., in a rectangle 2 cm by 3 cm the side lengths are factors and the area, 6 cm2, is the product of the factors); understand the relationship between the area of a parallelogram and the area of a rectangle, between the area of a triangle and the area of a rectangle, and between the area of a triangle and the area of a parallelogram; estimate and calculate the area of a parallelogram and the area of a triangle, using a formula; understand the relationship between area and lengths of sides and between perimeter and lengths of sides for squares, rectangles, triangles, and parallelograms; sketch a rectangle, square, triangle, or parallelogram given its area and/or perimeter; CAPACITY, VOLUME, AND MASS estimate and calculate the volume of rectangular prisms; develop rules for calculating the volume of rectangular prisms, generalize rules, and develop formulas (e.g., Volume = surface area of the base x height); determine the relationship between milligrams, grams, and kilograms. UNITS OF MEASURE create definitions of measurement concepts; describe measurement concepts using appropriate measurement vocabulary; research and report on uses of measurement instruments in projects at home, in the workplace, and in the community; make increasingly more informed and accurate measurement estimations based on an understanding of formulas and the results of investigations; PERIMETER AND AREA understand that irregular two-dimensional shapes can be decomposed into simple two-dimensional shapes to find the area and perimeter; estimate and calculate the perimeter and area of an irregular two-dimensional shape (e.g., trapezoid, hexagon); develop the formula for finding the area of a trapezoid; estimate and calculate the area of a trapezoid, using a formula; draw a trapezoid given its area and/or perimeter; develop the formulas for finding the area of a parallelogram and the area of a triangle; develop the formula for finding the surface area of a rectangular prism using nets; CAPACITY, VOLUME, AND MASS develop the formula for finding the volume of a rectangular prism (area of base x height) using concrete materials; understand the relationship between the dimensions and the volume of a rectangular prism; calculate the surface area and the volume of a rectangular prism in a problem-solving context; sketch a rectangular prism given its volume. Grade 8 UNITS OF MEASURE use listening, reading, and viewing skills to interpret and evaluate the use of measurement formulas; explain the relationships between various units of measurement; research, describe, and report on uses of measurement in projects at home, in the workplace, and in the community that require precise measurements; make increasingly more informed and accurate measurement estimations based on an understanding of formulas and the results of investigations; ask questions to clarify and extend their knowledge of linear measurement, area, volume, capacity, and mass, using appropriate measurement vocabulary; PERIMETER, CIRCUMFERENCE, AND AREA measure the radius, diameter, and circumference of a circle using concrete materials; recognize that there is a constant relationship between the radius, diameter, and circumference of a circle, and approximate its value through investigation; develop the formula for finding the circumference and the formula for finding the area of a circle; estimate and calculate the radius, diameter, circumference, and area of a circle, using a formula in a problem-solving context; draw a circle given its area and/or circumference; define radius, diameter, and circumference and explain the relationships between them; develop the formula for finding the surface area of a triangular prism using nets; CAPACITY, VOLUME, AND MASS develop the formula for finding the volume of a triangular prism (area of base x height); understand the relationship between the dimensions and the volume of a triangular prism; calculate the surface area and the volume of a triangular prism, using a formula in a problem-solving context; sketch a triangular prism given its volume.