Calculating magnification
advertisement

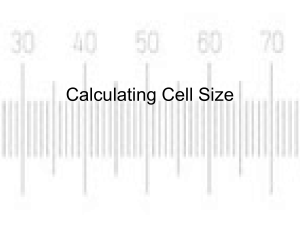
Calculating Magnification Magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens with the magnification of the ocular lens. The magnification of microscope lenses is engraved on the lens casing. What would be the magnification if you used a 10X eyepiece with a 40X objective lens? Multiply the eyepiece power by the objective lens power. 10 x 40 = 400 The magnification is 400X. What then is the magnification if you have an 8X eyepiece and a 10X objective? 8 x 10 = 80 The magnification is 80X. Calculating Field of View The field of view is the diameter of the circle of view you can see when looking down a microscope. The higher the magnification, the smaller the field of view. The field of view is calculated by viewing a microscope slide with a tiny ruler (usually only 1 or 2 mm long) printed onto the surface. By moving the ruler so that it lies across the diameter, you can measure the field of view for each magnification on your monocular microscope. Once you know the width of your field of view, you can then make estimates of the size of objects being viewed under the microscope. 1. If the field of view under low power (magnification x40) is 1.4 mm, what will be the field of view under high power (magnification x400)? 1.4 mm at x40 X mm at x400 400 is 10 times bigger than 40. X will therefore be 10 times smaller than 1.4 X = 1.4/10 X= 0.14mm 2. What will be the field of view under low power (magnification x150) if the field of view under medium power (magnification x600) is 0.02 mm? x600 is 4 times bigger than x150 Field of view will be therefore be 4 times bigger. 4x0.02= 0.08mm or (800 micrometers)