Indications for CRRT in the Critically Ill
advertisement

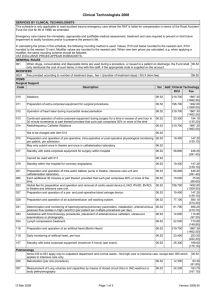
Indications for CRRT in the Critically Ill 16/8/10 Fluid Overload - patients with renal failure and have developed acute pulmonary oedema. - CRRT may be required to prevent or treat respiratory failure in this scenario. Acid - renal failure produces a situation where the patient is unable to excrete organic acids. - this can lead to a severe metabolic acidosis -> respiratory distress + encephalopathy Hyperkalaemia - hyperkalaemia can result in life threatening arrhythmias. - patients are particularly prone to this over a K+ of 6.5mmol/L - I would institute CRRT in patients while undertaking medical treatment to lower K+ until dialysis could be started. Extras/Others - toxins – dialyzable drugs in intoxication +/- haemofiltration with charcoal (lithium, theophylline, myoglobin) - sepsis – removal of cytokines mediating SIRS - uncontrolled electrolyte disturbances – hyponatraemia - uraemia (urea >30mmol/L) - as complications have minimized CRRT has been initiated earlier (oliguria, lower creatinine) - newer extracoroporeal techniques include ‘liver dialysis’ – filter coated with albumin to attract toxins that are normally cleared by the liver. Jeremy Fernando (2011)