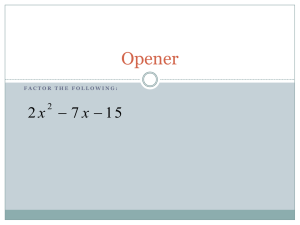
Bivariate Correlation and Regression
advertisement

Overview of Correlation & Regression Bivariate Correlation and Regression Bivariate correlation and regression evaluate the degree of relationship between two quantitative variables. Pearson Correlation (r), the most commonly used bivariate correlation technique, measures the association between two quantitative variables without distinction between the independent and dependent variables (e.g., What is the relationship between SAT scores and freshman college GPA?). In contrast, bivariate regression utilizes the relationship between the independent and dependent variables to predict the score of the dependent variable from the independent variable (e.g., To what degree do SAT scores [IV] predict freshman college GPA [DV]?). When to use bivariate correlation/regression? 1 IV (quantitative) relationship/prediction 1 DV (quantitative) Multiple Regression Multiple regression identifies the best combination of predictors (IVs) of the dependent variable. Consequently it is used when there are several independent quantitative variables and one dependent quantitative variable (e.g., Which combination of risk taking behaviors [amount of alcohol use, drug use, sexual activity, and violence—IVs] best predicts the amount of suicide behavior [DV] among adolescents?). To produce the best combination of predictors of the dependent variable, a sequential multiple regression selects independent variables, one at a time, by their ability to account for the most variance in the dependent variable. As a variable is selected and entered into the group of predictors, the relationship between the group of predictors and the dependent variables is reassessed. When no more variables are left that explain a significant amount of variance in the dependent variable, then the regression model is complete. When to use multiple regression? 2+ IV (quantitative) relationship/prediction 1 Source: DV (quantitative) Mertler, C. A., & Vannatta, R. A. (2005). Advanced and multivariate statistical methods: Practical application and interpretation (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Pyrczak. Bivariate I. Correlation Research Questions… Generically-Stated Research Question: II. Examples of Appropriately-Stated Research Questions: What is the relationship between students’ on-task behavior and academic achievement? What is the relationship between instructors’ assessment knowledge and the passage rates in their courses? What is the relationship between salary and years of teaching service? Examples of Inappropriately-Stated Research Questions: What is the effect of students’ on-task behavior on their academic achievement? What is the impact of instructors’ assessment knowledge on the passage rates in their courses? Sampling & Data… Samples should always be selected randomly (probability samples) Allows for generalization of results to larger population Unless the goal is only descriptive in nature (e.g., action research) Data must be quantitative III. What is the relationship between Variable A and Variable B? Scale of measurement (i.e., nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio) does not necessarily matter, as their exist numerous types of correlation coefficients that can be calculated Data Analysis & Interpretation… Analysis involves the calculation of a correlation coefficient (i.e., a quantitative measure of a relationship) Most common is a Pearson correlation coefficient (r)— correlation between two interval variables Numerous others exist for various combinations of variables… However, all are interpreted in similar manner; range from –1.00 to +1.00 (some range from 0.00 to +1.00) General rule of thumb for interpretation… Sample output from SPSS… Value of coefficient P-value (significanc e) Sample size Symmetrical matrix Multiple I. Regression Research Questions… Generically-Stated Research Question: Examples of Appropriately-Stated Research Questions: Which student demographic variables best predict academic achievement? What combination of student demographic variables (i.e., SES, ethnicity, gender, education status of mother/father, family income, age, and birth order) best predicts academic achievement in college chemistry courses? Examples of Inappropriately-Stated Research Questions: II. Samples should always be selected randomly (probability samples) Allows for generalization of results to larger population Unless the goal is only descriptive in nature (usually not the case for MR) Data must be quantitative III. What is the relationship between student demographic variables and academic achievement? Sampling & Data… Which combination of variables from a larger set of IVs best predicts the DV? Scale of measurement (i.e., nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio) should be interval or ratio (others will work, but perhaps result in less clear interpretation) Data Analysis & Interpretation… Analytic process… Multiple regression selects independent variables, one at a time, by their ability to account for the most variance in the dependent variable (rank order IVs) As a variable is selected and entered into the group of predictors, the relationship between the group of predictors and the dependent variable is reassessed When no more variables are left that explain a significant amount of variance in the dependent variable (i.e., that contribute significantly to the model), then the regression model is complete Example multiple regression… IVs — o BEGINNING SALARY o JOB SENIORITY o AGE o WORK EXPERIENCE o SEX & RACE CLASSIFICATION DV — o CURRENT SALARY Sample output from SPSS… Four (progressive) regression models, based on rank ordering Multiple Correlation: Pearson correlation between predicted and actual DV scores Contribution in variance at each step (model) Variance in DV accounted for by IVs Test of significance of each models’ predictabili ty Variables included in each model Tests of sig. for individual variables Coefficients used to develop regression (prediction) equation ZCurrentSalary = (.845)ZBeginningSalary + (-.145)ZWorkExperience + (.097)ZJobSeniority + (-.088)ZSexRace