Normalisation and statistics method
advertisement

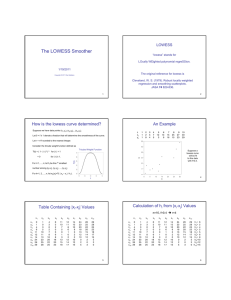
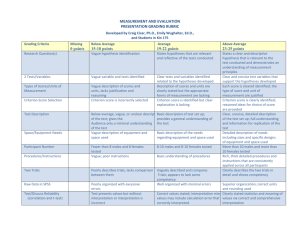
Normalisation and statistics method Per spot and per chip normalisation by Intensity dependant (LOWESS) normalisation. A Lowess curve was fit to the log-intensity versus log-ratio plot. 20% of the data was used to calculate the Lowess fit at each point. This curve was used to adjust the control value for each measurement. If the control channel was lower than 10, than 10 was used instead. The 50th percentile of all measurements in that sample divided each measurement. For samples where the bottom tenth percentile was less than the negative of the 50th percentile, it was used as a background and subtracted from all the other genes first. Statistical analysis was carried out based on the normalised data. Two-group, unpaired Welch t-test (variances not equal) was used for 2 groups comparison. Estimate experimental variance, including hybridisation of pairs of cDNAs on different batch of microarray slides on different days, indicated that our measurements fell within 95 percent confidence interval of 0.49 to 0.88 for the mean of 0.68 by paired T-test (Minitab). Hierarchical agglomerative clustering was performed by J-Express pro. The distance score is based on the Cosine correlation between two vectors containing values of similarities across multiple fields. A small value in the distance matrix implies that these two clusters/objects are more similar than clusters/objects with greater value. Then the average linkage WPGMA(weighted pair group method with arithmetic mean) is used to define the distance from each of the elements already in the matrix to the new cluster. The formulas: Cosine correlation: d ( x. y) ( xiyi) ( xi)2 ( yi)2 WPGMA: d (C (ij ), Ck ) D(ci, ck ) d (cj , ck ) 2