A REVIEW OF RADAR INTERFEROMETRY/IMAGING
advertisement
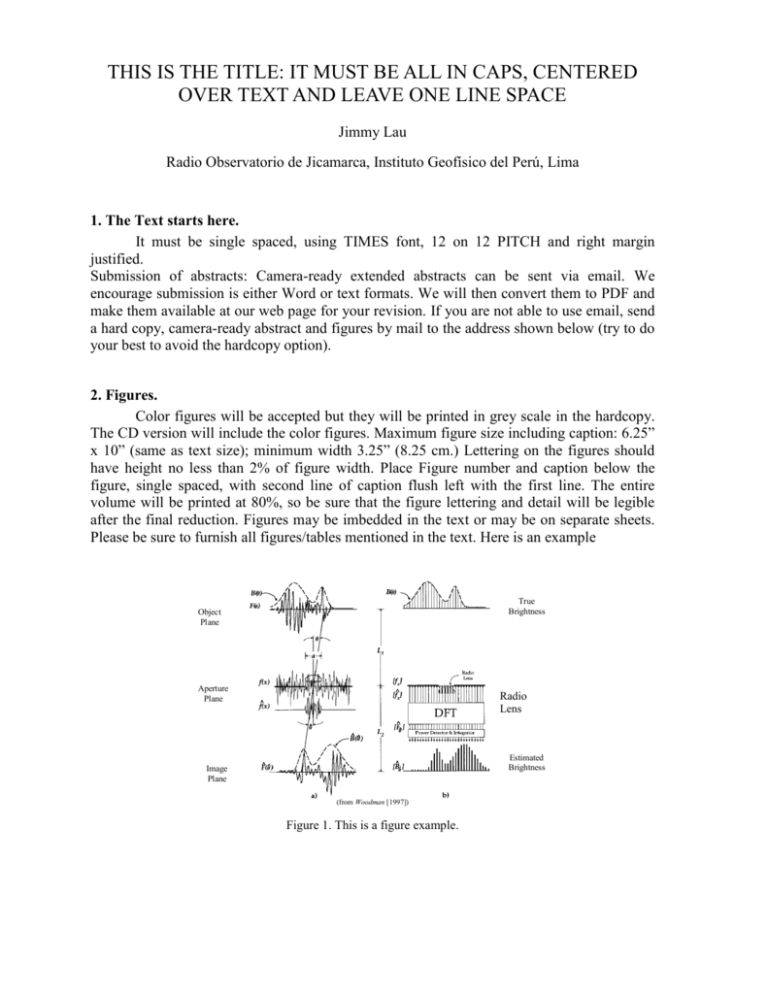
THIS IS THE TITLE: IT MUST BE ALL IN CAPS, CENTERED OVER TEXT AND LEAVE ONE LINE SPACE Jimmy Lau Radio Observatorio de Jicamarca, Instituto Geofísico del Perú, Lima 1. The Text starts here. It must be single spaced, using TIMES font, 12 on 12 PITCH and right margin justified. Submission of abstracts: Camera-ready extended abstracts can be sent via email. We encourage submission is either Word or text formats. We will then convert them to PDF and make them available at our web page for your revision. If you are not able to use email, send a hard copy, camera-ready abstract and figures by mail to the address shown below (try to do your best to avoid the hardcopy option). 2. Figures. Color figures will be accepted but they will be printed in grey scale in the hardcopy. The CD version will include the color figures. Maximum figure size including caption: 6.25” x 10” (same as text size); minimum width 3.25” (8.25 cm.) Lettering on the figures should have height no less than 2% of figure width. Place Figure number and caption below the figure, single spaced, with second line of caption flush left with the first line. The entire volume will be printed at 80%, so be sure that the figure lettering and detail will be legible after the final reduction. Figures may be imbedded in the text or may be on separate sheets. Please be sure to furnish all figures/tables mentioned in the text. Here is an example True Brightness Object Plane Aperture Plane Visibility Radio Lens Estimated Brightness Image Plane (from Woodman [1997]) Figure 1. This is a figure example. 3. Tables Place Table number and title above the table, single spaced. Maximum and minimum sizes as above. And now, the example Table 1. Chronological development of radar interferometry techniques related to MST radars. The different technique names adopted are marked in bold letters. Reference Description Woodman [1971] Pfister [1971] First use of RI to determine the inclination of the magnetic field over Jicamarca. First addition of phase measurements to a standard SA experiment. He noted that the phase of the CSF was a linear function of the Doppler velocities, and estimated a velocity that was in a good agreements with the apparent SA velocity. Rüster and Woodman [1976] Röttger and Vincent [1978] Farley et al. [1981] Röttger and Ierkic [1985] First MST RI measurements at JRO. Inhomogeneities were not detected Adams et al. [1986] Kudeki [1988] La Hoz et al. [1989] Kudeki and Woodman [1990] Röttger et al. [1990] Liu et al. [1990] Larsen and Röttger [1991]; Palmer et al. [1991] Briggs and Vincent [1992]; Sheppard and Larsen [1992] Doviak et al. [1996] Chau and Balsley [1998a] Show applicability of basic interferometry with MST radars. Formal “appearance” of the RI technique, to study plasma turbulence in the Ionosphere. Publish first MST RI studies measuring angle-of-arrivals (AOA) and introducing the postbeam steering (PBS) technique. Use imaging Doppler interferometry (IDI) to study the mesosphere with MF radar. RI observations of mesospheric layers. Relates slope of phase angle spectrum to “horizontal” wind. Use RI to investigate polar mesosphere summer echoes with an EISCAT VHF radar. Introduce the Poststatistics steering technique (PSS). Use the term spatial domain interferometry (SDI) or SI in order to discriminate from the frequency domain interferometry (FDI) introduced by Kudeki and Stitt [1987] Show analytically that there is equivalence between SA and SDI methods when turbulence is neglected. Use AOA information to get “corrected” vertical velocities. Have shown that a full-spectral analysis (FSA) applied to SDI data is equivalent to the well-known full correlation analysis (FCA) used with the standard SA method. Present a theory that ties the properties of turbulently advected scattering medium to the cross correlation and spectrum of signals in a general configuration of receivers and transmitter. Complement Doviak et al. [1996]’s development by adding off-vertical AOA contributions due to tilted layers, off vertical transmitting beams and geometrical effects. 3. References References in text should be by name and year (Lau and Jameson, 1981.) List citations alphabetically in the REFERENCES section using JGR format, i.e., Lau, J. L., and E. Jameson, The radial evolution of a single solar wind parcel, J. Geophys. Res., 86, 4574-4580, 1981. Here is an example: Later, radar interferometry was used by Roettger and Ierkic [1985] to study tilt angles, to improve velocity estimates, and to track scattering patches, by using longer integration times than those previously attempted. Since then, different techniques and theoretical works have developed. Bibliography Röttger, J. and H. M. Ierkic, Postset beam steering and interferomet applications of VHF radars to study winds, waves, and turbulence in the lower and middle atmosphere, Radio Sci., 20, 1461-1480, 1985.











