Lesson: Statistics and Parameters
advertisement

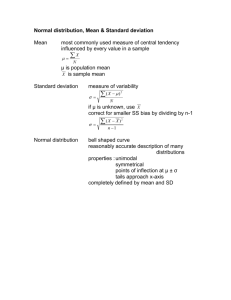
Assignment 8: Statistics and Parameters Psych 6250 Spring, 2010 Lesson: Statistics and Parameters 1. A measure that arises from your sample is called a ____________ 2. A measure that arises from your population is called a _____________ 3. The mean, median, mode, variance, and standard deviation of your sample are _____________ 4. The mean, median, mode, variance, and standard deviation of your population are_______________ 5. What symbol represents the mean of the sample?_____ Sample A: Y = 5, 11, 8, 4, 3 (this will be used in many questions below) 6. A researcher samples five scores from a population and obtains the following data. Compute the mean of Sample A. M= 7. What symbol represents the actual mean of the population?_____ 8. Is it possible to compute the actual mean of the population without measuring everyone in the population? (yes/no) 9. What symbol represents the estimate of the population mean based on the sample? _______ 10. An _________ __________ is one whose expected (mean) value equals the parameter it is trying to estimate. 11.: Is the sample mean an unbiased estimate of the population mean? (yes/no) 12. Does that mean that the sample mean will always equal the population mean? (yes/no) 13 Estimate the mean of the population from which Sample A was drawn. est. μ=_________ 14. What can we compute for sure with this sample? (select all that apply) a: est. μ b: μ c: M 15. Which of the following should increase the chances of getting an accurate estimate of μ out of the sample? (select all that apply) a: b: c: d: Draw a larger sample Draw a smaller sample Measure something people differ on a lot (i.e. has a large variance) Measure something people don’t differ on much (i.e. has a small variance) 16. Now we are going to start the process of computing the SS of Sample A using the computational formula. N=_____ 17. ΣY² =______ 18. ΣY=______ 19. (ΣY)² = 20. SS = 21. What symbol represents the variance of the sample? _____ 22. Compute the variance of Sample A (include its symbol in your answer). _________ 23. What symbol represents the variance of the population from which the sample was drawn?_______ 24. Would it be possible to compute the actual variance of the population without measuring everyone in the population? (yes/no) 25. What symbol represents the estimate of the variance of the population from which the sample was drawn? _______ 26 Is the sample variance an unbiased estimate of the population variance? (yes/no) 27. Which of the following is correct? a: The sample variance is usually greater than the population variance. b: The sample variance is usually less than the population variance 28. Estimate the variance of the population from which Sample A was drawn. _________ 29. What symbol represents the standard deviation of the sample? ________ 30. Compute the standard deviation of Sample A _____ 31. What symbol represents the standard deviation of the population from which the sample was drawn?_____ 32. What symbol represents the estimate of the standard deviation of the population based on the sample?_____ 33. Estimate the standard deviation of the population from which Sample A was drawn ._____ 34. Of the estimate of the population mean, variance, and standard deviation, which one is slightly biased? 35. You know that for some sample of 15 scores, that the variance of the sample equals 11. What is the estimate of the population variance? _______ 36. You know that for some sample of 9 scores, that the est.σ² =20. What is the variance of the sample? _______ 37. A ____________statistic simply describes the sample. 38. An ___________ statistic uses data from the sample to estimate the parameter of the population. 39. M, S², S are all.... a: descriptive statistics b: inferential statistics c: parameters 40 est. μ, est. σ², est. σ are all.... a: parameters b: descriptive statistics c: inferential statistics 41: μ, σ², σ are all.... a: inferential statistics b: descriptive statistics c: parameters 42: The 95% ____________ ____________ of the mean is an interval that we are 95% sure contains the true value of μ. SPSS Open up data file ‘Age.sav’, which presents the ages of the CEO’s from a sample of small companies (defined as those with annual sales greater than $5 million and less than $350 million). Source: Forbes, November 8, 1993 as provided in http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/DASL/DataArchive.html. In SPSS go to Analyze>>Descriptive Statistics>>Explore. Put the variable into the dependent list, click on ‘Plots’, under ‘BoxPlots’ select none, under ‘Descriptive’ select ‘Histogram’ and then view the output. Note that when SPSS reports the ‘variance’ it is giving the estimate of the population variance, and when it reports ‘std. deviation’ it is giving the estimate of the population standard deviation. Two of the values I will be asking for below are not directly provided by SPSS. For one of them you may need to pull out a formula from the lecture. For the other, ‘SS’, I’ll tell you how to do it. As SPSS gives you the est.σ², and we know that est.σ² = (SS)/(N-1), it is a simple matter to figure out that SS = (est.σ²)(N-1) First, look at the histogram to see what the distribution of ages for the CEO’s looks like. I won’t be asking a question about this but looking at a histogram of the data is almost always my first step in understanding the sample. 43. est. μ = _______ 44 & 45. The 95% confidence interval for the mean is _______ ≤ μ ≤ ________ 46. est.σ² =_______ 47. est.σ =_______ 48. SS=_______ 49. S²=_______