Hypothesis Testing:
advertisement

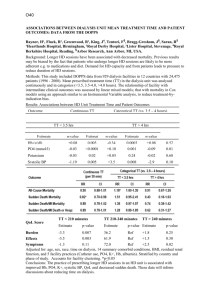
STAT 211 1 Handout 8 (Chapter 9): Inferences Based on Two Samples Population characteristics (parameter) Sample characteristics (statistics) _ 1 2 _ x y ^ ^ p1 p2 p1 p 2 12 / 22 s12 / s 22 1. One-sided (One tailed) test: A. Lower tailed: H0: population characteristics claimed constant value (Left-sided) Ha: population characteristics < claimed constant value B. Upper tailed: H0: population characteristics claimed constant value (Right-sided) Ha: population characteristics > claimed constant value 2. Two-sided (Two tailed) test: H0: population characteristics = claimed constant value Ha: population characteristics claimed constant value A. Independent Samples I. Population characteristics: Difference between two population means, 1-2. 0 is the claimed constant. 1 and 2 are the population means for X's and Y's, respectively. _ _ x and y are the sample means for X's and Y's, respectively. m and n are the sample sizes for X's and Y's, respectively. 12 and 22 are the population variances for X's and Y's, respectively. s12 and s 22 are the sample variances for X's and Y's, respectively. Test statistics: _ _ x y 0 z 2 1 m when both popn. distributions are normal and 12 , 22 are known n x y 0 z when there is large sample size (m>40 and n>40) and 12 , 22 are 2 2 s1 s 2 m n unknown _ 2 2 _ STAT 211 2 _ _ x y 0 t when both popn. distributions are normal and at least one sample size is 2 s1 s 22 m n small with unknown 12 , 22 are assumed to be different ( 12 22 ) and degrees of freedom, 2 s12 s 22 m n is used to look up the critical values. If v is not computed as integer, v 2 2 s12 / m s 22 / n m 1 n 1 it should be rounded down. Your textbook calls this two-sample t test. _ _ x y 0 (m 1) s12 (n 1) s 22 , s 2p when both popn. distributions are normal and at t mn2 1 1 sp m n least one sample size is small where unknown 12 , 22 are assumed to be the same ( 12 = 22 ) and degrees of freedom, v m n 2 is used to look up the critical values. Your textbook calls this pooled t test. Decision can be made in one of the two ways in hypothesis testing: a. Let z* or t* be the computed test statistic values. if test statistics is z if test statistics is t Lower tailed test P-value = P(z<z*) P-value = P(t<t*) Upper tailed test P-value = P(z>z*) P-value = P(t>t*) Two-tailed test P-value = 2P(z>|z*|)= 2P(z<-|z*|) P-value = 2P(t > |t*| )= 2P(t <- |t*| ) In each case, you can reject H0 if P-value and fail to reject H0 (accept H0) if P-value > b. Rejection region for level test: if test statistics is z Lower tailed test z -z Upper tailed test z z Two- tailed test |z | z/2 if test statistics is t t -t;v t t;v |t| t/2;v 100(1-)% confidence Intervals with the same assumptions, 12 22 _ _ x y z /2 m n s2 s2 _ _ x y z / 2 1 2 m n STAT 211 3 s12 s 22 _ _ when you assume 12 22 x y t / 2 ; v m n 1 1 _ _ when you assume 12 = 22 x y t / 2 ;v s p m n Example 1: Two types of plastic are suitable for use by an electronics component manufacturer. The breaking strength of this plastic is very important. It is known that 1 = 2 =1 psi. Random _ sample of size n1 =10 and n 2 =12 drawn from a normal distribution, we obtain x 1 =162.5 and _ x 2 =155. The company will not adopt plastic 1 unless its mean breaking strength exceeds that of plastic 2 by at least 10 psi. Based on the sample information, would they use plastic 1? Use the significance level 0.05 in reaching a decision. H 0 : 1 2 10 (adopt plastic 1) versus H a : 1 2 10 (do not adopt plastic 1) _ _ x y 0 (162.5 155) 10 5.84 test statistics, z 2 2 1 2 12 12 10 12 m n Decision: (i) reject H0 if z -z=-1.645. z =-5.84 < -1.645 then reject H0. (ii) P-value = P(Z<-5.84)=P(Z>5.84)=0. Since the P-value =0.05, reject H0. Conclusion: Do not adopt plastic 1. Example 2 (Exercise 9.2): We will use the given data in this exercise. i : true average tread lives for two competing brand of size P205/65R15 radial tires, i=1,2 Test H 0 : 1 2 0 versus H a : 1 2 0 _ m=45 x 42500 s1 2200 _ n=45 y 40400 s2 1900 Notice that sample sizes are large while population variances are unknown and this is a twotailed test. _ _ x y 0 (42500 40400) 0 Test statistics: z =4.8462 2 2 s1 s 2 2200 2 1900 2 45 45 m n Decision: (i) Reject H0 if z -z/2=-1.96 or z z/2 =1.96. z =4.8462 > 1.96 then reject H0. (ii) P-value = 2P(Z>4.8462)=2(0)=0. Since the P-value =0.05, reject H0. Conclusion: true average tread lives for two competing brand tires are different. STAT 211 4 If you prefer to answer the question computing the confidence interval, 95% confidence interval s2 s2 2200 2 1900 2 _ _ would become x y z / 2 1 2 (42500 40400) 1.96 m n 45 45 =(1250.67, 2949.33). You would see that zero does not fall into interval and you would reject H0. What would be different if this was an upper tailed test instead of two tailed test? (hypothesis, test statistics, decision, conclusion) What would be different if this was an upper tailed test with the hypothesized value 1000 instead of two tailed test with the hypothesized value 0? (hypothesis, test statistics, decision, conclusion) Example 3 (Exercise 9.8): The data is on the tensile strength test of two different grades or wire rod. Grade Sample size Sample mean Population Sample standard mean deviation _ AISI 1064 m=129 s1 =1.3 1 x =107.6 _ AISI 1078 n=129 s2 =2.0 2 y =123.6 (a) Does the data provide compelling evidence for concluding that the true average strength for 1078 grade exceeds that for the 1064 grade by more than 10kg/mm2? Sample sizes are large while population variances are unknown. . Notice that this is an uppertailed test. H 0 : 2 1 10 versus H a : 2 1 10 _ _ y x 0 (123.6 107.6) 10 Test statistics: z =28.57 2 2 s1 s 2 1.3 2 2 2 129 129 m n Decision: (i) Reject H0 if z z =1.645 if =0.05. z =28.57 > 1.645 and reject H0. (ii) P-value = P(Z>28.57)=0. Since the P-value =0.05, reject H0. Conclusion: the data provide compelling evidence that the true average strength for the 1078 grade exceeds that for the 1064 grade by more than 10. Or you can answer the same question using H 0 : 1 2 10 versus H a : 1 2 10 Notice that it became a lower tailed test instead of upper tailed test. STAT 211 5 _ _ x y 0 (107.6 123.6) 10 Test statistics: z = -28.57 2 2 s1 s 2 1.3 2 2 2 129 129 m n Decision: (i) Reject H0 if z - z =-1.645 if =0.05. z =-28.57 <- 1.645 and reject H0. (ii) P-value = P(Z<-28.57)=0. Since the P-value =0.05, reject H0. (b) Estimate the difference in a way that provides information about the precision and reliability s12 s 22 _ _ 95% confidence interval for 1 2 is x y z / 2 m n = 107.6 123.6 1.96 1.3 2 2 2 =(-16.84 , -15.16) 129 129 s2 s2 _ _ 95% confidence interval for 2 1 is y x z / 2 1 2 = (15.16 , 16.84) m n Example 4 (Exercise 9.18): i : true average densities for two different type of brick, i=1,2 Assume normality of two density distributions Test H 0 : 1 2 0 versus H a : 1 2 0 _ m=6 x 22.73 s1 0.164 _ n=5 y 21.95 s2 0.240 Sample sizes are small and population variances are unknown. . Notice that this is a two-tailed test. If the population variances are assumed to be different, _ _ x y 0 (22.73 21.95) 0 Test statistics: t =6.166 2 2 s1 s 2 0.164 2 0.24 2 6 5 m n Decision: (i) Reject H0 if t -t/2;v= -2.447 or t t/2;v =2.447 where =0.05 and v=6.886. t =6.166 > 2.447 and reject H0. (ii) P-value = 2P(t>6.166)=2(0.0005)=0.001. Since the P-value =0.05, reject H0. Conclusion: the true average densities for two different types of brick are different. If the population variances are assumed to be the same, STAT 211 6 _ _ x y 0 (22.73 21.95) 0 Test statistics: t = =6.396 where 1 1 1 1 sp 0.2014 6 5 m n (m 1) s12 (n 1) s 22 5(0.164) 2 4(0.24) 2 2 =0.0405 sp mn2 652 Decision: (i) Reject H0 if t -t/2;v= -2.262 or t t/2;v =2.262 where =0.05 and v=6+5-2=9. t =6.166 > 2.262 and reject H0. (ii) P-value = 2P(t>6.166)<2(0.0005)=0.001. Since the P-value =0.05, reject H0. Conclusion: the true average densities for two different types of brick are different. II. Population characteristics: Difference between two population proportions, p1-p2. p0 is the claimed constant. ^ ^ p 1 and p 2 are the sample proportions for X's and Y's, respectively. p1 and p 2 are the population proportions for X's and Y's, respectively. m and n are the large sample sizes for X's and Y's, respectively. ^ X Y m ^ n ^ p1 p2 The estimator for p is p mn mn mn ^ ^ p1 p 2 p0 Test statistics: z ^ ^ 1 1 p1 p m n Decision can be made in one of the two ways: (a) Let z* be the computed test statistic values. Lower tailed test P-value = P(z<z*) Upper tailed test P-value = P(z>z*) Two-tailed test P-value = 2P(z > |z*| )=2P(z <- |z*| ) In each case, you can reject H0 if P-value and fail to reject H0 (accept H0) if P-value > (b) Rejection region for level test: Lower tailed test z -z Upper tailed test z z Two- tailed test z -z/2 or z z/2 100(1-)% large sample confidence Interval: ^ ^ p1 p 2 z / 2 ^ ^ ^ ^ p1 1 p1 p 2 1 p 2 m n STAT 211 7 Example 5: Two different types of injection-molding machines are used to form plastic parts. A part is considered defective if it has excessive shrinkage or is discolored. Two random samples, each of size 300 are selected and 15 defective parts are found from machine 1 while 8 defective parts are found in the sample from machine 2. Is it reasonable to conclude that both machines produce the same fraction of defective parts, using the significance 0.05? If this analysis done by hand Sample sizes are large enough to satisfy the assumptions and it is a two-tailed test. ^ ^ ^ X Y 15 8 15 8 p =0.0383 where p 1 =0.05 and p 2 =0.0267 m n 300 300 300 300 ^ ^ p1 p 2 p0 (0.05 0.0267) 0 Test statistics: z =1.49 ^ ^ 0.0383(0.9617)(1 / 300 1 / 300) 1 1 p1 p m n (i) Reject H0 if z -z/2=-1.96 or z z/2 =1.96. -1.96< z=1.49 < 1.96 and fail to reject H0. . (ii) P-value = 2P(Z>1.49)=2(0.0681)=0.1362. Since the P-value > =0.05, fail to reject H0. Conclusion: Yes it is reasonable to assume that both machines produce the same fraction of defective parts The MINITAB output analyzing such data is Test and CI for Two Proportions Sample X N Sample p 1 15 300 0.050000 2 8 300 0.026667 Estimate for p(1) - p(2): 0.0233333 95% CI for p(1) - p(2): (-0.00733568, 0.0540023) Test for p(1) - p(2) = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = 1.49 P-Value = 0.136 Example 6 (Exercise 9.48(a)): Sample sizes are large enough to satisfy the assumptions and it is a two-tailed test. ^ ^ ^ X Y 63 75 63 75 p =0.2875 where p 1 =0.21 and p 2 =0.4167 m n 300 180 300 180 ^ ^ p1 p 2 p0 (0.21 0.4167) 0 Test statistics: z =-4.844 ^ ^ 0.2875(0.7125)(1 / 300 1 / 180) 1 1 p1 p m n Decision: (i) Reject H0 if z -z/2=-1.96 or z z/2 =1.96. |z| =4.844 > 1.96 and reject H0. (ii) P-value = 2P(Z>4.844)=2(0)=0. Since the P-value =0.05, reject H0. Conclusion: it is different for two groups of residents. The MINITAB output analyzing such data is Test and CI for Two Proportions STAT 211 8 Sample X N Sample p 1 63 300 0.210000 2 75 180 0.416667 Estimate for p(1) - p(2): -0.206667 95% CI for p(1) - p(2): (-0.292174, -0.121159) Test for p(1) - p(2) = 0 (vs not = 0): Z = -4.74 P-Value = 0.000 Population characteristics: Ratio of the two population variances, 12 / 22 or standard deviations, 1 / 2 . X and Y's are random sample from a normal distribution. 12 and 22 are the population variances for X's and Y's, respectively. s12 and s 22 are the sample variances for X's and Y's, respectively. m and n are the sample sizes for X's and Y's, respectively. s2 Test statistics: F 12 s2 Decision can be made in one of the two ways: III. (a) Let F* be the computed test statistic values. Lower tailed test P-value = P(F<F*) Upper tailed test P-value = P(F>F*) Two-tailed test P-value = 2P(F > F*) In each case, you can reject H0 if P-value and fail to reject H0 (accept H0) if P-value > (b) Rejection region for level test: Lower tailed test F F1-;m-1,n-1 Upper tailed test F F;m-1,n-1 Two- tailed test F F1-/2;m-1,n-1 or F F/2;m-1,n-1 Notice that F1-/2;m-1,n-1 = 1 / F/2;n-1,m-1 100(1-)% confidence Interval for 12 / 22 : s12 / s 22 F / 2;m 1,n 1 12 s12 / s 22 22 F1 / 2;m 1,n 1 Example 7 (Exercise 9.57): (a) On the F-table, column for 5 and row for 8 will give the area on the right 0.05 with F0.05:5,8 = 3.69 (d) F0.95:8,5 = 1/ F0.05:5,8 = 1/3.69 =0.271 (e) The percentile is the area on the left of the value and it means the area on the right of the value is 0.01. On the F-table, look at column for 10 and row for 12 with the area on the right 0.01. P( F F0.01:10,12 )= 0.99 then F0.01:10,12 = 4.30 (h) P(0.177 F 4.74) = P(F0.99:10,5 F F0.05:10,5) =1-(0.01+0.05)=0.94 where F0.99:10,5 = 1/F0.01:5,10 = 1/5.64=0.177 STAT 211 9 Example 8: A study was performed to determine whether men and women differ in their repeatability in assembling components on printed circuit boards. Two samples of 26 men and 21 women were selected and each subject assembled the units. The two sample standard deviations of assembly time were smen=0.98 min and swomen=1.02 min. Is there evidence to support the claim that men and women differ in repeatability for this assembly task? Use the significance level 0.02 and state any necessary assumptions about underlying distribution of the data. 2 2 H 0 : men women 2 2 H a : men women =0.02, m=26, n=21 s2 0.98 2 Test statistics: F 2men 0.9231 s women 1.02 2 Decision: Reject H0 if F F1-/2;m-1,n-1 = F0.99;25,20 =1/2.70=0.37 or F F/2;m-1,n-1= F0.01;25,20 =2.84. Since 0.37 < F=0.9231 <2.84, fail to reject H0. Conclusion: men and women do not differ in repeatability for this assembly task Example 9 (Exercise 9.62): H 0 : 12 22 H a : 12 22 =0.10, m=48, n=45 s12 21.45 2 1.2219 Test statistics: F 2 s 2 19.45 2 Decision: Reject H0 if F F1-/2;m-1,n-1 = F0.95;47,44 =1/1.6336=0.6121 or F F/2;m-1,n-1= F0.05;47,44 =1.6412 (The F-table on your book is not very detailed, you can use both degrees of freedom as 40 to look at the table. I gave you the real values using the computer programs.) Since 1.2219 is not larger than 1.6412 or smaller than 0.6121, fail to reject H0. Conclusion: the variances are the same. B. Dependent Samples- Paired Data Population characteristics: Difference between two population means, D =1-2. 0 is the claimed constant. Assumption: the difference distribution should be normal. _ Test statistics: t d 0 _ where D=X-Y and d and s D are the corresponding sample average sD / n and the standard deviation of D. Both X and Y must have n observations. Decision can be made in one of the two ways: (a) Let t* be the computed test statistic values. STAT 211 10 Lower tailed test P-value = P(t<t*) Upper tailed test P-value = P(t>t*) Two-tailed test P-value = 2P(t > |t*| )=2P(t <- |t*| ) In each case, you can reject H0 if P-value and fail to reject H0 (accept H0) if P-value > (b) Rejection region for level test: Lower tailed test t -t;n-1 Upper tailed test t t;n-1 Two- tailed test t -t/2;n-1 or t t/2;n-1 100(1-)% confidence Intervals with the same assumptions, _ s d t / 2;n 1 D n Example 10: The manager of a fleet of automobiles is testing two brands of radial tires. He assigns one tire of each brand at random to the two rear wheels of eight cars and runs the cars until the tires wear out. The descriptive statistics for the data are shown below (in kilometers). Find the 99% confidence interval on the difference in mean life. Which brand would you prefer based on this calculation? Is there an alternative method to answer this question instead of computing the confidence interval? Variable N Mean Median StDev SE Mean Minimum Maximum Q1 Q3 Brand1 8 38479 37067 5590 1976 32100 48360 34185 43525 Brand2 8 37611 36655 5244 1854 31950 47800 33491 41214 Difference 8 868 475 1290 456.1 -805 3020 N/A N/A Brand1 Brand2 Difference 36925 45300 36240 32100 37210 48360 38200 33500 34318 42280 35500 31950 38015 47800 37810 33215 2607 3020 740 150 -805 560 390 285 _ 99% confidence interval for 1 2 is d t / 2;n 1 sD 868 3.499 1290 =(-727.84 , 2463.84) n 8 Confidence interval only tells us that there is no difference between those brands. The MINITAB output analyzing such data is B1 B2 Difference N 8 8 8 Mean 38479 37611 868 StDev 5590 5244 1290 SE Mean 1976 1854 456 Test for equal true means in independent samples assuming equal true variances Difference = mu B1 - mu B2 Estimate for difference: 868 95% CI for difference: (-4944, 6681) T-Test of difference = 0 (vs not =): T-Value = 0.32 P-Value = 0.753 DF = 14 Both use Pooled StDev = 5420 STAT 211 11 Test for equal true means in independent samples assuming unequal true variances Difference = mu B1 - mu B2 Estimate for difference: 868 95% CI for difference: (-4986, 6723) T-Test of difference = 0 (vs not =): T-Value = 0.32 P-Value = 0.754 DF = 13 Test for equal true means in dependent samples 95% CI for mean difference: (-211, 1948) 99% CI for mean difference: (-728, 2465) T-Test of mean difference = 0 (vs not = 0): T-Value = 1.90 P-Value = 0.099 Test for equal variances: B1 versus B2 F-Test (normal distribution) Test Statistic: 1.136 P-Value : 0.870 Example 11 : An experiment to compare the yield (kg/ha) of Sundance winter wheat and Manitou spring wheat is considered. Data from nine different plots is given in the following table. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that true average yield for the Sundance winter wheat is more than 500 kg/ha than the Manitou spring wheat? Check the plausibility of any assumptions needed to carry out an appropriate test of hypothesis. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 S 3201 3095 3297 3644 3604 2860 3470 2042 3689 M 2386 2011 2616 3094 3069 2074 2308 1525 2779 D=S-M 815 1084 681 550 535 786 1162 517 910 H 0 : S M 500 or H 0 : S M 500 H a : S M 500 or H a : S M 500 The difference distribution should be normal. _ Use the differences and compute the sample mean, d =782.2222 s D =236.736. _ Test statistics: t d 0 sD / n 782.2222 500 236.736 / 9 and the standard deviation, =3.5764 Decision: (i) Since this is an upper tailed test, reject H0 if t t;n-1= t0.05;8 =1.86 or if the Pvalue=P(t>3.5764) is less than =0.05. Notice that test statistics, 3.5764 is large than 1.86. (ii) 0.001 <P-value < 0.005 by looking at the t-table. Reject H0 Conclusion: there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the true average yield in winter wheat is more than 500 higher than for spring wheat. STAT 211 12 Normal Probability Plot for difference ML Estimates - 95% CI 99 ML Estimates 95 Mean 782.222 StDev 223.197 90 Goodness of Fit Percent 80 AD* 70 60 50 40 30 1.416 20 10 5 1 0 500 1000 1500 Data Results from the MINITAB program Paired T for muS - muM N 9 9 9 S M Difference Mean 3211 2429 782.2 StDev 518 518 236.7 SE Mean 173 173 78.9 95% lower bound for mean difference: 635.5 T-Test of mean difference = 500 (vs > 500): T-Value = 3.58 P-Value = 0.004 More to discuss Two-sample T for muS vs muM S M N 9 9 Mean 3211 2429 StDev 518 518 SE Mean 173 173 Difference = muS - muM Estimate for difference: 782 95% CI for difference: (265, 1300) T-Test of difference = 0 (vs not =): T-Value = 3.20 Both use Pooled StDev = 518 F-Test (normal distribution) Test Statistic: 1.002 P-Value : 0.998 Levene's Test (any continuous distribution) Test Statistic: 0.094 P-Value : 0.763 P-Value = 0.006 DF = 16