BONES
advertisement

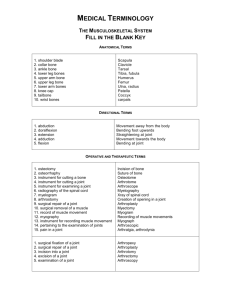
BONES COMMON TERM NAME SCIENTICIFIC TERMS Skull Upper jaw Collar bone Shoulder blade Breast bone Funny bone Rib cage Radius Ulna Wrist Hand Fingers Back bone Hip bone Thigh bone Kneecap Shin bone Outside leg bone Ankle Toes cranium mandible clavicle scapula sternum humorous rib cage lower outside arm bone lower inside arm bone carpal bones metacarpal phalanges vertebrae (spinal column/spine) pelvis femur (hardest bone) patella tibia (larger bone) fibula (smaller bone) metatarsal phalanges Twenty-two bones make up the skull. The largest bone in the human body is the femur. A baby has 300 bones in their body and an adult has 206 bones in their body. A person has 12 pairs of ribs with only 2 pairs of ribs attached to the spine. A person has 26 bones in their spine but born with 33. We have 65 joints in the human body. ALL ABOUT THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of bones are that they provide shape and support for your body. They also allow movement, produce blood cells, protects tissues and organs and they also store certain materials. Bones of the human body are living they contain living tissues, nerves, bone forming cells, and blood vessels. (but like non-living rocks in that they are hard and strong since they are made of minerals). Bone marrow is a soft material inside the bone. It can be yellow (fat and blood cells) or red (produces bodies blood cells). An example of a flat bone is the ribs, a long bone would be the femur or the humorous, and a short bone would be the carpal or the tarsal. A fracture is a break in the bone, while a compound fracture breaks through the skin. A “JOINT” VENTURE A joint is any place where two bones meet together. There are five kinds of joints, they are: JOINT EXAMPLE Ball & sockets shoulder & hip Gliding wrist & ankle Hinge elbow & knee (back & forth motion) Pivot neck Fixed skull (immovable- can’t move) Friction is reduced between bones that are positioned close to each other by cartilage (floating ribs, ear, nose) at the ends of bones. It reduces friction (acts as a cushion) and has synovial fluid (joint grease). Bones that meet at a joint are held in place by ligaments. Ligaments are tough connective tissues that attach bone to bone. ***ligaments attach bone to bone ***tendons attach muscle to bone WHAT KIND OF JOINT IS THIS? CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM FOR JOINTS Ball-and-socket joints: circular motion, free movement in all directions Fixed joints: immovable Hinge joints: bending in only one direction, back and forth motion Pivot joints: rotating motion, side to side movement Gliding joints: sliding motion of one bone past another JOINTS IN THE HUMAN BODY NAME OF JOINT Ankle joint Elbow joint Finger joint Hip joint Knee joint Neck joint Pelvic joint Shoulder joint Skull joint Toe joint Wrist joint TYPE OF JOINT gliding hinge hinge ball & socket hinge pivot fixed ball & socket fixed hinge gliding Joint Movements: Flexion: Occurs when you bend a joint. Extension: A movement that occurs when you straighten a bend in a joint. Abduction: A movement of a body part to a position away from your normal body’s position. Adduction: A movement of a part of your body back to its normal position. MUSCLES MAJOR MUSCLES of the BODY BODY MUSCLES MUSCLE LOCATION pectoral bicep deltoid trapezius tricep rectus abdominus gluteus maximus sartorius quadraceps hamstring gastrocnemius Achilles tendon chest muscle front part of upper arm upper back behind shoulder blade upper back muscle arm abdomen butt long thin muscle across quadracep front of thigh back of thigh calf muscle attaches calf muscle to ankle MUSCLES The muscles of the human body make up roughly one-half of its weight. Most of the muscles are under our control and are called voluntary muscles. Others, over which we have no control, are called involuntary muscles. Some muscles, such as the eyelids, are both voluntary and involuntary. Together, both voluntary and involuntary muscles account for the movement of all body parts and functions. There are three muscles types, skeletal, cardiac and smooth. Skeletal muscle is voluntary while both the cardiac and smooth muscles are involuntary. SKELETAL MUSCLE Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles attached to bones to create body movement. Tendons are tough connective tissues that connect muscle to bone. When the muscle appears striped or bended this is called striation. Ligaments hold bones together and tendons attach muscle to bones. CARDIAC MUSCLE The cardiac muscle is found in the heart, it is involuntary. Contraction of the cardiac muscle causes the heart to beat. The cardiac muscle is striated. SMOOTH MUSCLE Smooth muscles include the digestive system, skin, arteries, veins, bladder, liver, and the eyelids. It is involuntary control and it is not striated. Smooth muscles react slower and tires slowly. MUSCLES IN ACTION Muscles only do work by contraction. Therefore, muscles must work in pairs, because every flexion (contraction) must have an extension (opposite contraction) in order to be used again. Individual muscle fibers shorten and thicken during contraction. A bicep is a flexor muscle because it causes a flexion (bends) in a joint. A tricep is an extensor muscle because it causes an extension of the joint. Muscle fatigue is when the lack of oxygen in the muscle causes a build up of lactic acid. Muscle tone is when muscles are partially contracted allowing for a quicker response.