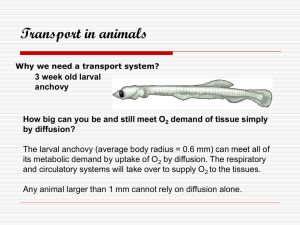
Heart Q & A
advertisement

Circulatory System, Blood, Heart & Heartbeat 1 The ABO blood group system has four blood groups. What are these four groups? A / B / AB / O 2 Name the chamber of the heart that receives blood back from the lungs. Left atrium (auricle) 3 What is the role of valves in the heart? To prevent backflow (of blood) 4 Suggest a reason why it is important to know a person’s blood group. Transfusion / to avoid reaction by mother to foetus / to prevent loss of foetus 5 Name the blood vessel that brings blood from the heart to the body. Aorta 6 How does a portal vein differ from other veins? Capillaries at both ends / joins two organs/ two named organs 7 The wall of capillaries is only one cell thick. How is this related to their function? Substances can diffuse easily/ in and out of blood / tissues/less fat content 8 Which has the bigger lumen (cavity), an artery or a vein? Vein 9 Why are valves not needed in arteries? Blood is under pressure / blood from heart / blood pumped 10 Valves are present in veins. What is their function? To prevent back flow of blood 11 Name the major blood vessels that carry blood 1. from the heart to the lungs 2. from the lungs to the heart. 1. Pulmonary artery; 2. Pulmonary vein 12 Name two types of cell found in the blood and give a function for each of them. Red blood cell / carries oxygen (also carries carbon dioxide); White blood cell / defence; Note: (allow Platelet / Blood Clotting ) Page 1 of 19 13 Name the liquid part of the blood. Plasma 14 What is blood plasma? Give a role for blood plasma. Plasma: blood without cells / watery liquid part of blood; Role: carries dissolved substances / named substance / waste / hormones / gases / blood clotting agent / water / antibodies / proteins / inorganic salts / fibrinogen / CO2 / Bicarbonate / Heat 15 State the results of your investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate Increases / comment on return to normal / different 16 Describe how you conducted the investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate after the period of rest /Exercise / description of exercise/ increased exercise/ pulse measured/ repeat/ average / compare / record / result 17 Different lifestyle factors have an effect on the health of our circulatory system. Name any two of these factors. Any two factors 18 Give two factors which cause an increase in heart rate. e.g. Exercise / anxiety / drugs / infection 19 Why is the wall of the right ventricle thicker than the wall of the left ventricle? Blood from the left ventricle must be pumped further / greater pressure 20 Name the arteries that supply the heart wall with blood. Coronary / Cardiac 21 Give the precise location of the heart in the human body. Thorax 22 The lymphatic system is another series of vessels carrying fluid in the body. Give any two functions of the lymphatic system. Returns fluid to blood / transport / lymphocytes (Immunity) 23 Name the blood vessels that bring this blood back from the lungs. Pulmonary vein 24 How did you measure the pulse? Page 2 of 19 Method described /count number of pulses /per unit time OR sensor (data logger) 25 At the start of the investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate of a human you asked the person who was about to do the exercise to sit down for a few minutes. Explain the purpose of this. Comparison /control / resting / normal 26 What is the role of the bicuspid valve? Stops back flow (of blood) / blood from atrium to ventricle 27 Give one reason why the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than the wall of the right ventricle. Pumps further/ maintains blood pressure / greater activity 28 Is the blood in the Aorta oxygenated or deoxygenated? Oxygenated 29 What is the average resting human heart rate? 69 – 75 30 Name two substances that are dissolved in the liquid part of blood. Products of digestion - glucose, amino acids, glycerol, fatty acids, minerals, vitamins; waste products - carbon dioxide, urea, uric acid; hormones - e.g. insulin, thyroxine, testosterone; plasma proteins - albumen, fibrinogen, prothrombin; antibodies - proteins which destroy pathogens; enzymes – thrombin; salts - e.g. NaCl, sodium bicarbonate 31 How did you measure the pulse resting rate? Use pulse monitor / read result in bpm or use of finger or wrist (radial pulse) / use timer or calculate in bpm / observe / count / repeat / average / record 32 State a possible effect of smoking on the pulse resting rate Raises rate 33 Answer the following in relation to the dissection of a heart. (i) What instrument did you use for the dissection? (ii) Describe how you carried out the dissection. (i) Scalpel / blade / scissors / knife; (ii) Ventral side up (identify left and right)/ section or words to that effect / expose left ventricle / expose right ventricle /section to show aorta) / pinning back/ [allow one] safety precaution 34 The hepatic portal vein carries blood from the alimentary canal to the … Liver 35 Name the upper chambers of the heart. Page 3 of 19 Atria / allow Auricle 36 Name two common blood-grouping systems. ABO and Rhesus 37 Describe how you investigated the effect of exercise on the pulse rate. (Measure) resting rate/ description of exercise/ measure rate during (or immediately after) exercise/ repeat / compare or state result / record 38 State one function of the liquid part of blood. Hold ‘cells’ and dissolved substances 39 What is the average pulse rate at rest? 65 to 79 bpm 40 Name the liquid part of blood. Plasma 41 Name the artery that supplies the heart muscle with blood. Coronary (artery) 42 What is the function of the bicuspid valve? Prevent backflow of blood from left ventricle to left auricle (atrium) 43 To where does the pulmonary artery carry blood? Lungs 44 State one factor that decreases heart rate and one factor that increases it. Decrease: sleep / drugs (sedatives); Increase: fear (fright) / exercise 45 What is the average resting rate of the human heart in beats per minute? 65 to 79 bpm 46 Blood contains red cells and white cells. State one function for each of these. Red: transports oxygen; White: protection against disease 47 Explain why the walls of the lower chambers of the heart are thicker than the walls of the upper chambers. They pump 48 Give two components of plasma. Page 4 of 19 Any two 49 Give the function of (i) Red blood cells (ii) White blood cells (iii) Platelets. (i) Transport O2 / CO2; (ii) e.g. to make antibodies; (iii) e.g. Blood Clotting 50 Name the blood vessel referred to in each of the following cases: (i) The vein connected to the lungs (ii) The artery connected to the kidneys (iii) The vein that joins the intestine to the liver. (i) Pulmonary (vein); (ii) Renal (artery); (iii) Hepatic Portal (vein) 51 What structure(s) protects the heart? Rib cage 52 Name the following blood vessels: 1. the vessels that carry blood from the aorta to the kidneys. 2. the vessels that supply the heart’s muscle with blood. 1. renal (arteries); 2. coronary or cardiac (arteries) 53 Name the valve between the upper and lower chambers on the left-hand side. Bicuspid (mitral) valve 54 Name the liquid part of blood. Plasma 55 Name the blood vessels that bring oxygen to the heart muscle. Coronary (arteries) / allow cardiac 56 The ABO blood group system has four blood groups. What are these four groups? A / B / AB / O 57 Name the chamber of the heart that receives blood back from the lungs. Left atrium (auricle) 58 What is the role of valves in the heart? To prevent backflow (of blood) 59 Suggest a reason why it is important to know a person’s blood group. Transfusion / to avoid reaction by mother to foetus / to prevent loss of foetus 60 Name the blood vessel that brings blood from the heart to the body. Page 5 of 19 Aorta 61 How does a portal vein differ from other veins? Capillaries at both ends / joins two organs/ two named organs 62 The wall of capillaries is only one cell thick. How is this related to their function? Substances can diffuse easily/ in and out of blood / tissues/less fat content 63 Which has the bigger lumen (cavity), an artery or a vein? Vein 64 Why are valves not needed in arteries? Blood is under pressure / blood from heart / blood pumped 65 Valves are present in veins. What is their function? To prevent back flow of blood 66 Name the major blood vessels that carry blood 1. from the heart to the lungs 2. from the lungs to the heart. 1. Pulmonary artery; 2. Pulmonary vein 67 Name two types of cell found in the blood and give a function for each of them. Red blood cell / carries oxygen (also carries carbon dioxide); White blood cell / defence; Note: (allow Platelet / Blood Clotting) 68 Name the liquid part of the blood. Plasma 69 What is blood plasma? Give a role for blood plasma. Plasma: blood without cells / watery liquid part of blood; Role: carries dissolved substances / named substance / waste / hormones / gases / blood clotting agent / water / antibodies / proteins / inorganic salts / fibrinogen / CO2 / Bicarbonate / Heat 70 State the results of your investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate Increases / comment on return to normal / different 71 Describe how you conducted the investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate after the period of rest Exercise / description of exercise/ increased exercise/ pulse measured/ repeat/ average / compare / record / result 72 Different lifestyle factors have an effect on the health of our circulatory system. Name Page 6 of 19 any two of these factors. Any two factors 73 Give two factors which cause an increase in heart rate. e.g. Exercise / anxiety / drugs / infection 74 Why is the wall of the right ventricle thicker than the wall of the left ventricle? Blood from the left ventricle must be pumped further / greater pressure 75 Name the arteries that supply the heart wall with blood. Coronary / Cardiac 76 Give the precise location of the heart in the human body. Thorax 77 The lymphatic system is another series of vessels carrying fluid in the body. Give any two functions of the lymphatic system. Returns fluid to blood / transport / lymphocytes (Immunity) 78 Name the blood vessels that bring this blood back from the lungs. Pulmonary vein 79 How did you measure the pulse? Method described /count number of pulses /per unit time OR sensor (data logger) 80 At the start of the investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate of a human you asked the person who was about to do the exercise to sit down for a few minutes. Explain the purpose of this. Comparison /control / resting / normal 81 What is the role of the bicuspid valve? Stops back flow (of blood) / blood from atrium to ventricle 82 Give one reason why the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than the wall of the right ventricle. Pumps further/ maintains blood pressure / greater activity 83 Is the blood in the Aorta oxygenated or deoxygenated? Oxygenated 84 What is the average resting human heart rate? Page 7 of 19 69 – 75 85 Name two substances that are dissolved in the liquid part of blood. Products of digestion - glucose, amino acids, glycerol, fatty acids, minerals, vitamins; waste products - carbon dioxide, urea, uric acid; hormones - e.g. insulin, thyroxine, testosterone; plasma proteins - albumen, fibrinogen, /prothrombin; antibodies - proteins which destroy pathogens; enzymes – thrombin; salts - e.g. NaCl, sodium bicarbonate 86 How did you measure the pulse resting rate? Use pulse monitor / read result in bpm or use of finger or wrist (radial pulse) / use timer or calculate in bpm / observe / count / repeat / average / record 87 State a possible effect of smoking on the pulse resting rate Raises rate 88 Answer the following in relation to the dissection of a heart. (i) What instrument did you use for the dissection? (ii) Describe how you carried out the dissection. (i) Scalpel / blade / scissors / knife; (ii) Ventral side up (identify left and right)/ section or words to that effect / expose left ventricle / expose right ventricle /section to show aorta) / pinning back/ [allow one] safety precaution 89 The hepatic portal vein carries blood from the alimentary canal to the … Liver 90 Name the upper chambers of the heart. Atria / allow Auricle 91 Name two common blood-grouping systems. ABO and Rhesus 92 Describe how you investigated the effect of exercise on the pulse rate. (Measure) resting rate/ description of exercise/ measure rate during (or immediately after) exercise/ repeat / compare or state result / record 93 State one function of the liquid part of blood. Hold ‘cells’ and dissolved substances 94 What is the average pulse rate at rest? 65 to 79 bpm 95 Name the liquid part of blood. Plasma Page 8 of 19 96 Name the artery that supplies the heart muscle with blood. Coronary (artery) 97 What is the function of the bicuspid valve? Prevent backflow of blood from left ventricle to left auricle (atrium) 98 To where does the pulmonary artery carry blood? Lungs 99 State one factor that decreases heart rate and one factor that increases it. Decrease: sleep / drugs (sedatives); Increase: fear (fright) / exercise 100 What is the average resting rate of the human heart in beats per minute? 65 to 79 bpm 101 Blood contains red cells and white cells. State one function for each of these. Red: transports oxygen; White: protection against disease 102 Explain why the walls of the lower chambers of the heart are thicker than the walls of the upper chambers. They pump 103 Give two components of plasma. Any two 104 Give the function of (i) Red blood cells (ii) White blood cells (iii) Platelets. (i) Transport O2 / CO2; (ii) e.g. to make antibodies; (iii) e.g. Blood Clotting 105 Name the blood vessel referred to in each of the following cases: (i) The vein connected to the lungs (ii) The artery connected to the kidneys (iii) The vein that joins the intestine to the liver. (i) Pulmonary (vein); (ii) Renal (artery); (iii) Hepatic Portal (vein) 106 What structure(s) protects the heart? Rib cage 107 Name the following blood vessels: 1. the vessels that carry blood from the aorta to the kidneys. 2. the vessels that supply the heart’s muscle with blood. 1. renal (arteries); 2. coronary or cardiac (arteries) 108 Name the valve between the upper and lower chambers on the left-hand side. Page 9 of 19 Bicuspid (mitral) valve 109 Name the liquid part of blood. Plasma 110 Name the blood vessels that bring oxygen to the heart muscle. Coronary (arteries) / allow cardiac 111 The ABO blood group system has four blood groups. What are these four groups? A / B / AB / O 112 Name the chamber of the heart that receives blood back from the lungs. Left atrium (auricle) 113 What is the role of valves in the heart? To prevent backflow (of blood) 114 Suggest a reason why it is important to know a person’s blood group. Transfusion / to avoid reaction by mother to foetus / to prevent loss of foetus 115 Name the blood vessel that brings blood from the heart to the body. Aorta 116 How does a portal vein differ from other veins? Capillaries at both ends / joins two organs/ two named organs 117 The wall of capillaries is only one cell thick. How is this related to their function? Substances can diffuse easily/ in and out of blood / tissues/less fat content 118 Which has the bigger lumen (cavity), an artery or a vein? Vein 119 Why are valves not needed in arteries? Blood is under pressure / blood from heart / blood pumped 120 Valves are present in veins. What is their function? To prevent back flow of blood 121 Name the major blood vessels that carry blood 1. from the heart to the lungs 2. from the lungs to the heart. Page 10 of 19 1. Pulmonary artery; 2. Pulmonary vein 122 Name two types of cell found in the blood and give a function for each of them. Red blood cell / carries oxygen (also carries carbon dioxide); White blood cell / defence; Note: (allow Platelet / Blood Clotting) 123 Name the liquid part of the blood. Plasma 124 What is blood plasma? Give a role for blood plasma. Plasma: blood without cells / watery liquid part of blood; Role: carries dissolved substances / named substance / waste / hormones / gases / blood clotting agent / water / antibodies / proteins / inorganic salts / fibrinogen / CO2 / Bicarbonate / Heat 125 State the results of your investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate Increases / comment on return to normal / different 126 Describe how you conducted the investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate after the period of rest Exercise / description of exercise/ increased exercise/ pulse measured/ repeat/ average / compare / record / result 127 Different lifestyle factors have an effect on the health of our circulatory system. Name any two of these factors. Any two factors 128 Give two factors which cause an increase in heart rate. e.g. Exercise / anxiety / drugs / infection 129 Why is the wall of the right ventricle thicker than the wall of the left ventricle? Blood from the left ventricle must be pumped further / greater pressure 130 Name the arteries that supply the heart wall with blood. Coronary / Cardiac 131 Give the precise location of the heart in the human body. Thorax 132 The lymphatic system is another series of vessels carrying fluid in the body. Give any two functions of the lymphatic system. Returns fluid to blood / transport / lymphocytes (Immunity) Page 11 of 19 133 Name the blood vessels that bring this blood back from the lungs. Pulmonary vein 134 How did you measure the pulse? Method described /count number of pulses /per unit time OR sensor (data logger) 135 At the start of the investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate of a human you asked the person who was about to do the exercise to sit down for a few minutes. Explain the purpose of this. Comparison /control / resting / normal 136 What is the role of the bicuspid valve? Stops back flow (of blood) / blood from atrium to ventricle 137 Give one reason why the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than the wall of the right ventricle. Pumps further/ maintains blood pressure / greater activity 138 Is the blood in the Aorta oxygenated or deoxygenated? Oxygenated 139 What is the average resting human heart rate? 69 – 75 140 Name two substances that are dissolved in the liquid part of blood. Products of digestion - glucose, amino acids, glycerol, fatty acids, minerals, vitamins; waste products - carbon dioxide, urea, uric acid; hormones - e.g. insulin, thyroxine, testosterone; plasma proteins - albumen, fibrinogen, prothrombin; antibodies - proteins which destroy pathogens; enzymes – thrombin; salts - e.g. NaCl, sodium bicarbonate 141 How did you measure the pulse resting rate? Use pulse monitor / read result in bpm or use of finger or wrist (radial pulse) / use timer or calculate in bpm / observe / count / repeat / average / record 142 State a possible effect of smoking on the pulse resting rate Raises rate 143 Answer the following in relation to the dissection of a heart. (i) What instrument did you use for the dissection? (ii) Describe how you carried out the dissection. (i) Scalpel / blade / scissors / knife; (ii) Ventral side up (identify left and right)/ section or words to that effect / expose left ventricle / expose right ventricle /section to show aorta) / pinning back/ [allow one] safety precaution Page 12 of 19 144 The hepatic portal vein carries blood from the alimentary canal to the … Liver 145 Name the upper chambers of the heart. Atria / allow Auricle 146 Name two common blood-grouping systems. ABO and Rhesus 147 Describe how you investigated the effect of exercise on the pulse rate. (Measure) resting rate/ description of exercise/ measure rate during (or immediately after) exercise/ repeat / compare or state result / record 148 State one function of the liquid part of blood. Hold ‘cells’ and dissolved substances 149 What is the average pulse rate at rest? 65 to 79 bpm 150 Name the liquid part of blood. Plasma 151 Name the artery that supplies the heart muscle with blood. Coronary (artery) 152 What is the function of the bicuspid valve? Prevent backflow of blood from left ventricle to left auricle (atrium) 153 To where does the pulmonary artery carry blood? Lungs 154 State one factor that decreases heart rate and one factor that increases it. Decrease: sleep / drugs (sedatives); Increase: fear (fright) / exercise 155 What is the average resting rate of the human heart in beats per minute? 65 to 79 bpm 156 Blood contains red cells and white cells. State one function for each of these. Red: transports oxygen; White: protection against disease Page 13 of 19 157 Explain why the walls of the lower chambers of the heart are thicker than the walls of the upper chambers. They pump 158 Give two components of plasma. Any two 159 Give the function of (i) Red blood cells (ii) White blood cells (iii) Platelets. (i) Transport O2 / CO2; (ii) e.g. to make antibodies; (iii) e.g. Blood Clotting 160 Name the blood vessel referred to in each of the following cases: (i) The vein connected to the lungs (ii) The artery connected to the kidneys (iii) The vein that joins the intestine to the liver. (i) Pulmonary (vein); (ii) Renal (artery); (iii) Hepatic Portal (vein) 161 What structure(s) protects the heart? Rib cage 162 Name the following blood vessels: 1. the vessels that carry blood from the aorta to the kidneys. 2. the vessels that supply the heart’s muscle with blood. 1. renal (arteries); 2. coronary or cardiac (arteries) 163 Name the valve between the upper and lower chambers on the left-hand side. Bicuspid (mitral) valve 164 Name the liquid part of blood. Plasma 165 Name the blood vessels that bring oxygen to the heart muscle. Coronary (arteries) / allow cardiac 166 The ABO blood group system has four blood groups. What are these four groups? A / B / AB / O 167 Name the chamber of the heart that receives blood back from the lungs. Left atrium (auricle) 168 What is the role of valves in the heart? To prevent backflow (of blood) 169 Suggest a reason why it is important to know a person’s blood group. Page 14 of 19 Transfusion / to avoid reaction by mother to foetus / to prevent loss of foetus 170 Name the blood vessel that brings blood from the heart to the body. Aorta 171 How does a portal vein differ from other veins? Capillaries at both ends / joins two organs/ two named organs 172 The wall of capillaries is only one cell thick. How is this related to their function? Substances can diffuse easily/ in and out of blood / tissues/less fat content 173 Which has the bigger lumen (cavity), an artery or a vein? Vein 174 Why are valves not needed in arteries? Blood is under pressure / blood from heart / blood pumped 175 Valves are present in veins. What is their function? To prevent back flow of blood 176 Name the major blood vessels that carry blood 1. from the heart to the lungs 2. from the lungs to the heart. 1. Pulmonary artery; 2. Pulmonary vein 177 Name two types of cell found in the blood and give a function for each of them. Red blood cell / carries oxygen (also carries carbon dioxide); White blood cell / defence; Note: (allow Platelet / Blood Clotting) 178 Name the liquid part of the blood. Plasma 179 What is blood plasma? Give a role for blood plasma. Plasma: blood without cells / watery liquid part of blood; Role: carries dissolved substances / named substance / waste / hormones / gases / blood clotting agent / water / antibodies / proteins / inorganic salts / fibrinogen / CO2 / Bicarbonate / Heat 180 State the results of your investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate Increases / comment on return to normal / different 181 Describe how you conducted the investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate after the period of rest Page 15 of 19 Exercise / description of exercise/ increased exercise/ pulse measured/ repeat/ average / compare / record / result 182 Different lifestyle factors have an effect on the health of our circulatory system. Name any two of these factors. Any two factors 183 Give two factors which cause an increase in heart rate. e.g. Exercise / anxiety / drugs / infection 184 Why is the wall of the right ventricle thicker than the wall of the left ventricle? Blood from the left ventricle must be pumped further / greater pressure 185 Name the arteries that supply the heart wall with blood. Coronary / Cardiac 186 Give the precise location of the heart in the human body. Thorax 187 The lymphatic system is another series of vessels carrying fluid in the body. Give any two functions of the lymphatic system. Returns fluid to blood / transport / lymphocytes (Immunity) 188 Name the blood vessels that bring this blood back from the lungs. Pulmonary vein 189 How did you measure the pulse? Method described /count number of pulses /per unit time OR sensor (data logger) 190 At the start of the investigation of the effect of exercise on the pulse rate of a human you asked the person who was about to do the exercise to sit down for a few minutes. Explain the purpose of this. Comparison /control / resting / normal 191 What is the role of the bicuspid valve? Stops back flow (of blood) / blood from atrium to ventricle 192 Give one reason why the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than the wall of the right ventricle. Pumps further/ maintains blood pressure / greater activity 193 Is the blood in the Aorta oxygenated or deoxygenated? Page 16 of 19 Oxygenated 194 What is the average resting human heart rate? 69 – 75 195 Name two substances that are dissolved in the liquid part of blood. Products of digestion - glucose, amino acids, glycerol, fatty acids, minerals, vitamins; waste products - carbon dioxide, urea, uric acid; hormones - e.g. insulin, thyroxine, testosterone; plasma proteins - albumen, fibrinogen, prothrombin; antibodies - proteins which destroy pathogens; enzymes – thrombin; salts - e.g. NaCl, sodium bicarbonate 196 How did you measure the pulse resting rate? Use pulse monitor / read result in bpm or use of finger or wrist (radial pulse) / use timer or calculate in bpm / observe / count / repeat / average / record 197 State a possible effect of smoking on the pulse resting rate Raises rate 198 Answer the following in relation to the dissection of a heart. (i) What instrument did you use for the dissection? (ii) Describe how you carried out the dissection. (i) Scalpel / blade / scissors / knife; (ii) Ventral side up (identify left and right)/ section or words to that effect / expose left ventricle / expose right ventricle /section to show aorta) / pinning back/ [allow one] safety precaution 199 The hepatic portal vein carries blood from the alimentary canal to the … Liver 200 Name the upper chambers of the heart. Atria / allow Auricle 201 Name two common blood-grouping systems. ABO and Rhesus 202 Describe how you investigated the effect of exercise on the pulse rate. (Measure) resting rate/ description of exercise/ measure rate during (or immediately after) exercise/ repeat / compare or state result / record 203 State one function of the liquid part of blood. Hold ‘cells’ and dissolved substances 204 What is the average pulse rate at rest? 65 to 79 bpm Page 17 of 19 205 Name the liquid part of blood. Plasma 206 Name the artery that supplies the heart muscle with blood. Coronary (artery) 207 What is the function of the bicuspid valve? Prevent backflow of blood from left ventricle to left auricle (atrium) 208 To where does the pulmonary artery carry blood? Lungs 209 State one factor that decreases heart rate and one factor that increases it. Decrease: sleep / drugs (sedatives); Increase: fear (fright) / exercise 210 What is the average resting rate of the human heart in beats per minute? 65 to 79 bpm 211 Blood contains red cells and white cells. State one function for each of these. Red: transports oxygen; White: protection against disease 212 Explain why the walls of the lower chambers of the heart are thicker than the walls of the upper chambers. They pump 213 Give two components of plasma. Any two 214 Give the function of (i) Red blood cells (ii) White blood cells (iii) Platelets. (i) Transport O2 / CO2; (ii) e.g. to make antibodies; (iii) e.g. Blood Clotting 215 Name the blood vessel referred to in each of the following cases: (i) The vein connected to the lungs (ii) The artery connected to the kidneys (iii) The vein that joins the intestine to the liver. (i) Pulmonary (vein); (ii) Renal (artery); (iii) Hepatic Portal (vein) 216 What structure(s) protects the heart? Rib cage 217 Name the following blood vessels: 1. the vessels that carry blood from the aorta to the kidneys. 2. the vessels that supply the heart’s muscle with blood. Page 18 of 19 1. renal (arteries); 2. coronary or cardiac (arteries) 218 Name the valve between the upper and lower chambers on the left-hand side. Bicuspid (mitral) valve 219 Name the liquid part of blood. Plasma 220 Name the blood vessels that bring oxygen to the heart muscle. Coronary (arteries) / allow cardiac Page 19 of 19