Histology of blood vessels
advertisement

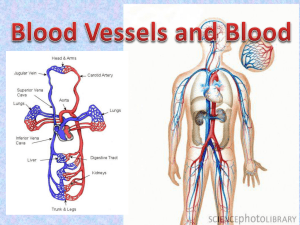
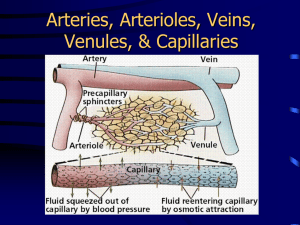
Histology of blood vessels Tubes of various sizes , carrying blood from the heart through the tissues and back to the heart again ,and thin- walled channels conveying lymph ,from the extensive circulatory system . Blood vessels are encountered in all tissues except epithelium ,some parts of the body are not supplied by lymphatic vessels . Blood vessels walls have considerable elasticity and constrict when the heart stops beating . materials carried by the blood are passed through the thin walls of the smallest vessels into the tissues. Capillaries ,pre capillaries Approximately 90% of all blood vessels are capillaries and pre capillaries. Capillaries are simple tubes of endothelium connecting arteries and veins. All vessels and even the heart , begin in the embryo as capillaries , adding layers of connective tissues and muscle as they developed capillaries are small their inside diameter is approximately that of an erythrocyte 8 to10 µ or little wider the capillary wall consist of thin endothelial cells are ovoid and stain rather lightly with hematoxylin they resemble the light nuclei of fibrocytes in the surrounding connective tissue in the surrounding connective tissue .the inner surface of the cells are in contact with blood .the outer surfaces rest on a basal lamina forming a continuous layer between the endothelium and surrounding loose fibrous connective tissue which contain its usual cells –fibrocytes ,macrophages , lymphocytes. The structure of capillary wall differs regionally in response to requirements for passage of fluid and solutes from the blood to intestinal spaces . thickness of the walls varies contacts between endothelial cells are relatively loose in many locations. Capillary permeability This term refers to the facility with which materials such as oxygen ,nutriments,products of cellular metabolism and hormones ,dissolved in blood plasma and tissue fluid ,are transported across the capillary wall.The net work of capillaries between the smallest arteries and veins is called the capillary bed . the density of capillary bed varies in different tissues . The next larger vessels is called precapillaries have afew smooth muscle cells in their walls. these and the arterioles are the vessels that contract and regulate the flow of blood into capillaries . Arteries All arteries large enough to be seen without magnification have walls consisting of three coats ( layer ) 1- the tunica intima is the endothelial lining with basal lamina and some connective tissue beneath it . 2-the middle coat or tunica media ,is formed by smooth muscle and connective tissue principally elastic fibers arranged in circular fashion . 3- the external coat or tunica adventitia (tunica externa) it is fibrous connective tissue with other structures in it arranged longitudinally . the three coats may be separated by elastioc membranes ,internal and external. Muscular arteries these are sometimes called distributing arteries they can regulate blood flow to different regions by contraction The smallest arteries ,called arterioles are members of the muscular artery class the tunica intima consist of endothelium ,basal , and an internal elastic membrane that may be incomplete in the smallest arterioles in cross sections the elastic membrane appears as acorrugated , highly refractive line throwing the endothelium into folds which bulge in to the lumen. The tunica media is a distinct muscular coat . the adventitia is about one third or one fourth as thick as muscular coat and merges with surrounding connective tissue although afew elastic fibers appear in the wall of the arteriols ,no external elastic membrane can be seen the smallest arterioles merge with pre capillaries . large and medium sized muscular arteries the structure of large and medium sized muscular arteries is consist of the tunica intima which formed by endothelium .basal lamina and a sub endothelial layer of fibrous connective tissue the internal elastic membrane is a well –developed fenestrated membrane .the muscle fibers of the tunica media are spirally arranged and may form 20-40 layers elastic fibers are interspersed among muscle fibers and a few collagenous and reticular fibers are demonstrable the tunica adventitia consist of fibrous connective tissue with longitudinal orientation where smooth muscle occurs in it fibers are arranged longitudinally lymphatic vessels are not seen in tunica media of the arteries but occure in the adventitia. muscular arteries are supplied with nerve fiber both motor fibers from the autonomic ganglia and sensory fibers from cranial and spinal nerves