Care of the Client Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle
advertisement
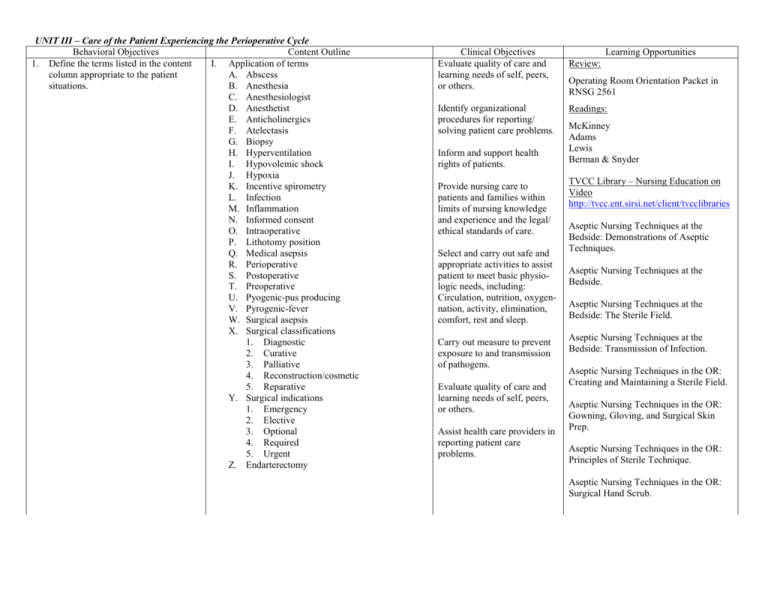
UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline 1. Define the terms listed in the content I. Application of terms column appropriate to the patient A. Abscess situations. B. Anesthesia C. Anesthesiologist D. Anesthetist E. Anticholinergics F. Atelectasis G. Biopsy H. Hyperventilation I. Hypovolemic shock J. Hypoxia K. Incentive spirometry L. Infection M. Inflammation N. Informed consent O. Intraoperative P. Lithotomy position Q. Medical asepsis R. Perioperative S. Postoperative T. Preoperative U. Pyogenic-pus producing V. Pyrogenic-fever W. Surgical asepsis X. Surgical classifications 1. Diagnostic 2. Curative 3. Palliative 4. Reconstruction/cosmetic 5. Reparative Y. Surgical indications 1. Emergency 2. Elective 3. Optional 4. Required 5. Urgent Z. Endarterectomy Clinical Objectives Evaluate quality of care and learning needs of self, peers, or others. Identify organizational procedures for reporting/ solving patient care problems. Inform and support health rights of patients. Provide nursing care to patients and families within limits of nursing knowledge and experience and the legal/ ethical standards of care. Select and carry out safe and appropriate activities to assist patient to meet basic physiologic needs, including: Circulation, nutrition, oxygennation, activity, elimination, comfort, rest and sleep. Carry out measure to prevent exposure to and transmission of pathogens. Evaluate quality of care and learning needs of self, peers, or others. Assist health care providers in reporting patient care problems. Learning Opportunities Review: Operating Room Orientation Packet in RNSG 2561 Readings: McKinney Adams Lewis Berman & Snyder TVCC Library – Nursing Education on Video http://tvcc.ent.sirsi.net/client/tvcclibraries Aseptic Nursing Techniques at the Bedside: Demonstrations of Aseptic Techniques. Aseptic Nursing Techniques at the Bedside. Aseptic Nursing Techniques at the Bedside: The Sterile Field. Aseptic Nursing Techniques at the Bedside: Transmission of Infection. Aseptic Nursing Techniques in the OR: Creating and Maintaining a Sterile Field. Aseptic Nursing Techniques in the OR: Gowning, Gloving, and Surgical Skin Prep. Aseptic Nursing Techniques in the OR: Principles of Sterile Technique. Aseptic Nursing Techniques in the OR: Surgical Hand Scrub. UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline 2. Compare and contrast the effects of II. Anatomy and Physiology surgery on the normal anatomy and A. Neurologic physiology of major systems across B. Respiratory the lifespan. C. Cardiovascular D. Hepatic and Renal E. Endocrine F. Immunology G. Developmental considerations 1. Infant 2. Child 3. Adolescent 4. Adult 5. Older adult 3. Analyze factors included in the assessment of the surgical patient, including the developmental and cultural considerations. III. General Physical Assessment A. Interview 1. Chief complaint 2. Precipitating event 3. Medical history 4. Family/social/occupational history 5. Medication history (prescription/nonprescription) 6. Knowledge of surgical procedure 7. Identify risk factors for surgery/anesthesia B. General Physical Assessment 1. Neurological a. Level of consciousness (LOC) 2. Psychosocial a. Anxieties b. Fear c. Mood d. Perception of event e. Emotional reaction/coping Mechanisms f. Availability of financial assistance 3. Nutritional status/chemical substance use a. Obesity b. Drug or alcohol Clinical Objectives Collaborate with other health care providers and members of the organization to solve patient care problems. Select and carry out appropriate nursing measures to promote psychosocial wellbeing. Administer medications and treatments safely. Learning Opportunities UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline 4. Respirations a. Respiratory (1) Rhythm (2) Depth (3) Effort b. Breath sounds c. Smoking d. Infection 5. Cardiovascular a. Blood pressure (1) Lying (2) Sitting (3) Standing b. Pulses c. Capillary refill time (CRT) d. Pre-existing conditions 6. Gastrointestinal (GI a. Palpation b. Auscultation 7. Hepatic and renal function 8. Endocrine function a. Blood glucose (diabetes) b. Use of steroid medications 9. Immunologic function a. Allergies b. Temperature 10. Previous medication therapy 11. Development considerations a. Age Specific (1) Sensory limitations (2) Mouth and teeth (3) Skin (4) Fears 12. Special Needs Patient C. Preoperative assessment 1. Nutrition a. Nothing by mouth (NPO) b. Dehydration 2. Preoperative check list 3. Baseline vital signs Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline D. Post-operative assessment 1. Airway patency 2. Vital signs 3. Neurological status 4. Tubings and drains 5. Surgical report a. Diagnosis (DX) – pre and post b. Medications given c. Problems occurred d. Pathology encountered e. Blood loss 6. I & O 7. Other data 8. Post anesthesia care unit (PACU) scoring guide E. Diagnostic tests 1. Laboratory studies a. Complete blood count (CBC) b. Prothrombin time (PT) c. Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) d. Electrolytes e. Urinalysis f. Type and cross match (TCX) 2. Radiology a. Chest x-ray b. X-rays 3. Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG) 4. Cultures 5. Frozen sections F. Cultural influences 1. Language 2. Health beliefs/practices 3. Spiritual beliefs 4. Religious practices G. Developmental 1. Age specific assessment data a. Vital signs b. Fluid/electrolytes c. Nutritional d. Physical changes 2. Behavioral/emotional response to health care providers Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline 4. Discuss legal and ethical issues related to patients undergoing a surgical procedure. IV. Legal/ethical issues A. Informed consent 1. Criteria 2. Responsibilities 3. Signatures B. Patient Rights C. Blood administration D. Confidentiality E. Privacy F. Patient advocate 5. Differentiate between the etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations of selected surgical procedures. V. Selected surgical procedures A. Abdominal surgeries 1. Laparoscopic a. Cholecystectomy 2. Open a. Appendectomy B. Tonsillectomy & adenoidectomy (T&A) C. Myringotomy & tube insertion D. Total knee replacement (TKR) E. Laparoscopic knee surgeries F. Fractures – cast care G. Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) hip H. Total hip replacement (THR) 6. Discuss analysis, planning, implementation and evaluation for the nursing management of patients undergoing a surgical procedure. VI. Selected nursing diagnoses/nursing implementation A. Knowledge deficit: Preoperative teaching 1. Independent interventions a. Assessment (1) Knowledge level (2) Developmental stage (3) Expectations b. Pertinent information (1) Exercises (2) Turning (3) Pain control c. Teaching aids Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline 2. Collaborative interventions a. Informed consent (1) Knowledge of surgical procedure (2) Information about complications (3) Legal b. Administer medications and monitor for desired effects and adverse/side effects (1) Narcotics (2) Analgesics (3) Sedatives (4) Tranquilizers (5) Anticholinergic c. Nutrition and fluids d. Intestinal preparation e. Skin preparation 3. Recognition of complications 4. Evaluate outcome of nursing interventions: Patient demonstrates understanding a. Methods of evaluation b. Patient verbalizes understanding B. High risk for intraoperative complications 1. Independent interventions a. Assessment b. Age related considerations 2. Collaborate intervention a. Roles of surgical team b. Positioning c. Skin care/Center for Disease Control standards (CDC) 3. Monitor for desired effects and adverse/side effects a. General anesthesia (1) Gas inhalation (2) Intravenous agents b. Conscious sedation c. Regional anesthesia (1) Topical (2) Spinal (3) Epidural Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline 4. Recognition of complications a. Arrest/Dysrhythmias b. Hypotension/hypertension c. Hemorrhage 5. Evaluation outcome a. Patient will return to preanesthetic level of consciousness (LOC) C. Ineffective airway clearance Post Anesthesia D. Care Unit (PACU) 1. Independent interventions a. Assessment respiratory function (1) Age related considerations (2) Maintain open airway b. Promoting lung expansion (1) Turn, cough, and deep breathe (2) Incentive spirometry (3) Splint incision 2. Collaborative interventions a. Administer oxygen b. Administer medications and monitor for desired effects and adverse/side effects (1) Narcan c. Diagnostic tests (1) Arterial blood gases (ABG) (2) Pulse oximeter 3. Recognizing complications a. Arrest/Dysrhythmias b. Hypertension/hypotension c. Respiratory depression d. Bronchospasms e. Laryngospasm f. Malignant/hyperthermia g. Hypothermia h. Aspiration i. Atelectasis Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline 4. Evaluation outcome a. Maintain patent airway with adequate exchange b. SaO2 94% or greater (>) E. Fluid and electrolyte imbalance (postoperative) 1. Independent interventions a. Assessment b. Age related hydration status c. Intake and output d. Monitor pertinent diagnostic tests e. Maintain skin integrity 2. Collaborative interventions a. Administer replacement fluid (1) Oral replacement solutions (2) Intravenous therapy b. Administration medications and monitor for desired effects/adverse effects (1) Potassium chloride (KCL) 3. Recognition of complications a. Hypovolemic shock b. Hyper/hypokalemia c. Hyper/Hyponatremia d. Fluid volume excess 4. F. Evaluation outcome: Patient will demonstrate adequate perfusion as exhibited by: a. Intake & Output b. Electrolyte balance c. Vital signs Pain and other postoperative discomforts 1. Independent interventions a. Assess coping strategies and related factors b. Pain assessment (1) Perception of pain (2) Pain assessment scales (3) Physiologic responses (4) Behavioral responses (5) Influencing factors Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) c. d. e. 2. Past experience with pain Anxiety Culture Age Placebo effect Provide physical care Manage anxiety Pain management strategies (1) Theories of acute pain management (2) Pharmacologic interventions (3) Nonpharmacologic measures (a) Massage (b) Ice and heat (c) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) (d) Distraction (e) Relaxation techniques (f) Guided imagery (g) Hypnosis (h) Skin Traction (i) Skeletal Traction f. Teach appropriate and safe ways to use analgesics Collaborative interventions a. Administer medications and monitor for desired effects and adverse/side effects (1) Analgesics (a) Preventive approach (around the clock schedule) (b) Individual doses (c) Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) (2) Opioids (3) NSAIDs (4) Routes (a) Parenteral (b) Oral Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline (c) Rectal (d) Intraspinal (5) Anticoagulants 3. Recognizing complications a. Respiratory depression and sedation b. Nausea and vomiting c. Constipation d. Inadequate pain relief e. Addiction and tolerance f. Impaired circulation 4. Evaluation of outcome a. Achieves pain relief b. Administers prescribed analgesic medications correctly c. Uses nonpharmacologic pain strategies as recommended d. Reports minimal side effects of interventions G. Potential other post operative complication 1. Independent interventions a. Assessment (1) Respiratory (2) Circulatory (3) Neurologic (4) Drainage (5) Comfort (6) Psychologic (7) Safety (8) Equipment b. Age related considerations c. Monitor pertinent diagnostic tests 2. Collaborative interventions a. Fluid and electrolyte replacement b. Medications 3. Recognition of complications a. Hypovolemia shock b. Hemorrhage c. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) d. Wound infection e. Peritonitis f. Evisceration Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities UNIT III – Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Behavioral Objectives Content Outline g. Dehiscence h. Urinary retention i. Gastrointestinal dysfunction j. Compartment Syndrome k. Fat Emboli 4. Evaluation outcome a. Patient will return to preanesthetic LOC, sensory – motor activity, vital signs 20% plus or minus. b. Patient will be able to perform activities of daily living. N:ADN/Spring 09/RNSG 2504 Unit III Care of the Patient Experiencing the Perioperative Cycle Clinical Objectives Learning Opportunities Revised 11/12