NURSING DIAGNOSIS
advertisement
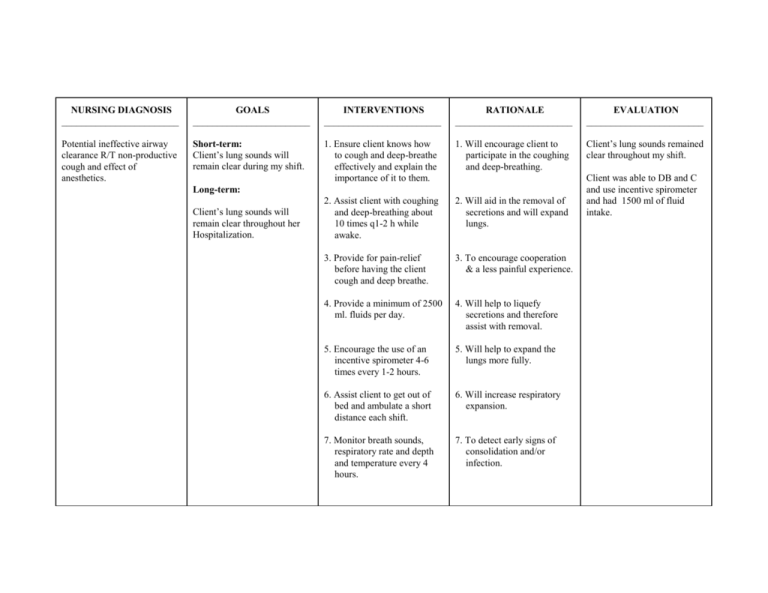
NURSING DIAGNOSIS ________________________ GOALS ________________________ INTERVENTIONS ________________________ RATIONALE ________________________ EVALUATION ________________________ Potential ineffective airway clearance R/T non-productive cough and effect of anesthetics. Short-term: Client’s lung sounds will remain clear during my shift. 1. Ensure client knows how to cough and deep-breathe effectively and explain the importance of it to them. 1. Will encourage client to participate in the coughing and deep-breathing. Client’s lung sounds remained clear throughout my shift. 2. Assist client with coughing and deep-breathing about 10 times q1-2 h while awake. 2. Will aid in the removal of secretions and will expand lungs. 3. Provide for pain-relief before having the client cough and deep breathe. 3. To encourage cooperation & a less painful experience. 4. Provide a minimum of 2500 ml. fluids per day. 4. Will help to liquefy secretions and therefore assist with removal. 5. Encourage the use of an incentive spirometer 4-6 times every 1-2 hours. 5. Will help to expand the lungs more fully. 6. Assist client to get out of bed and ambulate a short distance each shift. 6. Will increase respiratory expansion. 7. Monitor breath sounds, respiratory rate and depth and temperature every 4 hours. 7. To detect early signs of consolidation and/or infection. Long-term: Client’s lung sounds will remain clear throughout her Hospitalization. Client was able to DB and C and use incentive spirometer and had 1500 ml of fluid intake. NURSING DIAGNOSIS ________________________ GOALS ________________________ INTERVENTIONS ________________________ RATIONALE ________________________ EVALUATION ________________________ Alteration in comfort related to pain in surgical incision as evidenced by rating abd. pain @ 8 out of 10 and grimacing with movements. Short-term: 1. Assess location, quality, intensity and site of pain throughout shift. 1. To allow for appropriate intervention and documentation. Short-term: 2. Assess both verbal and nonverbal indicators of pain. 2. Both verbal and non-verbal cues will indicate pain intensity and relief. 3. Use pain-rating scale as per hospital policy. 3. Provides accurate determination of pain intensity and relief. 4. Administer analgesics prn and give promptly when asked. 4. Provides pain relief, decreases stress and anxiety. 5. Teach splinting of abd. area when coughing and deep breathing, laughing or sneezing. 5.Teaches client ways to help decrease pain. 1. Client will verbalize pain relief to tolerable level (23) 1 hour after given analgesic. 2. Client will state that changing positions and ambulating is more tolerable (2-3) by the end of the shift. Long-term: 1. Client will be able to tolerate oral analgesics instead of injections within 48 hours. Client verbalized pain relief with analgesics and stated pain decreased to between 2-4 at end of shift. - Goal met. 6. Administer analgesics prior to ambulation. 7. Teach client nonpharmacological pain relief measures (eg. Distraction, imagery). 8. Continually assess effectiveness of pain relief. 6. Ensures ambulation as pain free as possible, increases likelihood client will agree to ambulate again. 7. Teaches client alternative pain relief measures if pain meds not yet due. 8. Helps to ensure adequate pain relief. Long-term: Unable to assess at this point. Would assess in 48 hours.