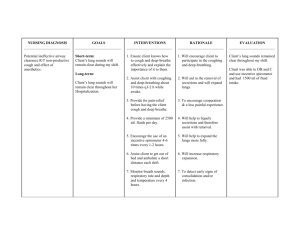
Pain Management Introduction ● Under recognized ● Misunderstood ● Inadequately tested ● Subjective ● No two people experience pain in the same way Knowledge, Attitudes and Beliefs ● Be respectful ● Look over their pain history ● Do not degrade their experience ○ “Frequent flier” Assumptions about patient pain ● Limits the ability to offer pain relief ● Accept the patients report of pain ● View experience through the patient's eyes Factors Influencing Pain ● Physiological ○ Age ○ Fatigue ■ Can cause increase in perception of pain ■ Can decrease the coping abilities ○ Genes ■ Genetic info passed from parents can affect a person's sensitivity to pain ○ Neurological function ■ Neuropathy/neurosurgery can reduce the ability to feel the pain ■ Diabetes (feet), less ● Social ○ Previous experience ■ Pain = pain ■ Having previous episodes of pain without proper treatment can result in fear and anxiety ○ Family and social network ■ Dependent upon others to help ○ Spiritual factors ■ Affect the way the patient views and copes with pain ● Psychological ○ Attention ■ Increased attention is associated with increased pain ■ Distraction is associated with a diminished pain response ● ● Massage ● Guided imagery ○ Anxiety and fear ■ Increased perception of pain ○ Coping style ■ Influences the ability to deal with the pain Cultural factors ○ Meaning of pain ■ Part of life, deal with it > lack of treatment ○ Ethnicity Critical thinking ● Attitudes and standards ● Creative planning ● Obtain acceptable outcomes ○ Pros and cons of different treatments Nursing Process ● Assessment ○ COLDSPA ■ Characteristics ■ Onset ■ Location ■ Duration ■ Severity ■ Pattern ■ Associated factors ○ PQRSTU (box 44.5 in textbook) ■ Palliative/provoking ● What makes your pain worse/better? ■ Quality ● Describe your pain for me. ■ Relief measures/Region ● What do you take at home to gain pain relief? ● What helps your pain go away? ● Show me where you are hurting ■ Severity ● On a scale of 0 to 10, how bad is your pain right now? ● What is the worst pain you have had in the past 24 hours? ● What is the average pain you have had in the past 24 hours? ■ Timing ● Do you have pain all the time, only at certain times, or only on certain days? ■ Unable to do ● ● What are you not able to do because of your pain? ● Who do you live with? How do they help you when you have pain? ○ ABCDE (box 44.6 in textbook) ■ Ask/assess pain regularly/systematically ■ Believe patient and family in their report of pain and what relieves it ■ Choose pain control options that are appropriate for patient, family, and setting ■ Deliver interventions in a timely, logical, and coordinated fashion ■ Empower patient and their family ○ Pain scale ■ Numerical scale ● 0 to 10 ■ Verbal descriptive scale ■ Visual analog scale ■ Wong-Baker faces pain scale ● Pediatric patients ● Non English speakers ○ Physical Examination ■ Pain can influence on activities of daily living (ADL) ● Need help showering, dressing, etc ○ Concomitant symptoms ■ Increases pain severity ○ Related Diagnoses ■ Difficulty coping ■ Fatigue ■ Impaired mobility ■ Impaired sleep ■ Social isolation Implementation ○ Health promotion ■ Different types of pain relief measures ■ Use measures patient believes are appropriate ■ Open mind ■ Keep trying ■ May not be totally eliminated, but substantial improvement is realistic ○ Maintain wellness ○ Non Pharmacological pain relief ■ Distraction ■ Music ■ Relaxation and guided imagery ■ Herbals ■ Cutaneous stimulation ■ Cognitive and behavioral approach ■ Reducing pain perception and reception ○ Acute Care (hospital setting) ■ Pharmacological pain therapies ● Analgesics ○ Nonopioids ■ Tylenol ■ Advil ○ Opioids ■ Percocet ■ Morphin ■ Hydromorphone ■ Too much can cause decreased vital signs ○ Adjuvants/co-analgesics ■ Not designed for pain relief, but have some aspect pain relief ● Patient controlled analgesia ● Topical and transdermal analgesics ● Local anesthesia ● Perineural local anesthetic infusion ● Epidural analgesia Safety Guidelines for Nursing Skills ● Patient is the only person who should press the button to administer the pain medication when PCA is used ● Monitor the patient for signs and symptoms of oversedation and respiratory depression ● Monitor for potential side effects of opioid analgesics