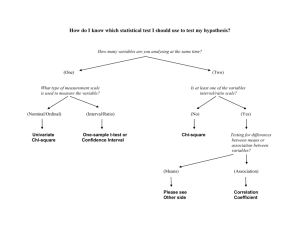
Statistical terms commonly used for research

Experimental Models
Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA): Statistical test to compare three of more treatment groups while controlling for the effect of one or more confounding variables
Analysis of variance (ANOVA): Test to compare three or more treatment group conditions, or the simultaneous manipulation of two or more independent variables.
Chi square test (
2 ): Test to compare observed frequencies within categories to frequencies expected by chance.
Correlation (r, r 2 ): The tendency for variation in one variable to be related to variation in a second variable.
Multiple regression analysis: Test to establish the predictive relationship between one dependent variable and a set of independent variables.
Paired t-test: Test to compare two means of samples or repeated measures; also called a correlated t-test.
Regression analysis: Test to examine the predictive relationship between a dependent and independent variable.
t-test: Test to compare two means; also called Student’s t-test unpaired t-test: Test to compare two means for independent samples; also called an independent t-test.
Statistics used in epidemiologic designs
Descriptive cohort study
Incidence: The number of a new cases of a disease or disorder in the population during a specific time period.
Mortality rate: The incidence of a death in a population
(determined by dividing the number of deaths during a specific time period by the total population at midyear).
Prevalence (P): The number of cases of a disease at a point in time, expressed as a proportion of a total population at risk.
Analytic cohort study / Case control study
Attributable risk (AR): An estimate used to quantify the risk of disease in an exposed group that is attributable to the exposure, by removing the risk that would have occurred as a result of other causes (risk in the unexposed group)
Odds ratio (OR): Relative risk in a case-control study.
Relative risk (RR): Ratio of incidence of disease the exposed subjects to the incidence of disease among the unexposed.
Studies for diagnostic and prognostic test
Likelihood ratio (LR): Indicates by how much a diagnostic test result will raise or lower the pretest probability of the target disorder.
Sensitivity: The proportion of people with the target disorder in whom the test result is positive.
Specificity: The proportion of people without the target disorder in whom the test result is negative.
Common terms
Confidence Interval (CI): The range of values within which a population value or parameter is estimated to fall, with a specific level of confidence (such as 95% confidence).
Dependent variable: Variable assumed to depend on or be influenced by another (independent) variable.
Statistical terms commonly used for research
Independent variable: The variable that is presumed to cause or determine a dependent variable; this variable is manipulated or controlled by the researcher, who sets its levels.
Mean: A measure of central tendency; the arithmetic average of all scores.
Median: A measure of central tendency; the middle score.
Mode: A measure of central tendency; the most frequent score
Nonparametric test: used with nominal or ordinal data
Null hypothesis: states that a potential treatment has no effect
p value: The likelihood that a difference is by chance.
Parameter: a characteristic of a population measured using ratio (continuous) data
Parametric test: used with interval or ratio data.
Range: The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a set of data.
Standard deviation (s): The average distance of scores from the mean of those scores
Standard error of mean (SEM): The standard deviation of theoretical distribution of sample means (indicates the average error in estimating a population mean).
Statistical Power (1-
): the probability that a study will reject a false null hypothesis (will not make a Type II error). As power increases, the chances of a Type II error decrease.
Type I error (
): A finding in a study that two groups are different when they are actually not different.
Type II error (
): A finding that two groups are not different when actually they are different.
Kinds of data for dependent variable
Nominal: data are in mutually exclusive categories (eg, patient lived or died)
Ordinal: data is ranked (improvement was good, fair, or poor)
Interval: numeric intervals of the data are equal but the scale has no true zero (eg, Fahrenheit temperature)
Ratio: a continuous numeric scale with a true zero point (eg, birth weight). Interval and ratio data are both continuous.
Bias
Experimenter bias: Occurs when behaviors, expectations, or attitudes of experimenter influences collection of the data.
Interviewer bias: Occurs when interviewer who collects the data knows the status of the subjects (has disease or not )
Observation bias: Occurs when systematic differences between the case and control groups occur because of the way information about a disease or exposure is obtained.
Rater bias: Occurs when the same rater is involved in both test and retest (rater's memory may influence rating).
Recall bias: Occurs when subjects who have experienced a particular disorder remember their exposure history differently.
Sampling bias: Occurs when individuals selected for a sample overrepresent or underrepresent population attributes that are related to the phenomenon being studied.
Selection bias: The process of selecting subjects results in initial differences between groups.
Kell Julliard, Asst VP for Research, Lutheran Medical Center, kjulliard@lmcmc.com, 718 630-6332
4/13/2020, d:\726896413.doc
Guide to Selecting Statistical Tests
Type of data
NONPARAMETRIC
Nominal
Ordinal
PARAMETRIC
Interval or ratio
Related
Two groups
Independent
Chi-square
McNemar’s
Sign test
Wilcoxon
signed
rank
Paired t
Chi-square
Fisher exact
(small sample)
Chi-square
Mann-Whitney U
Independent
Median test t
More than two groups
Chi-square
Chi-square
Kruskal-Wallis
ANOVA
4/13/2020, d:\726896413.doc