Guided Reading in the Junior Grades
advertisement

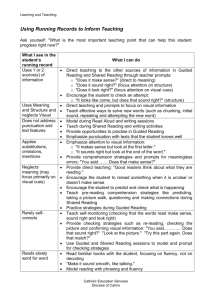
Guided Reading in the Junior Grades GUIDED READING CAN OCCUR IN ANY SUBJECT AREA What is Guided Reading? An instructional setting that enables teachers to work with small groups of students for twenty minutes to help them learn effective reading strategies. An approach designed to help individual students learn how to process a variety of increasing challenging texts with understanding and fluency. Why do Guided Reading? Supports students as they talk, think and question their way through a text. Allows opportunities to provide feedback to students. Allows the opportunity to coach and prompt students in effective reading and comprehension strategies. Allows building on of students’ current strategic skills and behaviours Engages students in meaningful discussions about the text Structure of a Guided Reading Lesson * depending on your text selection you may also cover many media literacy expectations 1.1,1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5,2.1 Planning Guided Reading Think about the last reading session in which you observed students. Consider your focus for the lesson and strategies that will be addressed. Select a text that will help build the readers skills. Read the text Plan your introduction and decide on the purpose of the lesson. You may want to place sticky notes on parts of the text that will be discussed before and after reading. Plan what questions you will ask and how to lead the discussions about the text Consider how you will support students with challenges within the text Determine how the session time will be spent, how much time will be given for the introduction, the reading and the after reading discussion For students who are not involved in guided reading, provide tasks that will keep them purposefully occupied Consider how you will assess leaning and how you will track your observations Before Reading (whole group) Reading Expectations 2.4, 2.3, 2.2, 2.1, 1.7, 1.3, 1.2 Explicitly state the purpose of the lesson and explain how it will benefit students as readings (purpose for reading, i.e., websites for information on a topic from different sources, for interest/enjoyment, for background knowledge) Encourage students to use highlighters or sticky notes to mark interesting, challenging or confusing text that can be discussed afterwards Draw attention to text features and how they communicate meaning (tables, indexes, captions, drop down menus) Discuss text form and elements of text and draw attention to characteristics that will communicate meaning (advertisement-use of layout, myth – use of supernatural, magazine – cover image and use of sidebars, report – opening tells purpose and goals, narrative – raising action holds attention and creates suspense) Prompt students to make predications (use CATS or THIEVES) Activate prior knowledge of a topic through discussion Remind students of strategies they might use to make meaning Discuss vocabulary that may be encountered in the text Determine how much of the text will be read in each session, one text is usually used over several sessions Create a balance between the amount of time given to active observation (listening) as students read and with discussions and questioning to promote higher level thinking. Remember that guided reading groups will use the same text for several sessions. During Reading (independent reading of the text, teacher listens to a student at a time, may pause reading and discuss) Reading Expectations 1.1,3.1, 3.2, 3.3 Demonstrate, prompt and reinforce the effective use of systems of strategies actions (rapidly solving words using base words, familiar words within larger words, monitor for meaning, use fix up strategies, use spelling patterns to solve words) Prompt for fluency and phrasing (adjust speed and expression to match purpose and form, use punctuation, read groups of words, read without pointing) Prompt for different uses of tone (voice going up with question marks, stressing appropriate words to convey meaning) Teacher provides each reader with the appropriate level of support Pause reading to discuss text and reading strategies they are using Record assessment observations about individual students and give effective feedback to improve reading Use strategic questioning to probe students’ thoughts and encourage higher-order thinking Stop and discuss the part of the text to ensure they understand it After Reading: Discussing the Meaning and Revisiting the Text (Whole Group) Reading Expectations 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, 1.8, 1.9, 2.1, 2.4, 2.2, 2.3, 4.1, 4.2 Oral Expectations 1.1, 1.2, 1.4, 2.2, 2.3 Gather evidence of comprehension from observing what students say about the text Engage students in a focused discussion about the text, maintain an appropriate balance between student and teacher talking Allow students to pose questions and clarify their understanding Extend understanding through oral discussion of questioning, summarizing, restating, determining importance, synthesizing information, making connections and inferring Help students to learn through discussion of meaning Discuss the text features, text patterns, text form and elements of style and how they communicate meaning Only after oral discussions engage students in activities that could deepen their understanding of the text (personal response, role play of a character. Graphic organizer – share these before reading in the next session) If appropriate, return to the text and have students re-read parts of the text After Reading: Teaching for Processing Strategies Reading Expectations 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.6, 1.7, 1.8, 1.9, 2.1, 2.4, 2.2, 2.3 Revisit the text to demonstrate or reinforce any aspect of reading Provide explicit demonstration of strategic actions using any part of the text that has been read Solving Words Monitoring and Checking Remembering information (summarizing) Predicating Synthesizing Maintaining fluency Making connections Analyzing Searching and using information Adjusting reading (purpose and genre) Inferring Critiquing After Reading: Word Work Reading Expectations 3.2, 3.1 Teach any aspect of word analysis – letter and sound relationships, breaking words apart Manipulation of words / Word games Work flexibly with base words, making new words by changing letters, adding prefixes and suffixes Take apart and understand words with several syllables (mis-rep-re-sen-ta-tion) Resources The Effective Guides: Volume Five Frequency and Groupings page 71 Text Selection Page 72 Teacher Preparation Page 73 Conducting a guided reading lesson page 74-75 Observational tracking sheet page 76 The Effective Guides: Volume Five Sample Guided Reading on making predictions page 35 Guiding Readers and Writers Grade 3 -6 Overview of Guided Reading page 193 Guided Reading Lesson: Fiction page 193 Guided Reading Lesson: Nonfiction Lesson page 201 Lesson frequency and number of texts page 207 Forming groups for Guided Reading page 216 Selecting texts page 223 – 228 Examples of text introductions page 234