The Stages of Schooling
advertisement

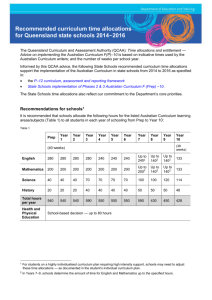
Stages of schooling To assist schools to implement the Australian Curriculum, State Schools is adopting the Stages of schooling as outlined in Table 1. Table 1 Stages of schooling 2014 2015 Early years of schooling Prep – Year 2 Upper primary Year 3 – Year 7 Year 3 – Year 6 Junior secondary Year 8 – Year 9 Year 7 – Year 9 Senior secondary Year 10 (transition to senior schooling) Year 11 – Year 12 In each stage of schooling, schools provide the curriculum to meet student needs and interests and according to the school and community context. Schools make local decisions about their school organisational structure and staffing arrangements in a culture of ongoing improvement which sets high expectations, monitors student progress and provides quality teaching focused on improving the achievement of every student. Curriculum provision Schools provide the F (Prep) – 12 curriculum as specified in the P-12 curriculum, assessment and reporting framework; and according to the schedule provided in State Schools implementation of Phases 2 & 3 Australian Curriculum F (Prep) – 10. Across these stages of schooling, the Australian Curriculum varies the emphasis given to each of the eight learning areas to address the nature of the learner in each stage. The Early years of schooling In Prep to Year 2, the Australian Curriculum gives priority to establishing literacy and numeracy and the other critical aspects of learning and development in the early years — social and physical development and sensory, cognitive and affective appreciation of the world. These skills are taught as part of the learning areas. In Prep, the first formal year of schooling, every student is recognised as a capable learner. Teachers build from each student’s diverse prior experience when planning to teach the required curriculum. They teach in ways known to engage young learners and to best support their learning and development. From entry to Prep and throughout the early years, schools and teachers assess, monitor and respond to each student’s learning. This ongoing monitoring of student progress informs the differentiation of teaching. This is critical in the early years when student learning and development of social, physical and cognitive skills occurs at such a rapid and variable rate. Across the early years, continuity of student learning and successful transitions are supported — from home or Kindergarten to Prep; from Prep into Year 1 and later into the upper years of primary. Stages of schooling Upper primary In Years 3 to 6, the Australian Curriculum continues to prioritise English and literacy and Mathematics and numeracy, along with the opportunity for a broad education that includes eight learning areas. The Year 3 curriculum is linked with Year 4 rather than with the early years. Schools provide opportunities for students to deepen their learning in particular areas according to their interests and needs. Teachers take into account that students are expanding the scope of their interests and are typically moving from concrete to abstract thinking. Teachers promote links between aspects of learning to deepen students’ knowledge and understanding and to show the connectedness and relevance of their learning. Junior Secondary In Years 7 to 9, Junior Secondary provides a bridge between primary and secondary school that is safe, strong and consistent for all students. At its core, Junior Secondary will respond to adolescent development and support transition from primary to secondary school. The six guiding principles provide schools and teachers with a strong foundation on which to develop appropriate strategies, practices and processes to bring about positive learning outcomes for students. Young adolescents will engage with a challenging curriculum through evidence-based approaches to teaching and learning, while consolidating literacy and numeracy skills. There will also be a strong emphasis on pastoral care for students. From Year 9, the Australian Curriculum provides increased opportunities for students to make choices about learning pathways and to deepen their understanding in learning areas. Year 10 Year 10 provides a transition year to senior schooling during which students can commence senior schooling pathways including vocational pathways. Schools provide the Year 10 Australian Curriculum as part of their Year 10 program which is also informed by the Queensland Curriculum and Assessment Authority Year 10 Guidelines. Schools design and deliver their overall Year 10 program to ensure all students are: fully engaged in learning that articulates to formal learning pathways; and receive the necessary preparation to continue senior secondary pathways. Schools ensure every Year 10 student completes a Senior Education and Training (SET) plan and has the opportunity for review in Years 11 and 12. Years 11 – 12 In Years 11 and 12, schools offer more opportunities for specialisation in learning, including through accredited vocational education and training. Schools support student choices about pathways through school and beyond — to attain a Senior Education Profile including a Queensland Certificate of Education, a Queensland Certificate of Individual Achievement, an International Baccalaureate Diploma, or a Tertiary Entrance Statement. Schools continue to implement the current Queensland Curriculum and Assessment Authority syllabuses; and ensure articulation from Australian Curriculum Year 10 programs to related courses in Years 11 -12. In Years 11 – 12, schools continue to prepare students to exit schooling with the underpinning knowledge, understanding and skills for successful lifelong learning and participation in local and global communities. Stages of schooling Page 2 of 2