1 - University of the West of England
advertisement

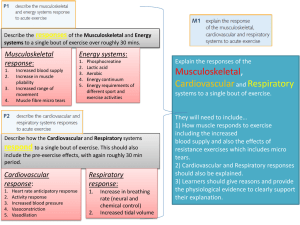
University of the West of England Faculty of Health and Life Sciences BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy Cardiovascular and Respiratory Syllabus Summary of the cardiovascular and respiratory teaching and learning throughout the programme We take a broad approach to the cardiovascular and respiratory education underpinning the subject specific considerations with wider physiotherapy principles, most notably rehabilitation and a holistic functional approach. We endeavour to cover a breadth of issues related to this subject from acute care of the critically ill through "ward care" and out into the community. Key areas of study over the three years incorporate: cardiovascular and respiratory anatomy and physiology, medical and surgical conditions and their management, recognition and care of the critically ill patient specific rehabilitation programmes and principles exercise physiology the provision of exercise testing and prescription to address cardiovascular and respiratory "fitness" literature evaluation and critique to assess evidence based practice in cardiovascular respiratory care review of current professional issues and changes that may affect cardiorespiratory care in the near future on call preparation Although cardiac, pulmonary and amputee rehabilitation are specifically addressed, there is a strong emphasis on the importance of rehabilitation generally with all patient groups along side the "chest physiotherapy and management". Lectures, seminars, practical session, and workshops are all used, enco mpassing a variety of teaching tools such as case studies, problem solving, videos, demonstration and practice of techniques and demonstration and use of relevant equipment.. Below are the learning outcomes and session outlines for the various modules throughout the course. In reality we are unable to fully encompass or indeed fully assess competency of all the learning outcomes during the contact time in university. Therefore there is an expectation for the students to address any "untaught" learning outcomes through self study and whilst on clinical placement. Similarly an important part of the assessment of their learning and competency, particularly their practical skills, needs to be assessed whilst on clinical placement. We are very grateful for the support of our clinical colleagues in this vital role. Year 1 Cardiovascular Cardiovascular Physiology Describe the gross and minute structure of the heart Describe the structure and function of the conducting system of the heart Relate the events of the cardiac cycle to the normal heart sounds and ECG Define cardiac output and explain the factors that affect it Explain the factors affecting venous return Compare the structure and function of the various types of blood vessels Define blood flow and peripheral resistance and explain the factors that affect them Define the term arterial blood pressure and give average values for the normal adult Explain the relationship between blood pressure, peripheral resistance and cardiac output. Explain the factors responsible for regulating blood pressure Cardiovascular disease Classify and briefly define the types of vascular disorders (arterial and venous) Explain how the pathological changes of atherosclerosis affect the normal structure of the arteries Identify the signs and symptoms of arterial disease using the Lower Limb and the Heart as examples of regions affected Identify the signs and symptoms of venous obstruction, and deep vein thrombosis using the lower limb as an example of the region affected Explain how the pathological changes of arterial and venous diseases give rise to the signs and symptoms List the predisposing factors relating to atherosclerosis, and deep vein thrombosis Outline the role of the physiotherapist in the prevention of vascular disease (with particular reference to atherosclerosis and deep vein thrombosis) Compare the physiotherapy management of patients with arterial and venous pathology State the surgical procedures that may be used to treat lower limb peripheral vascular disease Define the terms Heart Failure and Circulatory Failure (Medical Shock) Explain the Signs and symptoms of: Left Sided Heart Failure (LVF) Right Sided Heart Failure (RVF) Circulatory Failure Classify the causes of Circulatory Failure Define the terms Ischaemic Heart Disease and Myocardial Infarction Explain how Myocardial Infarction may affect Cardiac Function Outline of contact teaching sessions Lecture 1 Introduction to Cardiovascular disease Lecture 2 Physiology of Blood Pressure Seminar 1 Problem solving case study - Peripheral vascular disease Seminar 2 Problem solving case study – DVT Seminar 3 Problem solving case study - Shock Seminar 4 Problem solving case study - Heart failure Self study supported with workbook to cover learning outcomes Year 1 Respiratory Aims and learning outcomes. By the end of this module the students should be able to: Structure of Lungs Describe the gross structure of the thoracic cage Explain the functions of the thoracic cage List and Describe the arrangement of the thoracic contents Describe the gross structure of the lungs Explain the functions of the lungs Outline the gross structure of the upper respiratory tract Explain the function of the upper respiratory tract Describe the arrangement of the lower respiratory tract Explain how the histological structure of the following relate to their function: Trachea; Bronchi; Bronchioles; Respiratory Bronchioles; Alveoli Explain how the histological structure of the pleura relates to its function Explain how the changes in thoracic dimensions result in movement of air in and out of the lungs Physiology Define the following terms giving values for each: Tidal Volume; Functional Residual Capacity; Inspiratory Reserve Volume; Expiratory Reserve Volume; Inspiratory Capacity; Residual Volume; Total Lung Capacity; Vital Capacity; FEV 1; Dead Space; Minute Volume Discuss the factors which determine Vital capacity List the partial pressures of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in: Atmospheric Air; Alveolar Air; Mixed Expired Air; Arterial Blood; Venous Blood Explain why the differences in pressure occur in the above situations Explain how 02 and C02 diffuse across the respiratory membrane Explain how 02 and C02 are transported in the blood to the tissue cells List the factors which affect the rate and depth of respiration and Explain how these factors affect the respiratory centre Outline the cough reflex Explain the following terms (in relation to lung function) Compliance; Elasticity; Airway Resistance; Shunt; Laminar Flow; Turbulent flow; Surface tension; Ventilation and Perfusion Ratios; Airway Closure; Equal Pressure Points; Alveolar interdependence; Collateral ventilation Pathology - For each of the following conditions: Respiratory tract infections; Pneumonia; Asthma; Chronic Bronchitis; Emphysema; Bronchiectasis; Cystic Fibrosis; Abdominal surgery List the causes, incidence and distribution Describe the pathological changes (in outline) Explain how the pathological changes give rise to the signs and symptoms Outline the medical management Discuss the psychosocial implications Discuss the role of the physiotherapist in the management of the condition Define the following terms: Consolidation; Atelectasis; Restrictive Lung Disease; Obstructive Lung Disease; Dyspnoea; Hypoxia; Orthopnoea; Hypercapnia; Collateral ventilation Respiratory Assessment and Analysis Carry out a basic subjective and objective assessment and interpret key findings Demonstrate how you would ascultate a patient for breath sounds and interpret key findings. Plan and implement Physiotherapy treatment Demonstrate and explain the effects, uses and contraindications of the following physiotherapy techniques: Active Cycle of Breathing Techniques; Postural Drainage and positioning; Clapping, shaking and Vibrations; Control of Breathlessness; Mobilisation of the patient Suggest the relative value of these techniques in the management of the conditions specified. Recognise the following equipment used in respiratory care - nebulisers, humidifiers, inhalers, PEP, incentive spirometry, oximetry and oxygen therapy delivery devises. Outline of contact teaching sessions Introduction and the role of the physiotherapist in respiratory care Physiology Overview Lung Volumes Arterial Blood Gases and Respiratory Failure Breathlessness and mechanics Cystic Fibrosis Post op Physiotherapy Seminars. Gross Anatomy of the Respiratory Tract Pleural mechanics and disorders including chest drains Lung Function Tests Obstructive disease and management case studies Subjective Assessment Practice Observation(ribs and mechanics) and Palpation Postural Drainage Control of Breathlessness/Positioning Auscultation ACBT Manual techniques Post op Treatment Principles/Case Studies Asthma case study Pneumonia case study Oxygen/inhalers/nebulisers/PEP Year 2 October to November Care and Rehabilitation of the Critically Ill Aims and learning outcomes At the end of this part of the module the student should be able to: Critical Care Explain the signs and symptoms of Circulatory shock, Respiratory failure Classify the causes of Circulatory and Respiratory failure Identify devices used to monitor and observe the cardiovascular and respiratory systems Identify signs of cardiovascular instability Explain the significance of the following measurements: CVP; ECG; BP; Heart rate; PAWP; V02max; ICP; Fluid and electrolyte balance; Sa02; Pa02; PaC02; pH; Conscious level - coma scale Identify abnormal measurements in above values and discuss their significance Explain the implications of variations in above measurements when selecting and using physiotherapy techniques Classify the types of patient found on the intensive care unit Discuss the effects and dangers of physiotherapy techniques used in the intensive care unit Discuss the factors to be considered when selecting physiotherapy techniques with: Unconscious patients; Patients with respiratory failure; Patients with cardiovascular instability; Patients with multiple systems failure; Patients with severe respiratory disease; patients following neurosurgery; Patients following major trauma; Patients with chest trauma Explain the principles of care with the above patients on the intensive care unit Outline the principles of care and use of the following devices Positive pressure breathing equipment e.g. IPPB, CPAP; Endotracheal tubes; Tracheostomy tubes; Oxygen equipment; Nebulisers and Humidifiers; Manual hyperinflation; Suction; Chest drains; Tubes; CVP lines Discuss the role of the physiotherapist on the intensive care unit Discuss the psychosocial implications for critically ill patients and their families Thoracic Surgery Explain how the pathological changes of lung cancer and bronchiectasis may lead to the need for lung surgery Outline the following surgical procedures: Pneumonectomy, Lobectomy, Pleurectomy, Pleurodesis, Oesophagectomy Explain the possible complications of thoracic surgery Explain how physiotherapy modalities are modified in the pre and postoperative management of patients undergoing the above procedures Discuss the role of the physiotherapist in the management of patients undergoing thoracic surgery Cardiac Surgery Outline the following surgical procedures: Coronary artery by pass graft; Valve replacements Explain the possible complications of cardiac surgery Explain how physiotherapy modalities are modified in the pre and postoperative treatment of patients undergoing the above surgical procedures Discuss the role of the physiotherapist in the management of patients undergoing cardiac surgery Raised Intracranial Pressure Explain the dilemma facing physiotherapists in the management of patients with raised intracranial pressure (e.g. post TBI, or post neurosurgery) Explain how physiotherapy modalities are modified in the management of this group of patients Discuss the role of the physiotherapist in the management of patients with raised intracranial pressure Outline of contact teaching sessions Lectures Care and Rehabilitation of the Critically Ill - Introduction Respiratory Failure and its Management Assessment of the ITU patient Ventilation Modes, Positive pressure Thoracic Surgery Cardiac Surgery Acute management of raised intracranial pressure Seminars Monitoring. "Mrs Bowels" - surgical case study Chest xrays (2 x 1hr). Endo tracheal tubes and tracheostomies, oral and nasal airways. Mr Pypless and charts. (extubation case study) Suction (including closed system) and manual hyperinflation. Chest drain management. IPPB and CPAP. NIPPV and comparison of IPPB/CPAP/NIPPV. Developing Problem Lists and Management/ Treatment Plans from ITU Case Studies. Year 2 January to April Cardiorespiratory Rehabilitation Aims and learning outcomes Exercise Physiology Explain the acute effects of exercise on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems Explain the term VO2max and its significance Explain the purpose of incremental exercise tests Explain the effects of endurance type exercise on cardiovascular and pulmonary function Explore the health benefits of physical activity Identify key components of training programmes to improve cardiovascular endurance Amputee Rehabilitation Explain how Peripheral Vascular Disease may lead to the need for amputation State the indications for surgery Describe the possible levels for Lower Limb amputations Explain the particular management problems for patients with: Single above knee amputation; Single below knee amputation Indicate the types of prosthesis available Formulate a list of appropriate assessment procedures for each of the following stages: Preoperative; Postoperative; Post-prosthetic Explain the aims of physiotherapy for each of the above stages Pathology For each of the following conditions: Fibrosing Alveolitis; Lung Abscess; Tuberculosis; Pulmonary Embolism; Lung tumours; Cor Pulmonale Give a brief definition Outline the implications for Physiotherapy management Pulmonary Rehabilitation Outline the principles of use of oxygen therapy, nebulisers and medication in managing patients with COPD Explain the effects of exercise on breathlessness in patients with COPD Outline an exercise programme and education topics suitable for pulmonary rehabilitation Identfiy outcome measures appropriate for evaluating pulmonary rehabilitation Cardiac Rehabilitation Explain the recommendations for exercise and activity in Phase I, II, III and IV of Cardiac Rehabilitation Discuss the risks and benefits of exercise in patients with cardiac disease Demonstrate and teach suggested exercises suitable for patients in phase 111 cardiac rehabilitation. Outline of contact teaching sessions Lecture 1 Exercise physiology – acute effects Lecture 2 Endurance training principles Lecture 3 Endurance training principles (cont) Lecture 4 Amputee rehabilitation Lecture 5 Cardiac rehabilitation Lecture 6 Pulmonary rehabilitation Lecture 7 Oxygen, nebulisers and medication in COPD Practical workshop 1 Amputee rehabilitation Practical workshop 2 Fitness testing Practical workshop 3 Cardiac rehabilitation Seminar 1 Pathology presentations Seminar 2 Exam question practice Year 3 November and December Appraising Physiotherapy in Practice Outline of teaching This part of the curriculum is designed to get the students to critically evaluate the evidence base, literature and the current professional issues which may affect their practice in the future. Lectures Current issues in respiratory care Evaluation of physiotherapy in respiratory care ARDS Chest trauma Paediatric critical care Seminars Review of evaluation of research papers Current issues in cardiorespiratory care (acute care and community care / professional issues) On call preparation Weaning – theory with equipment e.g. NIPPV, cough assist Summary. We aim to build up a fundamental knowledge and understanding of cardiorespiratory anatomy, physiology, pathology and management in year 1. We develop this further during year 2 with specific issues around critical care and rehabilitation principles and programmes. More complex issues are introduced and explored. In year 3, we believe students are more able to critically appraise that which they have learnt in years 1 and 2. Therefore, the emphasis of their cardiorespiratory education is directed more towards evaluation of the evidence base and also their own personal learning. This change in emphasis is in order to put into context that which they have learnt both in the university and on placement with the ultimate aim of developing them towards competent reflective autonomous professionals. We endeavour to keep the curriculum current and appropriate to cover the majority of the issues that may be needed by physiotherapist working in the varied setting of today's healthcare provision. Inevitably due to the constraints of the packed undergraduate curriculum, there is some selection of material which we need to make in order to cover what we regard as the most salient issues. We do review this regularly but would always value any feedback from our clinical colleagues, either on this or any other aspect of the undergraduate cardiorespiratory physiotherapy education. We all contribute to various parts of the education and can be contacted via UWE. Many thanks Jacqueline Mullan, (0117 3288859), Sandy Thomas 0117 3288626), and Anne Konsta (0117 3288414)