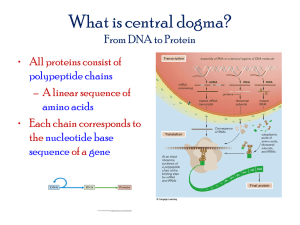
26. Metatranscriptomics - Microbial Genome Program
advertisement

Advancing Science with DNA Sequence AUG AUG AUG AUG AUG AUG AUG Metatranscriptomics: Challenges and Progress Shaomei He DOE Joint Genome Institute Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Metatranscriptomics Metatranscriptome The complete collection of transcribed sequences in a microbial community: Protein-coding RNA (mRNA) Non-coding RNA (rRNA, tRNA, regulatory RNA, etc) Metatranscriptomics studies: Community functions Response to different environments Regulation of gene expression Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Evolving of Metatranscriptomics cDNA clone libraries + Sanger sequencing Microarrays RNA-seq enabled by next-generation sequencing technologies. Sorek & Cossart, NRG (2010) 11, 9-16 RNA-seq is superior to microarrays in many ways in microbial community gene expression analysis. Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Challenges in Metatranscriptomics Wet lab Low RNA yield from environmental samples Instability of RNA (half-lives on the order of minutes) High rRNA content in total RNA (mRNA accounts for 1-5% of total RNA) http://www.nwfsc.noaa.gov/index.cfm Bioinformatics General challenges with short reads and large data size Small overlap between metagenome and metatranscriptome, or complete lack of metagenome reference http://cybernetnews.com/vista-recovery-disc/ Advancing Science with DNA Sequence rRNA Removal Methods Method rRNA feature used Input Manipulate RNA raw RNA Before cDNA synthesis Subtractive hybridization RNase H digestion Conserved sequence High Exonuclease digestion 5’ monophosphate Gel extraction Size Biased poly(A) tailing 2o structure Low Sequence feature Low No High abundance Low No Yes During cDNA synthesis Not-so-random primers After cDNA synthesis Library normalization w/ DSN Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Validation of two rRNA removal kits Subtractive Hybridization Exonuclease Digestion MICROBExpress Bacterial mRNA Enrichment (Ambion) mRNA-ONLY Prokaryotic mRNA Isolation (Epicentre) mRNA 5’ PPP mRNA rRNA 5’ P rRNA Capture Oligo Magnetic Bead Hyb 5’ Monophosphate Dependent Exonuclease Exo Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Objectives Validate the performance of Hyb and Exo kits on “synthetic” microbial communities, using Illumina sequencing to evaluate: Efficiency of rRNA removal Fidelity of mRNA relative transcript abundance Treatments: Hyb 2 x Hyb Exo Hyb + Exo Exo + Hyb Advancing Science with DNA Sequence What we learned rRNA removal efficiency for both kits was community composition and RNA integrity dependent. Exo degraded some mRNA, introducing larger variation than Hyb. Combining Hyb and Exo provided higher rRNA removal than used alone, but the fidelity was significantly compromised. Hyb had high fidelity, but its performance was limited by rRNA probe target range and RNA integrity. Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Customized subtractive hybridization Stewart et al, ISME J (2010) 4, 896–907 Customized probes specific to communities of interest Probes cover near-full-length rRNA, and should also capture partially degraded (fragmented) rRNA It has been applied on marine metatranscriptome samples to substantially reduce rRNA. Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Duplex-specific nuclease (DSN) Yi et al, Nucleic Acids Res, 2011, 1-9 Total RNA RNA-seq library construction Denature ds-DNA at high temp Re-anneal to ds-DNA at lower temp. DSN degrades DNA duplex which is presumably from abundant transcripts. Library normalization using DSN • Efficient on E. coli (final rRNA% = 26 ± 11%) • Preserved mRNA relative abundance • Little reduction of the very abundant mRNA Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Still efficient and “faithful” for microbial communities? Relative abundance of OTU (%) Typical species rank abundance 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 1 101 201 301 401 501 601 701 801 901 1001 Rank of OTU Environmental microbial communities are very diverse, with a long tail of minor community members. Epicentre Ribo-Zero TM Kit Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Another subtractive hybridization-based kit. Ribo-Zero depletion 100000 R² = 0.9999 10000 High fidelity! 1000 100 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.01 1 100 10000 No Depletion - Cindi Hoover, JGI Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Test on a real sample from cow rumen Sample % rRNA % Map (rumen metagenome) % Other No depletion control 82.4 3.4 10.5 Ribo-Zero Metabacteria 15.9 27.7 55.2 4.9 26.7 56.3 Ribo-Zero Metabacteria + Human/Mouse /Rat Effective even on complex metatranscriptome samples. - Cindi Hoover, JGI Advancing Science with DNA Sequence What else about RiboZeroTM kit Giannoukos et al, Genome Biology 2012, 13:r23 • • • • Outperformed other four tested kits/methods Effective even on highly fragmented RNA sample But needs sufficient input RNA (e.g. > 1 ug) For environmental samples with very low RNA yield, no rRNA depletion is the recommendation. How about Archaea? Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Termite Hindgut Metatranscriptomics - A case study (Preliminary results) Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Termite samples in this study Species: Family: Habitat: Diet: Nasutitermes corniger Termitidae Laboratory colony Dry wood Amitermes wheeleri Termitidae Subtropical desert Cow dung Aim: Determine system-specific differences between termite species with different diets. Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Overview of sequencing efforts Nasutitermes Amitermes (Lab colony) Dry wood (Arizona desert) Cow dung Sanger at a QC level 454-titanium Illumina GAIIx – 1 x 34 bp 1 lane 1 lane Illumina GAIIx – 2 x 76 bp 1 lane 1 lane Illumina GAIIx – 2 x ll3 bp 1 lane 3 lanes community analysis 16S pyrotag Metagenomics Metatranscriptomics Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Bioinformatics workflow - Edward Kirton, JGI Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Summary Metatranscriptomics is being advanced by nextgeneration sequencing technologies. RiboZero kit is promising to knock down high rRNA content for more effective RNA-seq. Bioinformatically removing rRNA reads should increase computational speed in de novo assembly, and improve the assembly of low-abundance mRNAs. Need to investigate algorithm that is more sensitive and computationally efficient to do this for large datasets. Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Acknowledgement • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Phil Hugenholtz Susannah Tringe Edward Kirton Kanwar Singh Erika Lindquist Feng Chen Jeff Froula Falk Warnecke Natalia Ivanova Martin Allgaier Zhong Wang Tao Zhang Cindi Hoover R&D group Production group Many others! • Omri Wurtzel • Rotem Sorek • Hans Peter Klenk • Rudolph Scheffrahn • Jose Escovar-Kousen