Auxinas
advertisement

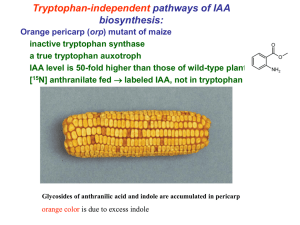
Accción hormonal de las auxinas en plantas ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? ¿Qué metabolitos constituyen las auxinas? ¿Qué procesos son regulados por las auxinas? ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ¿Qué queda por hacer? Accción hormonal de las auxinas en plantas ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? ¿Qué metabolitos constituyen las auxinas? ¿Qué procesos son regulados por las auxinas? ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ¿Qué queda por hacer? ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? Darwin (1890s) studied phototropism – movement towards light Darwin and others studied coleoptiles – tissues that protect monocot leaves during germination. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Darwin, C., and Darwin, F. (1881) The power of movement in plants. Appleton and Co., New York.; Photos courtesy of Dr. R.L. Nielsen ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? Cutting off or covering the coleoptile tip interferes with the response These experiments showed that the light signal is perceived at the tip, although the bending occurs at the base. Untreated coleoptile bends Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Coleoptiles with tips shielded from light or removed do not bend ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? Darwin concluded that a signal moves from tip to base “We must therefore conclude that when seedlings are freely exposed to a lateral light some influence is transmitted from the upper to the lower part, causing the latter to bend.” Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Charles Darwin image courtesy of Patche99z ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? Boysen-Jensen (1913) showed that the transmitted influence can move through a gelatin block Before After The signal cannot move through a solid block or butter, demonstrating that it is a water- soluble chemical. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? Repositioning the tip can induce bending in uniform light Tip removed and replaced to one side Tip removed Control Before Tip removed and replaced Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Asymmetric tip placement causes bending Paal (1919) showed that removing the tip and replacing it on one side of the base is sufficient to cause bending. After ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? In the 1930s, auxin was purified and shown to promote growth Angle of curvature is proportional to amount of auxin in block Frits Went collected auxin from shoot tips into agar blocks... ...and showed that the material collected in the agar blocks was the growthpromoting substance. This bending assay for the growthpromoting effect of auxin was used as a basis for its purification. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Redrawn from Went, F.W. (1935) Auxin, the plant growth-hormone. Bot. Rev. 1: 162-182. Accción hormonal de las auxinas en plantas ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? ¿Qué metabolitos constituyen las auxinas? ¿Qué procesos son regulados por las auxinas? ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ¿Qué queda por hacer? ¿Qué metabolitos constituyen las auxinas? Auxinas: estructura química Went FW (1928) Wushstoff und wachstum. Rec Trav Bot Neerl 25: 1–116 Auxinas naturales (libres o conjugadas) IAA IBA (indole butyric acid) 4-Cl-IAA (4-cloroindole-3-acetic) PAA (phenylacetic acid) Indole-3-acetic acid Auxinas sintéticas Derivadas de IAA NAA (naphtyl-acetic acid) Derivadas del PAA 2,4-D, 2,4,5-T (otros efectos: herbicidas) Antiauxinas: PCIB: 2-(p-chlorophenoxy)-2-isobutyric acid Accción hormonal de las auxinas en plantas ¿Cuándo y por qué se descubren las auxinas? ¿Qué metabolitos constituyen las auxinas? ¿Qué procesos son regulados por las auxinas? ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ¿Qué queda por hacer? ¿Qué procesos son regulados por auxinas? Auxinas en plantas superiores Procesos de Crecimiento y Desarrollo - dominancia apical - iniciación de raíces - tropismos - diferenciación de vasos - fructificación Fisiología Celular - extrusión de protones - división y elongación celular - regulación de la expresión génica Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY ¿Qué procesos son regulados por auxinas? Auxin’s role in apical dominance was known in the 1930s Bud Length Decapitate Replace apex with agar block: without or with auxin. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Auxin suppresses bud outgrowth No auxin Auxin Thimann, K.V., and Skoog, F. (1934). On the inhibition of bud development and other functions of growth substance in Vicia faba. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B. 114: 317-339 with permission; Went, F.W. and Thimann, K.V. (1937) Phytohormones. The Macmillan Company, New York. ¿Qué procesos son regulados por auxinas? Auxin’s root-promoting properties were also known by the 1930s Adventitious roots are initiated from grape stems treated with auxin A more recent experiment in which radish roots were dipped into auxin and initiated lateral roots at a frequency proportional to auxin concentration. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY µM IAA Thimann, K.V. (1938). Hormones and the analysis of growth. Plant Physiol. 13: 437-449. Kerk, N.M., Jiang, K., and Feldman, L.J. (2000). Auxin metabolism in the root apical meristem. Plant Physiol. 122: 925-932. ¿Qué procesos son regulados por auxinas? Gravitropism is a response to a change in orientation relative to gravity GRAVITY VECTOR Shoots are negatively gravitropic – they grow away from the center of gravity vertical Lower side Roots are positively gravitropic – they grow towards the center of gravity horizontal length Upper side time Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Luschnig, C., Gaxiola, R.A., Grisafi, P., and Fink, G.R. (1998) EIR1, a root-specific protein involved in auxin transport, is required for gravitropism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genes Dev.12: 2175-2187. Accción hormonal de las auxinas en plantas ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? ¿Qué metabolitos constituyen las auxinas? ¿Qué procesos son regulados por las auxinas? ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ¿Qué queda por hacer? ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? Dissecting auxin action Catabolism Synthesis IAA Conjugation Transport Perception (receptor) TF activation/ inactivation Target genes Biological Functions Auxin’s effects depend upon its synthesis, transport, perception, signaling, and target gene responses. Most of these functions are controlled by many genes with differing cell specificities. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Adapted from Kieffer, M., Neve, J., and Kepinski, S. (2010). Defining auxin response contexts in plant development. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 13: 12-20. ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? Auxin response pathway regulation -positive and negative feedback (self-regulation) -environmental factors -hormone interaction Conjugation Catabolism Synthesis IAA Transport Perception (receptor) TF activation/ inactivation Target genes Biological Functions Gravity, Nutrient nutrient status, ionic Ionic environment, pathogens, Pathogens, Light: directionality, intensity, wavelength Ethylene, brassinosteroids, cytokinin, gibberellic acid, jasmonic acid, strigolactones.... Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Adapted from Kieffer, M., Neve, J., and Kepinski, S. (2010). Defining auxin response contexts in plant development. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 13: 12-20. ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? Tools in auxin research •Auxin quantification from tissue or cell extracts •Expression of auxin-induced genes •In situ detection by auxin-specific antibodies •Orientation of PIN auxin-transport proteins Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? Cell-specific auxin measurements Dissociate cells and isolate protoplasts Recently the resolution of GC-MS measurements have been greatly refined. Separate into single-cells Laser Charged plates deflect cells into labeled and unlabeled pools. Start with roots expressing GFP in defined cell populations Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Petersson, S.V., Johansson, A.I., Kowalczyk, M., Makoveychuk, A., Wang, J.Y., Moritz, T., Grebe, M., Benfey, P.N., Sandberg, G., and Ljung, K.(2009) An auxin gradient and maximum in the Arabidopsis root apex shown by high-resolution cell-specific analysis of IAA distribution and synthesis. Plant Cell 21:1659-1668. ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? Cell-specific auxin measurements Auxin amount The highest auxin concentration is in the quiescent center (QC) of the root apex. Using this method, a high resolution map has been produced of auxin concentration in the Arabidopsis root apex. QC Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Petersson, S.V., Johansson, A.I., Kowalczyk, M., Makoveychuk, A., Wang, J.Y., Moritz, T., Grebe, M., Benfey, P.N., Sandberg, G., and Ljung, K.(2009) An auxin gradient and maximum in the Arabidopsis root apex shown by high-resolution cell-specific analysis of IAA distribution and synthesis. Plant Cell 21:1659-1668. ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? Chemical analysis of auxin levels from plant extracts Chemical analysis by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is an important way to quantify auxin. This experiment shows an auxin gradient from tip to base in young leaves but not mature leaves. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Edlund, A., Eklof, S., Sundberg, B., Moritz, T., and Sandberg, G. (1995) A microscale technique for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry measurements of picogram amounts of indole-3acetic acid in plant tissues.Plant Physiol. 108: 1043-1047. ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? Monitoring auxin response by reporter gene transcription GUS (or GFP) TGTCTC AuxRE The DR5 reporter construct is widely used to monitor auxin response-level. Hours of staining DR5 consists of seven repeats of an auxin-response element (AuxRE) which is a binding site for auxin-responsive transcription factors (ARFs). Auxin-response level increases with exogenous auxin (NAA) Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Ulmasov, T., Murfett, J., Hagen, G., and Guilfoyle, T.J. (1997). Aux/1AA proteins repress expression of reporter genes containing natural and highly active synthetic auxin response elements. Plant Cell 9: 1963-1971. ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? DR5 expression reveals high auxin activity in the root apex and QC Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers, Ltd. Blilou, I., et al. (2005) The PIN auxin efflux facilitator network controls growth and patterning in Arabidopsis roots. Nature 433: 39-44. ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? Auxin can be detected by anti-auxin antibodies Auxin accumulation during lateral root initiation DR5::GUS Primary root Anti-IAA antibody Anti-IAA antibody + auxin QC Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Negative control Reprinted from Benková, E. et al. (2003) Local, efflux-dependent auxin gradients as a common module for plant organ formation. Cell 115: 591-602, with permission from Elsevier. Accción hormonal de las auxinas en plantas ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? ¿Qué metabolitos constituyen las auxinas? ¿Qué procesos son regulados por las auxinas? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ¿Qué queda por hacer? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? yucca: un mutante de biosíntesis de IAA obtenido por “activation tagging” Zhao et al. (2001) Science 291:306 light dark roots Wt yucca Wt yucca activation tagging yucca “yucca”: un fenotipo indicativo de un mutante relacionado con auxinas Wt Wt yucca ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? yucca es un mutante con niveles más altos de IAA Zhao et al. (2001) Science 291:307 MS (4weeks) MS+IPAR IPAR = isopentenil adenina ribósido Wt yucca Wt yucca Supresión del fenotipo yucca MS (7weeks) +IPAR Wt yucca DR5-GUS = gen delator de auxinas iaaL = gen DR5-GUS yucca-DR5-GUS yucca yucca-iaaL iaaL de enzima que conjuga IAA y Lys ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? Auxin biosynthesis pathways cloned from bacteria cloned from plants Indole-3-glycerolphosphate tryptamine FLOOZY (Petunia) TAA1 flavin monooxygenase tryptophan aminotransferase N-hydroxyl tryptamine Indole-3-acetaldoxime Indole-3-propionic acid Indole-3-acetamide SUR2 1-aci-Nitro-2-Indolylethane Indole-3-acetonitrile Indole-3-acetaldehyde Indolic glucosinolates ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? Auxin biosynthesis: novel diagram Tao et al (2008) Cell 133: 171 ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? Biosynthesis and homeostasis IAA is produced from tryptophan (Trp) via several semi-independent pathways and one Trp-independent pathway (blue arrow). Mutations inYUCCA genes (circled) affect embryogenesis and in TAA1 genes affect environmental responses. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY The IAOx pathway may be restricted to Arabidopsis and its close relatives. Sugawara, S., et al. (2009) Biochemical analyses of indole-3-acetaldoxime-dependent auxin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106: 5430-5435. ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? Auxin synthesis is developmentally and environmentally controlled Methyl Jasmonate Ethylene Red / Far-red light ratio Temperature Auxin biosynthesis is influenced by other hormones and environmental conditions Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Sugawara, S., et al. (2009) Biochemical analyses of indole-3-acetaldoxime-dependent auxin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106: 5430-5435. ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? ¿Funciones diferentes para las diferentes rutas? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? Auxin homeostasis is also controlled by conjugation and degradation Overexpression of an auxin conjugating enzyme encoded by a GH3 gene reduces auxin levels in the plant and causes a dwarfed phenotype. IAA GH3 genes are auxininduced Rice (GH3 genes) Arabidopsis Wild-type GH3.13 overexpression Wild-type Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY GH3.13 overexpression Zhang, S.-W., et al., (2009) Altered architecture and enhanced drought tolerance in rice via the cown-regulation of indole-3-acetic acid by TLD1/OsGH3.13 activation. Plant Physiol. 151:1889-1901. Staswick, P.E., et al., (2005) Characterization of an Arabidopsis enzyme family that conjugates amino acids to indole-3-acetic acid. Plant Cell 17: 616-627. ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? Auxin homeostasis - summary Catabolism Synthesis IAA Conjugation Transport Auxin homeostasis is maintained by its synthesis catabolism conjugation transport All of these processes are tightly regulated Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Accción hormonal de las auxinas en plantas ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? ¿Qué metabolitos constituyen las auxinas? ¿Qué procesos son regulados por las auxinas? ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ¿Qué queda por hacer? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? Localized auxin synthesis produces developmentally important gradients YUCCA1::GUS expression DR5::GFP expression (auxininducible promoter) The development of the Arabidopsis female gametophyte involves an auxin-gradient, which is generated in part by a gradient of auxin-biosynthesis. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY From Pagnussat, G.C., Alandete-Saez, M., Bowman, J.L., and Sundaresan, V. (2009) Auxin-dependent patterning and gamete specification in the Arabidopsis female gametophyte.Science 324: 1684-1689. Reprinted with permission from AAAS. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Polar transport of auxin was recognized in the 1930s A segment cut from a coleoptile can move auxin from tip to base. The upper agar block was loaded with auxin, which the segment translocated to the lower block. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY When the segment is inverted, it is unable to transport auxin from base to tip. This experiment, carried out by H.G. Van der Weij revealed that auxin in the shoot is translocated from tip to base. Adapted from Went, F.W. (1935) Auxin, the plant growth-hormone. Bot. Rev. 1: 162-182. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Polar Auxin Transport Auxin moves long distances through the phloem. Auxin also moves via auxin transport proteins. Auxin normally moves from the tip of the shoot towards the tip of the root. At the root tip, auxin changes direction and moves short distances up the root again (basipetally). Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Reprinted with permission from Macmillan Publishers, Ltd. Robert, H.S., and Friml, J. (2009) Auxin and other signals on the move in plants. Nat. Chem. Biol. 5: 325-332. Reprinted from Muday, G.K., and DeLong, A. (2001). Polar auxin transport: Controlling where and how much. Trends Plant Sci. 6: 535–542, with permission from Elsevier. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Auxin transport – chemiosmotic model Indole-3-acetic acid is a charged anion (IAA-) in the cytoplasm (pH 7). In the more acidic cell wall (pH 5.5) some is uncharged (IAAH). The uncharged form crosses the plasma membrane into the cell where it is deprotonated and unable to exit other than through specific transporters. Cell wall pH 5.5 A proton ATPase maintains the differential pH gradient Cytoplasm pH 7 H+ IAA- IAAH IAA- + H+ Cell-to-cell polar auxin transport IAAH IAA- + H+ Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Redrawn from Robert, H.S., and Friml, J. (2009) Auxin and other signals on the move in plants. Nat. Chem. Biol. 5: 325-332. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Auxin moves through efflux and influx carrier proteins ABCB ABCB The AUX1/LAX influx carriers contribute to movement of IAAH into the cytoplasm. The PIN family of proteins contributes to directional movement of auxin out of the cell. Cell-to-cell polar auxin transport ABCB The ABCB transporters contribute to auxin transport in a diverse ways. (These were formerly referred to as MDR or PGP proteins). Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Reprinted with permission from Macmillan Publishers, Ltd. Robert, H.S., and Friml, J. (2009) Auxin and other signals on the move in plants. Nat. Chem. Biol. 5: 325-332. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Auxin transport: influx and efflux factors - Influx carriers (4 members in Arabidopsis) The most studied: AUX1 Related to a small subfamily of amino acid transporters, the amino acid/auxin:proton symport permeases (AAAP), which show homology to bacterial proteins of the amino acid/polyamine/choline (APC) permease family, - Efflux carriers PIN family (8 members in Arabidopsis) ABCB-type (ATP- binding casette subfamily B) - Inhibitors NPA TIBA 1-naphthylphthalamic acid blocks some aspect of the endocytic step in PIN protein cycling 2, 3, 5-triiodobenzoic acid leads to an intracellular accumulation of PIN protein associated with endosomes (Abas et al. 2006) ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Auxin transport: influx and efflux ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? AUX1 takes up auxin into the cell AUX1/LAX Carriermediated auxin uptake There are several genes encoding proteins like AUX1; these are the LAX proteins (Like AUX1). Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Auxin uptake is disrupted in aux1 mutants. Reprinted with permission from Macmillan Publishers, Ltd. Marchant, A. et al., (1999) AUX1 regulates root gravitropism in Arabidopsis by facilitating auxin uptake within root apical tissues. EMBO J. 18: 2066–2073. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Auxin transport is facilitated by AUX1/LAX proteins In the aux1 mutant, auxin transport is disrupted, so auxin moves more slowly from shoot to root. DAG = Days After Germination Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Marchant, A., Bhalerao, R., Casimiro, I., Eklof, J., Casero, P.J., Bennett, M., and Sandberg, G. (2002). AUX1 promotes lateral root formation by facilitating indole-3-acetic acid distribution between sink and source tissues in the Arabidopsis seedling. Plant Cell 14: 589-597 Reprinted from Muday, G.K., and DeLong, A. (2001). Polar auxin transport: Controlling where and how much. Trends Plant Sci. 6: 535–542, with permission from Elsevier. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? The ABCB proteins are important for auxin transport ABCB PGP WT abcb19-2 abcb19abcb19-1 abcb1 2 – abcb1 Arabidopsis encodes 21 ABCB proteins, many of which are necessary for proper auxin transport. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY WT abcb19-1 Loss-of-function of some ABCB genes causes diverse phenotypes including dwarfism and altered tropisms. Wu, G., Lewis, D.R., and Spalding, E.P. (2007) Mutations in Arabidopsis multidrug resistance-like ABC transporters separate the roles of acropetal and basipetal auxin transport in lateral root development. Plant Cell 19: 1826–1837. Noh, B., Murphy, A.S., and Spalding, E.P. (2001) Multidrug Resistance–like genes of Arabidopsis required for auxin transport and auxin-mediated development. Plant Cell 13: 2441–2454. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? The PIN proteins are named for the pinformed mutant pin-formed, which has a mutation in the PIN1 gene, makes some abnormal leaves and then a bare inflorescence. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Galweiler, L., Guan, C., Muller, A., Wisman, E., Mendgen, K., Yephremov, A., and Palme, K. (1998). Regulation of polar auxin transport by AtPIN1 in Arabidopsis vascular tissue. Science 282: 2226 – 2230, reprinted with permission from AAAS. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Exon-intron structure of the eight AtPINs in Arabidopsis Transmembrane domains Translated exon sequence Chromosomal location and duplication events -recent - old 647 aa 351 aa Paponov et al (2005) TIPS 10:171 ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Auxin gradients and transport during embryogenesis Petrasek et al (2009) Development 136: 2681 ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? The distribution of PIN proteins contributes to the auxin gradients Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Křeček , P., Skůpa , P., Libus, J., Naramoto, S., Tejos, R., Friml J., and Zažímalová, E. (2009) The PIN-FORMED (PIN) protein family of auxin transporters. Genome Biology 10: 249. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Auxin transport in the root tip AUX1 Petrasek et al (2009) Development 136: 2682 PIN1 PIN2 PIN4 PIN3 PIN7 ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Auxin transport in developing lateral roots Petrasek et al (2009) Development 136: 2682 ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Immunolocalization of the AtPINs a) Columnella cell layer b) + quiescent centre c) + quiescent centre d) More diffuse Columbia e-f) More expression No change in localization g-h) NPA affects PIN4 localization Do PIN4 compensate de loss of function of PIN1 by NAPA? i) At he bottom of each cell j) At the bottom in cortical cells At the top in the epidermal layer k-l-m) low level expression in the epidermis n-o-p) same pattern of expression (Usually PIN1) Untreated seedlings 4h NPA ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? PIN proteins cycle between plasma membrane and endosome --- Brefeldin A blocks endocytosis and traps PIN proteins in endosomes endosome Plasma membrane Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Redrawn from Kleine-Vehn, J., et al. (2009). PIN auxin efflux carrier polarity is regulated by PINOID kinasemediated recruitment into GNOM-independent trafficking in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21: 3839-3849. ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? Auxin transport - summary Regulated movement of auxin is critical for phototropism, gravitropism, embryonic pattern formation and organogenesis. Auxin transport proteins have been identified. Factors that control their position and activity are under investigation. Arabidopsis has 6 AUX1/LAX proteins, 21 ABCB proteins and 8 PIN proteins - we don’t yet understand all the complexity of auxin transport! Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Accción hormonal de las auxinas en plantas ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? ¿Qué metabolitos constituyen las auxinas? ¿Qué procesos son regulados por las auxinas? ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ¿Qué queda por hacer? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Aproximaciones en la búsqueda de receptores Estrategia BIOQUÍMICA: - utilización de hormonas marcadas - mezcla con extractos proteicos - purificación de fracciones marcadas - aislamiento del receptor - Análisis de la secuencia N-terminal - Construcción de oligonucleótidos - Rastreo de una biblioteca de cDNA - Secuenciación de clones positivos ABP maíz Woo et al (2002) EMBO J 21:2877 Estrategia GENÉTICA: - generación de mutantes (de pérdida o ganancia de función) - selección por alteración de la respuesta hormonal TIR1 - localización de la mutación en el genoma At ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Auxin Perception: Two receptors? 1972 Perception (receptor) ABP1 Hertel R, Thomson KS, Russo VEA In vitro auxin binding to particulate cell fractions from corn coleoptiles Planta 107: 325-340 IAA 2005 Perception (receptor) SCFTIR1 Stefan Kepinski & Ottoline Leyser The Arabidopsis F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor Nihal Dharmasiri, Sunethra Dharmasiri & Mark Estelle The F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor Nature 26 de mayo ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Aislamiento de la auxin-binding protein (ABP) de maíz - Purificación: Mr: 40-45 kD (20 kD) Análisis de la secuencia N-terminal Construcción de oligonucleótidos Rastreo de una biblioteca de cDNA Secuenciación de clones positivos Estructura primaria de la proteína Análisis de la estructura 10 21 32 42 51 63 80 Woo et al. (2002) EMBO J 21:2877-2885, 92 104 117 151 163 NH2- -COOH GQRTPIHRHSCEE auxin-binding domain - Problemas pendientes: localización y función WDEDCFEAAKDEL K-channel domain ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? AUXIN-BINDING Protein1 is necessary for cell division and expansion Wild-type control EtOHinduced ABP1antisense Loss-of-function of ABP1 is embryo-lethal. Plants were produced that carry an inducible antisense construct that silences the ABP1 gene. They were grown for 12 days in noninductive conditions. At day 12, ABP1 was silenced and plant growth was severely restricted. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Braun, N., et al. (2008). Conditional repression of AUXIN BINDING PROTEIN1 reveals that it coordinates cell division and cell expansion during postembryonic shoot development in Arabidopsis and tobacco. Plant Cell 20: 2746-2762. ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Elementos de la respuesta a auxinas Two families of transcription factors, > ARF (auxin response factors), bind DNA directly and either activate or repress transcription depending on the ARF > Aux/IAA proteins, exert their effects by binding to the ARF proteins. The effect of Aux/IAA binding is to repress transcription Complejo SCF-TIR1: ubiquitinación de Aux/IAA (en presencia de IAA) > SCF: SKP1, Cullin and F-box protein. > TIR1 (F-box): Transport Inhibitor Response1 (tir no responden a auxinas) La interacción SCF-Aux/IAA no se debe a etiquetado del sustrato (fosforilación, glicosilación ...) sino a “modificación” en TIR1 ¿Cómo promueven las auxinas la interacción SCF-Aux/IAA)? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Aux/IAA genes Aislamiento - Inducción rápida tras tratamiento con IAA - Similaridad de secuencia con Aux/IAA previos - En ensayos de doble híbrido con proteínas Aux/IAA Fuentes (probablemente sólo en plantas) - dicots: guisante, soja, M truncatula, A thaliana (25), tomate, tabaco, algodón ... - monocots: maíz, arroz ... - árboles: pino ... -Localización nuclear de la proteína Estructura - Dominios conservados I Mutaciones en el dominio II las hacen “indegradales” II Inestabilidad III IV Dimerización (con Aux/IAA y ARF) ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? TIR1 binds to the conserved degron in domain II I II III QVVGWPLVRSYRK I II III QVVGWPPVRSYRK Wild-type degron Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY IV Mutant degron IV Mutating the degron prevents the Aux/IAA protein from binding to TIR1 and being subsequently proteolyzed; the mutant proteins are more stable. This image shows the crystal structure of TIR1 complexed with auxin and the domain II region of an Aux/IAA protein. ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Mutations in some Aux/IAA genes cause an auxin-resistant phenotype Dominant, gain-of-function mutations in Aux/IAA genes all map to the conserved degron sequence in domain II I II III IV QVVGWPPVRSYRK Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Nagpal, P., et al. (2000) AXR2 encodes a member of the Aux/IAA protein family. Plant Physiol, 123: 563-574. ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Aux/IAA genes are induced by auxin In the 1980’s, the new techniques of molecular biology allowed scientists to isolate genes that were strongly and rapidly induced by auxin. One family of these auxininduced genes is known as the Aux/IAA genes. GmAux22 GmAux28 Control 15 30 60 90 Auxin treatment (mins) Auxin depleted Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Walker, J.C. and Key, J.L. (1982) Isolation of cloned cDNAs to auxin-responsive poly(A)+RNAs of elongating soybean hypocotyl. PNAS 79: 7185-7189. ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Aux/IAA proteins are very short-lived nuclear proteins Many of the Aux/IAA proteins have a very short half-life, suggesting a regulatory function. A fusion protein with GUS shows nuclear accumulation PS-IAA6 Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Abel, S., Oeller, P.W., and Theologis, A. (1994). Early auxin-induced genes encode short-lived nuclear proteins. PNAS 91: 326-330. ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ARF (auxin response factors) Características - Familia de 23 genes en Arabidopsis - Dominios C-terminales homógos al III y IV de las proteínasAux/IAA III Unión a DNA (Activación de la transcripción) IV Dimerización - Se unen a los dominios TGTCTC AuxREs (específico de plantas) - Activan o reprimen la transcripción por unión directa a los sitios TGTCTC con otras ARFs o Aux/IAAA que no están unidas al DNA ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ARFs are transcription factors that bind auxin-inducible promoters Increasing amounts of ARF1 DNase footprint analysis showing ARF1 binding to an auxin-response element (AuxRE) In DNase footprinting, the site at which a protein binds to DNA can be identified because that region is protected from DNase endonuclease digestion. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Reprinted from Ulmasov, T., Hagen, G., and Guilfoyle, T. (1997). ARF1, a transcription factor that binds to auxin response elements. Science 276: 1865 – 1868 with permission from AAAS. ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Some ARFs are transcriptional activators and some repressors The Arabidopsis ARF protein family Confirmed activators ARF 2-4, 9 are confirmed repressors We don’t know much about the ARF repressors yet. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Reprinted from Guilfoyle, T., and Hagen, G. (2007). Auxin response factors. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 10: 453 – 460 with permission from Elsevier. ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Aux/IAA proteins repress the activity of Auxin Response Factors (ARFs) ARF and Aux/IAA proteins have sequence similarity in their Cterminal regions through which they can homodimerize. ARF DNAbinding domain Activation / repression domain ARF homodimer ARF Aux/IAA heterodimer IN PLANT BIOLOGY IV Aux/IAA I Teaching Tools III II III IV ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Model for auxin-regulated transcriptional control Low auxin level Some ARFs are complexed with Aux/IAA repressors, interfering with their action High auxin level Aux/IAAs are degraded by SCFTIR1mediated proteolysis, relieving repression of ARFs to activate or repress gene expression. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? The auxin signaling pathway is amazingly short! Auxin INPUT Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY OUTPUT ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Perhaps the diversity of auxin responses is correlated with the diversity in signaling proteins Arabidopsis has 29 Aux/IAA proteins Auxin Arabidopsis has 23 ARF proteins OUTPUT INPUT TIR1 is related to five other auxinreceptor proteins, AFB1 – AFB5. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY The number of potential interactions between ARFs and Aux/IAA proteins is quite large, and has the potential to precisely control auxininduced gene expression in a vast number of combinations. ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? F-box-proteins >700 in Arabidopsis TIR1 AFB1 } AUXIN SIGNALING F-BOX AFB5 COI1 (jasmónico) 74 in humans 53 in mice Dharmasiri et al. (2005) Developmental Cell 9:109–119 ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? La respuesta a auxinas: mecanismo de acción hormonal: proteolisis de elementos de respuesta Aux/IAA Aux/IAA Auxin No hay fosforilación > Fosforilación de Aux/IAA > Ubiquitinación Aux/IAA Aux/IAA > Proteolisis Aux/IAA > Desbloqueo de ARF > Inducción de procesos > Inducción de Aux/IAA ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Detección de complejos TIR1-Aux/IAA: Pull-down experiments Interacción > Aux/IAA con TIR1 Dos tipos de Aux/IAA > GST-IAA7 > biotinylated 17 aa peptide domain II TIR1 Detección: Estelle Leyser > extracts from tir1-1 GVG-TIR1-myc seedlings anti-myc antibody Hay interacción si se forman complejos proteína (GST/biotina) que se detectan con anti-myc antibody ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Ensayos con 3H-IAA Binding to proteins Auxin binds directly to SCF-TIR1 positive signal in assays with GST-IAA7 negative signal in assays with GST-AXR2-1 (que no se une a SCF-TIR1) Competición con auxinas frías benzoic acid L-tryptophan IC50 2,4-D, 1-NAA IAA (mM) 1.4 1.3 0.12 (valores obtenidos con extractos crudos) ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? Inhibition of auxin signaling: terfestatin A Yamazoe et al (2005) Plant Phys 139:779 Terfestatin A (TrfA): terphenyl-b-glucoside - isolated from Streptomyces sp. F40 screen for compounds that inhibit the expression of auxin-inducible genes in Arabidopsis - specifically inhibited the expression of primary auxin-inducible genes in roots, did not affect abscisic acid and cytokinin related-genes. - blocked the auxin-enhanced degradation of Aux/IAA repressor proteins without affecting interaction between Aux/IAAs and TIR1. - TrfA treatment antagonized auxin responses in roots primary root inhibition, lateral root initiation, root hair promotion, and root gravitropism, - only limited effects on shoot auxin responses. TrfA acts as a modulator of Aux/IAA stability ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? terfestatin A: effects on root growth Yamazoe et al (2005) Plant Phys 139:779 ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? 2-FAA is a potent inhibitor of auxin-mediated events Sungur et al (2007) Plant Cell Physiol. 48: 1693 Compound A (A) = 2-hydroxy-N-(5-propyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl) acetamide (HTA) + 2-furylacrylic acid (2-FAA) BA3–GUS seedlings (GUS activity for 12 h) mock 5 mM IAA (2h) 5 mM IAA + 5 mM A 5 mM IAA + 10 mM HTA 5 mM IAA + 5 mM 2-FAA Accción hormonal de las auxinas en plantas ¿Por qué y cuándo se descubren las auxinas? ¿Qué metabolitos constituyen las auxinas? ¿Qué procesos son regulados por las auxinas? ¿Cómo abordar el estudio de la acción de las auxinas? ¿Dónde se producen y a través de qué rutas se sintetizan las auxinas? ¿Cómo se transportan a los tejidos diana? ¿Cómo se perciben las auxinas? ¿Qué queda por hacer? ¿Qué queda por hacer? Auxin action in whole-plant processes Auxin in action! Promote lateral organ initiation at the shoot apical meristem Light responses Cell elongation Responses to pathogens Inhibit branching in the shoot Integrate growth signaling pathways Control patterning and vascular development Maintain stemPromote cell fate at the branching in the root Integrate growth root apical meristem Response to nutrient signaling pathways distribution and Responses to symbionts – abundance nodule formation Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers, Ltd: NATURE Wolters, H., and Jürgens, G. (2009). Survival of the flexible: Hormonal growth control and adaptation in plant development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10: 305–317. Copyright 2009. ¿Qué queda por hacer? How does auxin affect so many processes in plant growth and development? Perception (receptor) The answer is not immediately obvious..... Some auxin-regulated genes are clearly connected with downstream functions, others are more difficult to interpret. Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY Target genes Auxin-induced gene products Aux/IAA proteins GH3 (auxin conjugation) ACS (ethylene synthesis) Jasmonic acid synthesis CKX (cytokinin degradation) Transcription factors Auxin-repressed gene products Cell wall proteins ARRs (Cytokinin signaling) Transcription factors Biological Functions ¿Qué queda por hacer? Ongoing investigations Where does auxin elimination fit in? Catabolism Synthesis Conjugation IAA What regulates auxin synthesis? Teaching Tools IN PLANT BIOLOGY What do all those transport proteins do? What controls their activity and distribution?? Transport Perception (receptor) What are the other TIR1 like proteins doing, and what does ABP1 do? TF activation/ inactivation Why so many ARFs and Aux/IAAs? What are the target genes, and what do they do? Target genes Biological Functions How do all these pieces fit together to make a functioning plant???? Adapted from Kieffer, M., Neve, J., and Kepinski, S. (2010). Defining auxin response contexts in plant development. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 13: 12-20.