RNA PURIFICATION Trizol Method & Modifications
advertisement

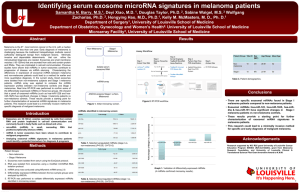
ISOLATION OF URINARY EXOSOMAL miRNAs: COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF DIFFERENT METHODS Sarath Kiran Channavajjhala1, Marzia Rossato2, Francesca Morandini1, Annalisa Castagna1, Flavia Bazzoni2 and Oliviero Olivieri1 1 University of Verona, Department of Medicine, Unit of Internal Medicine, Verona, Italy 2 University of Verona, Department of Pathology and Diagnostics, Verona, Italy Quantification of microvescicle size BACKGROUND Urinary exosomes are low density and stable membrane vesicles originating from epithelial cells lining the renal tubules and contain proteins, lipids, mRNA, miRNA but are devoid of DNA. (Thery, C et al., J. Immunol. 2001; Valadi, H et al., Nat. Cell Biol. 2007). miRNAs comprise a novel class of endogenous, small (20-22 nucleotides), noncoding RNAs that negatively regulate gene expression via degradation or translational inhibition of their target mRNAs (Mraz, M et al., BBRC 2009 and Weber, J.A et al., Clinical Chemistry 2010). Urinary microvescicles were isolated by ultrafiltration and analyzed by using Zeta sizer. The table shows the % of vesicles in the nano size range and the lower graph represents the size distribution by number of isolated vesicles (n = 4). Exosomal RNA yield 70 Biogenesis of miRNAs (Liu, N et al., Developmental Cell 2010) Total RNA Yield (ng/ml) 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1T 2T 3T 4T UF + Trizol methods AIM OF THE STUDY 5T 1C 2C 3C 4C UF + Columns 5C Exoquick To identify and develop a robust and economical method for isolation of urinary exosomal miRNAs that can be routinely used for the analysis of miRNAs in different pathological conditions. Urinary exosomes were isolated using Ultrafiltration (UF) (from 25ml Urine) or Exoquick Reagent (5 ml urine), total RNA was purified by several methods (refer to Material and Method section for details) and quantified by using Ribogreen assay. RNA purification by Trizol (4T), miRNeasy (4C) and Seramir (5C) were selected for further small RNA analysis. MATERIALS & METHODS Bioanalyzer analysis of purified exosomal RNA EXOSOMES PURIFICATION Urinary Exosomes Isolation: • Ultrafiltration, UF (Cheruvanky, A et al., AJRP 2007) • Exoquick Reagent (System Biosciences) Urine Exosomes UF + Trizol (80% miRNA) UF + miRNeasy (87% miRNA) Exoquick + Seramir (67% miRNA) UF + Trizol+ miRNeasy (93% miRNA) Exosome Size Validation: • Flowthrough Zeta Sizer Nano Range ZS (Malvern) RNA PURIFICATION Trizol Method & Modifications: • 1 CE + IP @ RT for 10 min • 1 CE + IP @ -200C for overnight • 2 CE + IP @ -200C for overnight • 2 CE + IP @ -800C for 1hr • 1 CE + IP @ -800C for 1hr CE – Chloroform Extraction IP – Isopropanol Precipitation Commercial Columns : • RNeasy kit, Qiagen • MiRcury kit, Exiqon • RNA mini kit, Ambion • miRNeasy kit, Qiagen • Seramir kit, SBI (5T) (4T) (3T) (2T) (1T) Exosomal RNA isolated with the indicated methods was analyzed using RNA Nano 6000 Kit in an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer. The electropherograms show the size distribution in nucleotides (nt) and fluorescence intensity (FU) of total RNA purified from exosomes. The peak at 4 nt is an internal standard. CONCLUSIONS (1C) (2C) (3C) (4C) (5C) RNA QUANTIFICATION • Ribogreen for the quantification of single stranded RNA (total RNA yield) • Agilent Bioanalyzer for the evaluation of RNA integrity and the presence of small RNA fraction 1. Urinary exosomes could be efficiently isolated by ultrafiltration method as demonstrated by light scattering analysis. 2. The RNA yield differed substantially between the different RNA isolation methods tested. 3. Bioanalyzer electropherograms demonstrated the presence of miRNAs (ranging in size from 18 to 25 nt) in the purified exosomal RNA. 4. The combination of ultrafiltration for exosomes isolation and TrizolmiRNeasy for exosomal RNA purification was the most efficient in terms of total RNA yield and % of miRNA recovery.