Isoelectric focusing
advertisement

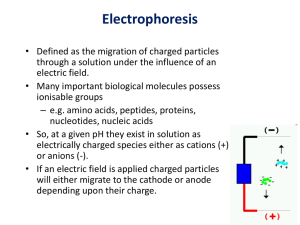
ELECTROPHORESIS Prof/ Azza abd al baky • Electrophoresis is the migration of charged molecules,particles or ion in a liquid medium under the influence of an electric field • Various types – defined by support used 1. Paper – amino acids, small peptides 2. Polyacrylamide – Proteins, small DNA/RNA (<500bp) 3. Agarose – DNA/RNA • Good preparative and analytical method Proteins move in the electric field. Their relative speed depends on the charge, size, and shape of the protein instrumentation and reagents: (1) Two buffer boxes contain the buffer used in the process. (2) Each buffer box contains an electrode made of either platinum or carbon, the polarity of which is determined by the mode of connection to the power supply. (3)The electrophoresis support on which separation takes place may contact the buffer directly, or by means of wicks (4)The entire apparatus is covered to minimize evaporation and protect the system (5) The power supply to provide electrical power. General Procedure Factors affecting migration rate Sample Electric field Buffer Supporting media The sample Charge Size Shape The electric field Current Voltage Resistance Heat The Buffer Composition Concentration PH The Supporting media Adsorption Electro-osmosis Molecular sieving Types of ELECTROPHORESIS Zone electrophoresis Slab Gel Electrophoresis Disc electrophoresis lsoelectric Focusing electrophoresis Two-Dimensional (2D) Electrophoresis Capillary electrophorsis Microship electrophorsis GEL ELECTROPHORESIS What is a gel? Gel is a cross linked polymer whose composition and porosity is chosen based on the specific weight and porosity of the target molecules. Types of Gel: Agarose gel. Polyacrylamide gel. • Gel electrophoresis uses a cross-linked polymers (agarose) that contain various pores. • Pores allow molecular sieving, where molecules e.g. DNA, can be separated based upon there mobility through the gel. A highly purified uncharged polysaccharide derived from agar. Used to separate macromolecules such as nucleic acids, large proteins and protein complexes. It is prepared by dissolving 0.5% agarose in boiling water and allowing it to cool to 40°C. It is fragile because of the formation of weak hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic bonds. Used to separate most proteins and small oligonucleotides because of the presence of small pores. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. Detection Dye e.g. ethidium bromide Audioradiography 32P, Blotting (see later) Uses Analytical- Can determine size of DNA fragment, Preparative – Can identify a specific fragment based on size Silver staining is usually 10-100 times more sensitive than Coomassie Blue staining, but it is more complicated. Faint but still visible bands on this gel contain less than 0.5 ng of protein! Electrophoretic method that separates proteins according to the iso-electric points Is ideal for seperation of amphoteric substances Seperation is achieved by applying a potential difference across a gel that contain a pH gradient Isoelectric focusing requires solid support such as agarose gel and polyacrylamide gel Separates proteins by their isoelectric points (pI) Each protein has own pI = pH at which the protein has equal amount of positive and negative charges (the net charge is zero) IEF 4-6.5 pH gradient Zavialov A. Mixtures of ampholytes, small amphoteric molecules with high buffering capacity near their pI, are used to generate the pH gradient. Positively and negatively charged proteins move to – and +, respectively, until they reach pI. PI of proteins can be theoretically predicted. Therefore, IEF can also be used for protein identification. 1. 2. 3. Using specific probes that are labelled specific sequences of DNA can be identified. There are three main hybridization techniques which vary in the sample blotted and the probes used; Northern Blot-Transfer of an RNA sample separated and identified using DNA or RNA probes. Southern Blot-Transfer of an DNA sample separated and identified using DNA or RNA probes. Western Blot- Transfer of an Protein sample separated and identified typically using an antibody. Blotting – Transfer of DNA, RNA or Proteins, typically from a electrophoresis gel to a membrane e.g. nitrocellulose. This membrane can then be subject to further techniques such as hybridization. Hybridization – Process where two complementary single strands of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) form a double helix. WB is a protein detection technique that combines the separation power of SDS PAGE together with high recognition specificity of antibodies An antibody against the target protein could be purified from serum of animals (mice, rabbits, goats) immunized with this protein Alternatively, if protein contains a commonly used tag or epitope, an antibody against the tag/epitope could be purchase from a commercial source (e.g. anti-6 His antibody) 1. Separation of proteins using SDS PAGE 2. Transfer of the proteins onto e.g. a nitrocellulose membrane (blotting) 3. Immune reactions 4. Visualization This technique combines the technique IEF (first dimension), which separates proteins in a mixture according to charge (PI), with the size separation technique of SDS-PAGE second dimension). The combination of these two technique to give two-dimension(2-D)PAGE provides a highly sophisticated analytical method for analysing protein mixtures. Using this method one can routinely resolve between 1000 and 3000 proteins from a cell or tissue extract and in some cases workers have reported the separation of between 5000 and 10000 proteins. The result of this is a gel with proteins spread out on its surface. These proteins can then be detected by a variety of means, but the most commonly used stains are silver and coomasie staining. In CE, the classic techniques of electrophoresis are carried out in a small-bore, fused silica capillary tube, the outer diameter of such tubes typically varies from 180 to 375 micrometer, the inner diameter from 20 to 180 micrometer, and the total length from 20 cm up to several meters. This capillary tube serves as a capillary electrophoretic chamber that is connected to a detector at its terminal end and, via buffer reservoirs, to a high-voltage power supply The main advantage of CE comes from efficient heat dissipation compared with traditional electrophoresis. Improved heat dissipation permits the application of voltages in the range of 20 to 30 kV, which enhances separation efficiency and reduces separation time in some cases to less than 1 minute The following problems may be encountered when peforming gel electrophoresis. 1. Discontinuities in sample application: may be due to dirty applicators, which are best cleaned by agitating in water followed by gently pressing the applicators against absorbent paper. Caution must be used, and it is inadvisable to clean wires or combs by manual wiping. 2. Unequal migration of samples across the width of the gel may be due to dirty electrodes causing uneven application of the electrical field or to uneven wetting of the gel. 3. Distorted protein zones may be due to A.bent applicators. B.incorporation of an air bubble during sample application. C.over application of sample. D.excessive drying of the electrophoretic support before or during electrophoresis. 4. 5. 6. Irregularities (other than broken zones) in sample application probably are due to excessively wet agarose gels. Parts of the applied samples may look washed out. Unusual bands are usually artifacts that may be easily recognized. Atypical bands in an isoenzyme pattern may be the result of binding by an immunoglobulin. An irregular, but sharp protein zone at the starting point that lacks the regular, somewhat diffuse appearance of proteins may actually be denatured protein resulting from a deteriorated serum. الحمد هلل رب العالمين