Techniques
advertisement
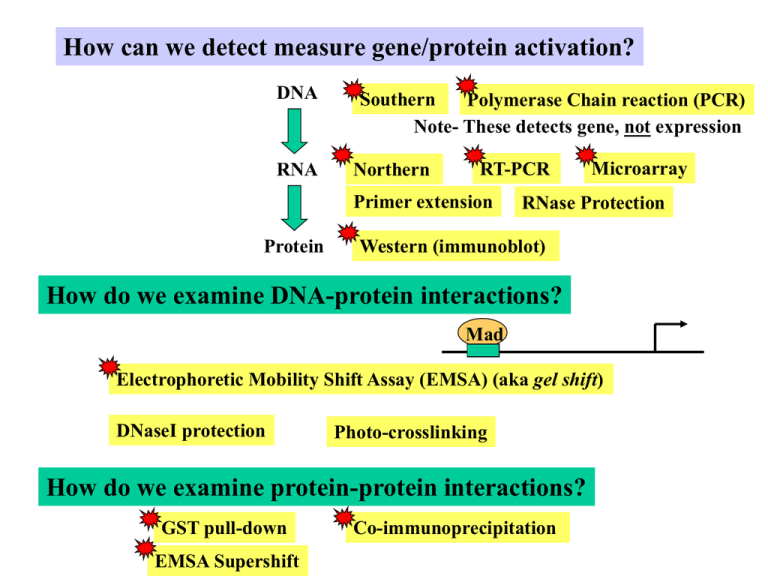
How can we detect measure gene/protein activation? DNA RNA Southern Polymerase Chain reaction (PCR) Note- These detects gene, not expression Northern RT-PCR Primer extension Protein Microarray RNase Protection Western (immunoblot) How do we examine DNA-protein interactions? Mad Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) (aka gel shift) DNaseI protection Photo-crosslinking How do we examine protein-protein interactions? GST pull-down EMSA Supershift Co-immunoprecipitation Techniques to know to understand signal transduction 1. __________- Detect DNA only 2. ___________- Detect RNA 3. ___________- Detect RNA of ____ of expressed genes 4. ________ ( Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction- to detect RNA) 5. ________________________ Detect protein 6. _______________- Detect proteins in situ 7. _________- protein-DNA interactions 8. ________– Protein-protein interactions 9. ______________- Protein-protein interactions Separation of DNA/RNA/Proteins by gel electrophoresis (-) Electrode Protein mixture (+) Electrode Polyacrylamide Gel Direction of current _________________________ used for RNA and DNA separation ________________________ gel electrophoresis is used for protein separation Large proteins Direction of current Small proteins RNA detection 1. Southern analysis- to determine if gene is present/defective 2. Northern transfer and analysis 1 2 3 1 1. Northern transfer to _____ membrane 28S 18S 2 3 Ras detected 2. Hybridize with Ras _____ probe 3. Wash and expose to _____ Stained gel Film exposed to probed membrane 3. Microarrays- monitor expression of several genes at once Genome-wide analysis- yeast RNA detection 4. RT-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Fig. 4.17 One copy mRNA many copies DNA 4. RT-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Example- detect RasGAP gene RNA isolated for cells Cell mRNA _____ Load onto __________ gel Agarose gel electrophoresis RT-PCR Components of a Western analysis Protein detection 5. Western Analysis Polyacrylamide gel elecrophoresis, transfer to nylon membrane 1. Protein separation 2. Detection Secondary Ab (Anti-rabbit Ab) Alkaline peroxidase Primary Ab (Rabbit Anti-Ras) RAS Ras protein If use antibody to phospho-Ras, then detect slower migrating phopho-Ras 5. Western Analysis- Example After 132 kD 86 kD 43 kD 32 kD 17 kD 5000 1000 500 100 Imidazole (mM) Wash 0 25 Lysate Nickel Column, Imidizole elution Flowthrough Before Bacterial Cell Lysate pTAT-HNF4 Anti-HA Anti-HNF4 Probe for specific protein using antibodies Fraction 2 Dialysis 132 kD 3 4 Liver Onto nylon membrane PAGE Ion Exchange 5. Western Analysis How do we detect activated (phosphorylated) proteins? If use anti-phosphotyrosine (anti-pY) antibody… ….observe ______________________ proteins If use anti-phosphoERK (anti-p-ERK) antibody… ….observe only ____________________ If use anti-ERK (anti-p-ERK) antibody… ….observe ___________________ 6. Western Immunostaining Analysis Detect protein inside of a cell? Enzyme or __________ molecule __________ Ab (Anti-rabbit Ab) __________ Ab (Rabbit Anti-Ras) RAS Cell 6. Immunostaining- example 1 GP73 in human tissues Colon Lung Kidney Prostate GCH Liver Liver Immunohistochemistry Kladney et. al. Gene 249:53 2000 6. Immunostaining- example 2 Upregulation of GP73 expression by adenovirus infection is specific 7. EMSA – Detect Detects DNA DNA–protein –protein complex interaction Cell lysate + ____________ DNA DNA-protein complex Commonly used to identify ___________ factor (SMAD, STAT, NF-kB, etc.) binding to ________________ Unbound DNA NF-kB 8. Supershift – “An EMSA with antibody added” Cell lysate + Radiolabeled DNA + _________ to protein of interest Anti-NF-kB LPS U C LPS CHx +CHx - - - + - +- supershift NF-kB Used to 1. Verifies _______ of protein in DNA/protein complex 2. Identify ______ ________ in the DNA-protein complex NF-kB + 9. Co-immunopreciptiation- Protein-protein interactions receptor Grb2 Ras Cell RasGEF Do these interact?? Lyse cell Primary Ab Immunoprecipitate (Rabbit Anti-RasGEF) with anti-RasGEF Ab RasGEF PAGE Transfer to membrane Grb2 protein Probe with anti- Grb2 antibody and secondary antibody Only detect Grb 2 only if it is binding to RasGEF in cells






