PowerPoint Presentation from April
advertisement

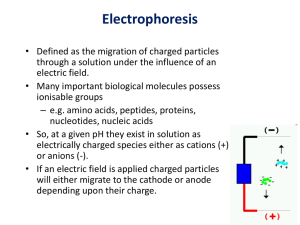
CEG Protein Analysis Workshop Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis Yu Liang, Ph.D. Proteomics Core Facility at UC Medical Center From Genotype to Phenotype Genome: DNAs Transcriptome: RNAs Proteome: Proteins Physiome: Metabolites Biome: Environment Beyond the Genome Proteins are ultimately responsible for all biological processes that take place within cells. Protein dynamics reflect the state of biological system at a given time Detection and identification of posttranslational modifications (PTM) Proteomics Overview Sample Preparation (I) Enzymatic Digestion 2-D Electrophoresis Spot Detection & Image Analysis (II) Peptide-Mass Fingerprinting Protein Identification Peptide Sequencing via MS (IV) (III) (V) Database Search (VI) Personnel Yu Liang, Ph.D. Research Associate MSB 5301 Tel: 558-2347 liangyu@ucmail.uc.edu http://www.med.uc.edu/proteomics/ John Maggio, Ph.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pharmacology & Cell Biophysics Proteomics Core Equipment Genomic Solutions Investigator 2-D Electrophoresis System Genomic Solutions Gel Casting System Genomic Solutions ProImage Image Acquisition System Dell Optiplex Image Analysis Computers New: Fuji Fluorescent Image Analyzer FLA5100 (Phosphoprotein staining and DIGE) Genomic Solutions 2D Electrophoresis System pH phaser isoelectric focusing system Investigator 2-D electrophoresis running system 2-D Image (Fluorescent Staining) • mouse cardiac • 250 g loading • pH 3-10 IEF strips • 12.5% SDS-PAGE • File ID: mb699 Customized Core Services Complete 2-D Gel Service with Spot Picking for MS Analysis Complete 2-D Gel Service, or (1) IEF Only (2) SDS-PAGE (large format) Only (3) SDS-PAGE Plus (staining & imaging) (4) Gel Staining (fluorescent, Sypro Ruby) (5) Image Analysis Only (6) Image Analysis Plus (spot pick) Two new services: (1) Phosphoprotein staining by Pro-Q Diamond fluorescent dye (2) Difference gel electrophoresis (DIGE) by Cydye labelling Sample gels Control Experimental 2-D Image Control Experimental • mouse cardiac; 250 g loading; pH 3-10 IEF strips; 12.5% SDS-PAGE; file ID: sc13con vs. sc08iso; spot ID: S8-1 2-D Image Control Experimental Spot ID: S8-1 • mouse cardiac; 250 g loading; pH 3-10 IEF strips; 12.5% SDS-PAGE; file ID: sc13con vs. sc08iso 2-D Image Control PTM? Downregulation? Experimental • mouse cardiac; 250 g loading; pH 3-10 IEF strips; 12.5% SDS-PAGE; file ID: sc5bcon vs. sc15iso 2-D Gel Analysis 2-D Gel Analysis 2-D Gel Analysis Deliverables Fluorescence-stained 2-D gels Electronic image files Spot list Normalized volumes of spots Plus Free access to our software for further analysis Free advice and consultation on further protein characterization as well as 2-D image analysis www.med.uc.edu/proteomics www.med.uc.edu/proteomics Contact Protocols Price list Services News & Events Feedback Publications On-line order FAQs FAQs How do I get started? What do I get for my result? How much protein should I load for the 2-D gel analysis? How long will it take to get the results? Who is responsible for preparation of protein samples? What protocol should I use for protein solubilization? Sample Preparation The most important step towards the success of 2-D electrophoresis Basic rules: keep everything simple use high-purity reagents Keep proteins denatured and in solution: 7M urea, 2M thiourea, and 4% CHAPS. Break disulfide bonds: 20 mM DTT. (NOT 2-ME) Prevent protein modification: protease inhibitors; phosphatase inhibitors. NO ionic detergent, esp. SDS. Non-ionic detergents are OK, e.g. Triton X-100 and NP-40. Keep salt concentration below 10 mM. Clean up interfering substance, including salt, nucleic acids, lipids, and polysaccharides: acetone (TCA) precipitation and commercial kits. New Fuji FLA 5100 Pro-Q diamond fluorescent staining for phosphoproteins Multiplexing using DIGE Multiplexing by Difference Gel Electrophoresis (DIGE) DIGE with CyDye labeling of protein (Amersham Web Site) Multiplexing by Difference Gel Electrophoresis (DIGE) Comparison of samples within the same gel eliminates gel-to-gel variation Including the internal standards improves statistical confidence of comparing samples for protein abundance changes Reduces number of gels needed to be run in the experiment: 2 comparing groups with 6 individuals, 36 gels for regular 2-D gels 12 gels for 2-dye DIGE 6 gels for 3-dye DIGE Post-Translational Modifications Important for biological processes, particularly signal transductions Most cellular processes are regulated by reversible phosphorylation of proteins Studies of phosphorylated proteins involve radioisotope-labeling and specific antibodies Pro-Q Diamond Staining of a 2-D gel Selectively stains phosphoproteins in 2-D gel Allows direct in-gel detection of phosphate groups attached to tyrosine, serine, or threonine residues NO NEED for antibody and radioisotope Signal correlates with the number of phosphate groups Fully compatible with mass spectrometry Ratio of Pro-Q diamond to Sypro Ruby =phosphorylation level/total protein Blue: Pro-Q Diamond phosphoprotein gel stain Red: SYPRO Ruby total protein stain (Molecular Probes Website) Samples Wanted… Among 0.5~1 million proteins in human proteome, what’s your favorite one? We are here to help the hunting. Please send your samples to: Proteomics Core MSB5301 Tel: 558-2347 Special Thanks… Dr. John Maggio Dr. Limbach’s MS Core Dr. Stephen Macha http://www.chembus.uc.edu/massnew/maintbl.asp