Seminar 20121113
advertisement

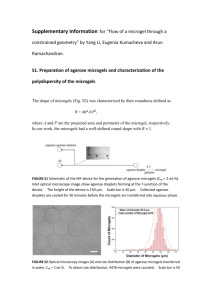
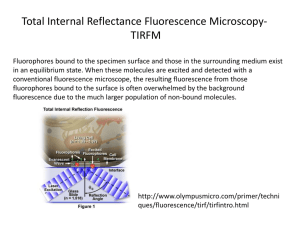
Micron-sized particles Li Junhua 20121113 Abstract • Micron-sized agarose particles were prepared using emulsification/ gelation method as a reservoir for protein or peptide drugs. The size of agarose microgels were measured by microscope and the ruler. In this study, nerve growth factor (NGF) aqueous solution with fluorescence BSA were premixed to the microgels for encapsulation. The 3D collagen gel culture of differentiated PC12 cells was employed to examine the effects of released NGF from agarose microgels on those axons growth. To understand the released amount of proteins from microgel particles in different solution, fluorescence BSA in d.water, PBS and DMEM supernatant was measured by fluorescence spectrophotometer in different time intervals, respectively. Results suggested that after 3days incubation, encapsulated microgels in DMEM culture buffer released more protein (13.6%) than in d.water (2%) or in PBS (3.8%). More experiments are needed to confirm the results. Introduction Collagen gel culture Particle PC12 cell (differentiated) TOPIC 1. Make the micron-sized particles 2. Measure the size 3. NGF/fluBSA encapsulation and release study Methods of making micron-sized particles • Transport across Oil-water Interface • Reverse Phase Evaporation • Emulsification/gelation method (Agarose microgel particles) • ... Preparation of Vesicles DOPC (1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-Glycero-3-phosphocholine) Lipids Suspension (1mM DOPC in Mineral Oil) W/O Emulsions 10wt% agarose gel + 1mM DOPC in Mineral Oil Stand for 1hr Water Phase (PBS) Centrifuge 4,000rpm for 2min. Collect Vesicle solution (using 18 gauge of needle) Vesicle Transport across oil/water interface Preparation of Vesicles: Reverse Phase Evaporation (REV) Method Lipids: Phosphatidylcholine,phosphatidylglyc erol, cholesterol, etc. Organic solvent(ether): diethyl ether, isopropyl ether, Halothane, trifluorotrichloroethane, etc. Advantage ・High concentration vesicle solution Disadvantage ・Leaving the small amounts of ether in the solvents Preparation of Agarose microgels (Emulsification/gelation) 1. Make 3% agarose with calcein, heat until 96C 2. Make w/o Emulsion (3% agarose in olive oil), stir (sonicate) at 96C, cool down until around 5C 3. Add acetone, stir (vortex) 10 min 4. Collect the microgels by filtration (aperture 1µm), acetone washes the filter several times 5. Freeze-dry overnight, dried powder NGF + fluBSA Encapsulation and Release study 1. 20 µl of NGF + fluBSA aqueous solution 2 mg of freeze-dried microgels Store at R.T. for 30—60min 2. Add 1 ml of d.water/PBS/DMEM, shake (sonication) 3. Examine the particles’ size and the release of fluorescent BSA by fluorescence spectrophotometer. Nikon lenses and ruler Nikon plan fluor 10x lens: 1 pix = 648 nm Nikon plan fluor 20x lens: 1 pix = 324 nm Nikon plan fluor 40x lens: 1 pix = 164 nm Nikon plan fluor 60x lens: 1 pix = 107.5nm Microgel’s size (40x) N1: 5.7µm N2: 3.2µm N3: 2.5µm Li: 2.5µm Microgel size: 5.3 µm (20x) Microgel size: 4.2 µm (20x) PC12 cell culture in collagen gel (Microgels with fluBSA + NGF) (20x) PC12 cell culture in collagen gel (Microgels with NGF + fluBSA) (40x) Microgel size: 3.7 µm x 2.5 µm PC12 cell culture in collagen gel (Microgels with NGF + fluBSA) (20x) Fluorescence BSA releases from microgel particles by fluorescence spectrophotometer 1200 1000 800 DMEM+fluBSA+NGF 600 DMEM+fluBSA 400 water+fluBSA+NGF water+fluBSA 200 0 10min 30min 50min 18h Fluorescence BSA releases from microgel particles by fluorescence spectrophotometer 300 274 276 250 200 150 2d+ 4d 100 91 89 54 50 16 17 23 25 18 0 d.water d.water+fluBSA DMEM DMEM+fluBSA fluBSA fluBSA releases from microgels in d.water, PBS or DMEM buffer 350 320 310 293 300 277 260 250 235 220 216 200 30min 150 3d 100 63 55 50 1615 0 2121 2019 2019 1615 2325 2525 2424 2521 5854 5552 siRNA : small interfering RNA short interfering RNA silencing RNA P: 5’ Phosphate OH: 3’ hydroxyl • Double-stranded molecules, 20-25 nucleotides in length • The main role of siRNA is involved in RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, to knock down the target gene expression • An important tool for drug development and biomedical research of genes of unknown function. Mechanism of RNA interference pathway Dicer: ribonuclease protein RISC: RNA-induced silencing complex Process of siRNA transfection: Reagent: Lipofectamine RNAiMax Lipofectamine 2000 FuGENE6 etc. Time course of silencing of filamin A gene expression by siRNAs C. Huang et al. FEBS letters 580 (2006) 1795-1800