Foam stability
advertisement

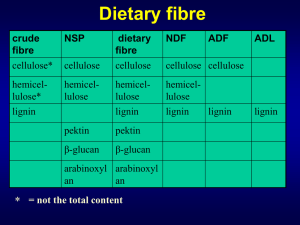
Challenges for Improving Wheat Quality Peter Shewry (Rothamsted Research and the University of Reading) The major grain components determine end use quality starch UK usage of wheat 2013 Total= 14 m tonnes feed milling seed other gluten proteins cell walls (fibre) vitamins minerals phytochemicals distilling biofuels livestock feed food processing Human health Challenges for Wheat Quality in Europe • Reduce N requirement for growing high yielding bread making wheats • Increase STABILITY of yield and quality • Improve health benefits The high grain protein requirement for bread making results in N applications above the optimum for yield 16 14 12 Grain yield 10 (tonnes/Ha) 8 Grain protein % 6 (%N x 5.7) 4 2 0 48 144 192 240 288 N application (kg/Ha) cost of N fertiliser Improved quality with reduced N • Exploit grain protein deviation (GPD) • Improve quality at low protein • Exploit non-protein sources of quality Grain protein deviation (GPD): Mean grain N contents and yields for 47 wheat cultivars grown at Rothamsted Research between 2004 and 2012. Exploiting GPD: project components Six cultivars • Trials • 11 environments (sites or years) • Analyses • Yield • Grain protein • Milling and baking • Transcriptomics (21 dpa) WITH GPD Hereward: Group 1, stable high protein Cordiale: Group 2, medium protein, Marksman: Group 2, medium protein, WITHOUT GPD Xi 19: Group 1, medium protein Malacca: Group 1, medium protein Istabraq: Group 4, low protein, suitable for feed and biofuel Transcriptomics 2009 and 2010 2011 Expression of 8770 genes varied with varietyand/or environment (out of 60000 total) CO He IS Ma MK XI Co Co Ma MK IS He Xi Expression data processed to remove effects of 1. Nitrogen fertilisation 2. Yield Identified 136 transcripts related to cultivar differences in GPD Expression of genes positively related to GDP in 2009 (open circles), 2010 (closed circles) and 2011 (open squares) The samples are sorted along the xaxis according to the cultivar With GPD Red: Hereward Green: Cordiale Yellow: Marksman Without GPD Blue: Istabraq Black: Malacca Purple: Xi19 The challenge is to confirm gene function - genetic analysis - transgenesis Can we identify new sources of improved and STABLE quality? • Lipids by MS/MS • LMW metabolites by NMR and ESI-MS The role of lipids in determining gas bubble stability in wheat dough • Formation of visco-elastic gluten network during mixing • Expansion of the network by entrapment of CO2 during proofing • Retention of gas bubble structure through to baking These are determined by: • Gluten viscoelasticity • Lipids at the gas bubble interface Surface active lipids can be studied in dough liquor Centrifuge dough Foam stability Electrode Foam Over -foaming to separation and collect active lipids. Jet Surface composition and structure Surface tension & surface rheology Dough liquor zoom microscope digital camera Foam microconductivity to measure stability. Dough liquor Pendant drop Langmuir trough allows sampling of surface lipids for MS analysis Lipidomics Extraction MS analysis Data Processing Direct infusion: CTC PAL +NL (341.00): 40 MCA scans from Sample 5 (BD_5_DGDG) of 2013-04-03LOUISE-FLOUR_DGDG.wiff (Nanospray) Max. 2.5e6 cps. 2.5e6 2.4e6 2.3e6 2.2e6 2.1e6 2.0e6 1.9e6 1.8e6 1.7e6 1.6e6 1.5e6 Intensity, cps MS/MS 4000 QTRAP 1.4e6 1.3e6 1.2e6 1.1e6 1.0e6 9.0e5 8.0e5 7.0e5 6.0e5 5.0e5 4.0e5 3.0e5 2.0e5 1.0e5 0.0 900 905 910 915 920 925 930 935 940 945 950 955 m/z, Da 960 965 970 975 980 985 990 995 1000 Separates, identifies and and quantifies over150 molecular species Lipids in Foaming of dough liquor Foam stability Drainage volume (ml) 20 15 10 5 0 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 Time (min) Comparison of phospholipids in flour and dough liquor of cv Hereward 70 60 % mol 50 DL HEREWARD 40 30 HEREWARD FLOUR 20 10 0 LPC PA PC PE PG PI Will allow • Selection of improved lines • Innovative milling to concentrate lipids High stable quality at lower N can be achieved by combining • Exploit GPD • High dough strength at lower protein • Novel non-protein sources of quality This will be facilitated by new technologies Improving wheat quality for diet and health- major components in grain • Dietary fibre • Minerals (Fe, Zn, Se) • B vitamins (folates) • Methyl donors (betaine) Bread contributes significantly to the daily intake of dietary fibre in the UK (% adult intake) Energy Protein Carbohydrate Fibre 13 12 21 20 White bread 8 8 14 11 Wholemeal Bread 2 2 3 5 All bread Fibre is deficient in EU diets • UK intake 14g/day • EFSA recommended 25g/day Source: Steer et al. Proc Nutr Soc/ 2008, 67, E363. Some potential mechanisms for benefits of DF Improved bowel function Reduce cholesterol Slow glucose absorption, improve insulin sensitivity Reduce colorectal cancer • Decreased transit time • Increased stool bulk • Reduce absorption • Fermentation in colon to short chain fatty acids • Slow digestion and absorption due to increased viscosity • Inhibit amylase and absorption of sugars • Beneficial effects of butyric acid on colonocytes • Dilute and reduced exposure to carcinogens Based on slide provided by Janet Cade, Leeds Some take home messages from metaanalyses of fibre and health • 10% reduction in risk of colon cancer with10g/day extra cereal/wholegrain fibre • 5% reduction in risk of breast cancer with 10g/day extra soluble fibre • 7% reduction in risk of stroke with 7g/day extra total fibre Thanks to Janet Cade, University of Leeds Diversity screen of 150 bread wheat lines and 50 other cereals grown at Martonvasar in 2004/5 Types Geographical origins Western Europe France, UK, Netherlands 34 West-Central Europe Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Czech Republic,Poland 22 South Europe Italy, Bulgaria, Serbia, Croatia 28 South Continental Europe Hungary, Romania 14 Steppe Russia, Ukraine Land races and old variety populations 14 Old and transitional varieties 13 Americas USA, Canada, Mexico, Argentina 30 Asia, Near East, Australia China, Korea, Australia, Turkey 15 l Aims: identify variation determine heritability Modern varieties Germplasm accessions Winter type Spring type Spelt durum wheat T. monococcum T. dicoccum Rye Barley Oats 64 117 26 184 37 5 10 5 5 10 10 5 Arabinoxylan (AX) is the major dietary fibre component in wheat grain White flour Bran 2-3% fibre 45-50 % fibre 70% AX 50% AX The contents of soluble and total AX fibre vary widely in bran and white flour of 150 wheat lines 25 15 150.00 250.00 200.00 10 50.00 5 0.00 0 THESEE CHINESE-… CF99007 SAVA MANITAL KEY SULTAN95 MALACCA BILANCIA KUKRI ALBA RIBAND GALAHAD THATCHER KANZLER CUBUS CHARA ISENGRAIN KRASNODA… BISCAY TREMIE JUBILEJNAJ… CF99102 LIBELLULA ATLAS-66 PRODUTTORE GRANBEL SARATOV-29 BUCK-… SUNSTAR AUTONOMIA COURTOT KARL-92 BARANJKA CF99105 LONA GENE AMADEUS VALORIS DEKAN SEU-SEUN-27 CATBIRD TOMMI STEPHENS MANITOBA AGRON ALABASSKA… PROBSTDO… APACHE NOMADE MIETI AKTEUR SCOUT66 POBEDA TAMARO HEREW ARD FERTODI-293 BANKUTI-1201 MILAN BALKAN MOMTCHIL NAP-HAL VONA SAGITTARIO CARDINAL SU321 ZVEZDA ARINA SADOVO-1 BEGRA UKRAINKA HANA ETOILE-DE-… BEZOSTAJA-1 ALBATROS-… SOLUBLE: 0.3-0.85% BEGRA BARANJ KA STEPHENS ALBA KANZLER PLAINSMAN-V CHARA GERONIMO KEY ALABASSKAJ A MONOPOL BUCK-CATRIEL HEREW ARD AURORA RAVENNA SOISSONS NAP-HAL SCOUT66 CLAIRE AUGUSTA RED-RIVER QUALITAL MV-PALOTAS PRODUTTORE RIBAND GENE GLENLEA PASTOR KORW ETA DISPONENT AVALON J UBILEJ NAJ A-50 KIRKPINAR-79 FLAMURA-85 THATCHER RUSALKA MEXIQUE-50 MALACCA GALAHAD J ANZ SU321 B16 BALKAN FUNDULEA-29 AGRON CARMEN APACHE KLEIN-… CF99007 KRASNODARS… MANITAL MARIS-… CAPHORN HANA COURTOT LIBELLULA MV-SUBA SUNSTAR SPARK ATAY-85 DEKAN VALORIS G K-TISZATAJ MOMTCHIL SEU-SEUN-27 BISCAY RENAN TOMMI TAM200 RECITAL LYNX SARATOV-29 AMADEUS CUBUS YUMAI-34 SOLUBLE: 0.3-1.4% 100.00 Yumai 34 30 GLENLEA CAMP-REMY AKTEUR KORW ETA RUSALKA ATAY-85 COURTOT UKRAINKA DEKAN GERONIMO BISCAY SPARTANKA KIRKPINAR-79 TALDOR PALESIO MIETI SULTAN95 CHARA TOMMI JANZ ALBATROS-… AGRON CLAIRE KANZLER APACHE BLUE/AG KUKRI SUNSTAR ETOILE-DE-… VONA MILLENNIUM GUARNI THESEE CADENZA BLASCO GEREK-79 ARINA HANA RAVENNA KIRAC66 RENAN CF99102 KARL-92 FLAMURA-85 SAVA KRASNODAR… GRANBEL MV-PALOTAS SARATOV-29 KEY CHINESE-… AUTONOMIA PAN MANITAL RECITAL MOMTCHIL SAGITTARIO MEXIQUE-50 GALAHAD ATLAS-66 AMADEUS CAMPARI RIALTO B16 JUBILEJNAJA… BALKAN SU321 CARMEN LASTA CF99007 LYNX SEU-SEUN-27 MILAN BILANCIA YUMAI-34 CHINESE-SPRING SOISSONS SAVA QUALITAL TALDOR GLENLEA AUTONOMIA LONA FREDRICK FLEISCHMANN-… ORNICAR OBRIY BISCAY CAPO POBEDA RAVENNA BEGRA THATCHER ARTHUR-71 SPARTANKA JUBILEJNAJA-50 GLORIA MONOPOL FLAMURA-85 AKTEUR CAMP-REMY FUNDULEA-29 AUGUSTA HANA NS-RANA-1 BLASCO SAGITTARIO ATAY-85 BLUE/AG RED-FIFE ALBA SCOUT66 HEREW ARD AGRON ARINA DEKAN HERZOG ALBATROS-… JANZ B16 ESTICA ELLVIS RENAN CLAIRE PROBSTDORFE… BLE-DES-DOMES TOMMI SKOROSPELKA-… CHARA MALACCA BALKAN CF99102 SU321 AMADEUS CATBIRD KIRKPINAR-79 AVALON MILLENNIUM UKRAINKA SEU-SEUN-27 MOULIN MAGDALENA-FR CUBUS GRANBEL AZTECA67 MANITAL CF99007 CAMPARI MIETI YUMAI-34 % SOLUBLE: 20-50% % SOLUBLE: 2-5% TOTAL: 1.35-2.75% TOTAL: 12.7-22.1% Yumai 34 1.60 1.40 1.20 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 0.90 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00 FLOUR BRAN 20 Data of Kurt Gebruers, Christophe Courtin and Jan Delcour (KU Leuven) AX content of flour and bran is highly heritable Exploiting natural variation in AX fibre: Yumai 34 A Chinese wheat variety released in 1998 in Henan province High fibre content (total and soluble) High viscosity of aqueous extracts Good breadmaking quality 3 2.5 2 TOT-AX 1.5 WE-AX 1 0.5 0 Yumai 34 Mean 151 lines Healthgrain Diversity screen data from Gebruers et al (2008) J. Ag. Food Chem., 56, 9740-9749. Relative Viscosity 3.00 2.50 2.00 1.50 1.00 Yumai 34 Control Yumai 34 Control Exploiting natural variation in AX fibre: Yumai 34 x Ukrainka AX content 2.500 TOT WE Relative viscosity 2.000 1.500 1.000 Ukrainka Yumai 34 0.500 2.400 2.200 Ukrainka Yumai 34 2.000 1.800 1.600 1.400 1.200 1.000 0.000 96 F6 lines + parents Fibre analysis Genotyping Transcriptome analysis of bulk segregants Ukrainka Yumai 34 New sources of variation: the Watkins collection Collected by Board of Trade for A E Watkins (University of Cambridge) From markets and farms in1920s and 30s Initially several thousand but now down to1300 From 34 countries Held at JIC Core collection 119 lines Total and WE-AX in wholemeal flours of the Watkins lines WE-AX Yumai 34 TOT-AX Yumai 34 40% WE-AX as % of TOT-AX Yumai 34 0% Exploring the role of AX fibre in the human GI tract SMALL INTESTINE effects of AX on digestion, viscosity and mass transfer prebiotic effects of AX: SCFAs, “good bacteria” COLON ferulate and vascular function/blood pressure dough fermentation and IBS Conclusions- Priorities • Develop N efficient wheat with good quality at low grain N • New protein and non-protein sources of qualitygreater stability? • Improve health benefits DF is an important target with established health benefits and high heritability Thanks GPD Malcolm Hawkesford Yongfang Wan Gemma Chope (Campden BRI) Simon Penson (Campden BRI) Ellen Mosleth Faergestad (Nofima/Oslo) Millers and bakers Breeders DIETARY FIBRE Rowan Mitchell Alison Lovegrove Mark Wilkinson Till Pellny Jackie Freeman Ondrej Kosik Zoltan Bedo (MTA) Mariann Rakszegi (MTA) GRAIN LIPIDS Richard Haslam (RRes) Peter Wilde (IFR) Louise Salt (IFR) Irene Gonzalez-Thuillier Paola Tosi (Reading) Simon Penson (Campden BRI) Peter Skeggs (Hovis)