fibre
advertisement

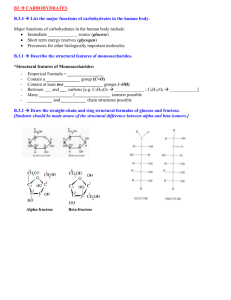
Dietary fibre crude fibre cellulose* NSP hemicellulose* lignin hemicellulose cellulose dietary fibre cellulose NDF hemicellulose lignin hemicellulose lignin lignin pektin pektin β-glucan β-glucan arabinoxyl arabinoxyl an an * = not the total content ADF ADL cellulose cellulose lignin Cellulose • cell wall structure (10-15 thousand glucose units) • does not soluble in water • higher animals and humans can’t digest • bacteria in the rumen and large intestine produce cellulase enzyme The structure of starch and cellulose starch cellulose Hemicelluloses • closely associated with cellulose • can bind water • not homogenous structure (glucose, galactose, mannose, xylose, arabinose polymers) • can metabolise only bacteria Pectic subtances • the first compound of primary cell walls • the linear chain of galacturonic acid • good water absorbing capacity • soluble in hot water, but animals can not digest • contains considerable gelling properties (jam making) Lignin • is not a well defined compound • alcohol polymer • high résistance to chemical degradation • binding to cell wall polysaccharides, mostly cellulose • wood products and straw are rich • do not solve in water • from nutritional point of view has a negative effect Other fibre compounds • -glucan, arabinoxylan (wheat, barley, rye, oats) – anti-nutritive effect – increasing the viscosity of the digesta – decrease the digestibility of nutrients – sticky droppings, Salmonella contamination of eggs • chitin – a linear polymer of glucose amine, containing insects, fungi, and green algae • exudate gums – produces from wounds of plants, contains arabinose, galactose, glucuronic acid The effect of fibre in the nutrition of ruminants • chewing, rumination, producing saliva, rumen contraction • structural fibre (min. 75% of crude fibre) • only microbes in the digestive tract produce digestive enzymes (cellulase, hemicellulase etc.) • energy source, precursor of volatile fatty acids • has an influence on the time of rumen fermentation, the transport time of chyme in the intestine Rumen degradation of dietary carbohydrates hemicellulose cellulose pectin starch sucrose lactose CH3 C=O COOH pyruvate acetate propionate butyrate The effect of fibre in the nutrition of monogastric animals • bacterial degradation only in the caecum and large intestine (horse, rabbits) • peristaltic movement of the intestine horse > rabbit > pig > poultry 12-20% 10-14% 3-8% 3-6% • young animals need less • high fibre decrease the digestibility of the other nutrients • increase endogenous losses • chyme transport time decrease • high fibre means less concentrated food • satiety feeling Symptoms of fibre deficiency • • • • rumen function disturbances constipation anorexy oesophageal and stomach ulcers Crude fibre content of some feedstuffs (%) alfalfa corn silage 6,9 12,9 hay (good quality) barley straw barley 25,8 35,6 4,9 wheat corn grain full fat soybean extracted soybean meal 2,6 2,6 6,9 13,5 sugar beet potato pumpkin 1,2 0,7 0,8 Fibre requirement of different animal species (%) young pigs (10-20 kg) 2,5 older pigs (70-110 kg) 3,5 broiler chick (0-3 hét) 2-3 broiler chick (5-6 hét) 3-4 laying hen 5 horse 12-16 rebbit 11-12 milking cow 17-23 Effect of dietary fibre in the human nutrition • requirement: 30-40 g/day • consumption: 15-25 g/day Consequences of fibre deficiency : • large bowel problems, diseases (constipation, diverticuloses, colon or rectal cancer) • metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes high blood lipid parameters)