dCAPS Genotyping Slides
advertisement

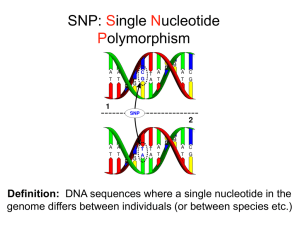
PCR-Based Genotyping Methods An introduction to PCR-RFLP/CAPS, and dCAPS Common PCR-based Genotyping Methods for SNP Analysis SNPs can have up to 4 alleles (A/C/G/T), but two alleles are most common. These methods can only positively detect one allele. • PCR-RFLP / CAPS - • Polymerase Chain Reaction - Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms Also called Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequences (CAPS) A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) where one allele creates (or removes) a naturally occurring restriction site. Amplifying the sequence surrounding these SNPs from individuals, cutting the products with a restriction enzyme and resolving on a gel will reveal which alleles an individual carries. dCAPS - derived Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequences For SNPs that do not create a natural restriction site. Uses mismatches in one PCR primer to create or remove a restriction site for one allele. Genotyping – PCR-RFLP / CAPS [T/A] SNP EcoRV site: GATATC GATATC T/T GATATC GAAATC A/A GAAATC GATATC T/A GAAATC Genotyping – PCR-RFLP / CAPS [T/A] SNP EcoRV site: GATATC GATATC T/T GATATC PCR primers GAAATC A/A GAAATC L 200 GATATC T/A GAAATC 100 150 bp 50 bp 200 bp 50 T/T A/A T/A How do you genotype a SNP that does not make a restriction site? 5 Genotyping - dCAPS • Derived CAPS uses a mismatched PCR primer to create or remove a restriction site based on the genotype of a SNP. • Advantages: - Can be used when the SNP does not create a natural CAPS/RFLP marker. - Can be used to change a natural CAPS marker from a site using an expensive or rare enzyme to a cheap or common enzyme. • Disadvantages: - Mismatches in primer lowers PCR specificity. - Laborious compared to hybridization with gene chip methods for SNP detection. - Finding the right enzyme. Can use web site: http://helix.wustl.edu/dcaps/dcaps.html to find dCAPS primers for SNPs. 6 Dog SNP dCAPS example • Dog SNP #1 (DS1) is polymorphism of C/T on chromosome 10 in the dog genome. The C allele is associated with small size and weight (< 30 lb). • We will create a dCAPS primer set that is a positive assay for the C allele using BamHI enzyme (C will be cut with BamHI). BamHI site: 5’-GGATCC-3’ 3’-CCTAGG-3’ DS1 Locus: 5’-GCCTTGTCCTAAATGTAGTCGATA[C/T]N(119) TCTTCTCCCCTTCTGGGTTTAAA-3’ Dog SNP dCAPS example • The reverse primer will be a standard reverse primer with no mismatches about 100 bp downstream of SNP. – In this case the best primer site was 123 bp downstream of the SNP. BamHI site: 5’-GGATCC-3’ 3’-CCTAGG-3’ DS1 Locus: 5’-GCCTTGTCCTAAATGTAGTCGATA[C/T]N(119) TCTTCTCCCCTTCTGGGTTTAAA-3’ 3’-AGAAGAGGGGAAGACCCAAA-5’ Dog SNP dCAPS example • The Forward primer will be mismatched to create the BamHI site with the C allele but not the T allele. • We will need to mutate two sites: the first and fifth site in the recognition sequence. • This will create a GGATCC site with the C allele and a GGATCT site with the T allele (only the C will be cut by BamHI) BamHI site: 5’-GGATCC-3’ 3’-CCTAGG-3’ DS1 Locus: 5’-GCCTTGTCCTAAATGTAGTCGATA[C/T]N(119) TCTTCTCCCCTTCTGGGTTTAAA-3’ 3’-AGAAGAGGGGAAGACCCAAA-5’ Dog SNP dCAPS example • The Forward primer will be mismatched to create the BamHI site with the C allele but not the T allele. • We will need to mutate two sites: the first and fifth site in the recognition sequence. • This will create a GGATCC site with the C allele and a GGATCT site with the T allele (only the C will be cut by BamHI) BamHI site: 5’-GGATCC-3’ 3’-CCTAGG-3’ Important Note: The primer does not overlap or mutate the SNP! DS1 Locus: 5’-GCCTTGTCCTAAATGTAGTGGATC-3’ 5’-GCCTTGTCCTAAATGTAGTCGATA[C/T]N(116) TCTTCTCCCCTTCTGGGTTTAAA-3’ 3’-AGAAGAGGGGAAGACCCAAA-5’ Dog SNP dCAPS example 1. PCR with dCAPs primers 2. Digest products with BamHI 3. Run on gel Expected results for three genotypes: – Homozygous C/C – 143, 20 bp – Homozygous T/T – 163 bp – Heterozygous C/T – 163, 143, 20 bp Note: The 20 bp product will run off gel, since we run gel long enough to resolve between 163 and 143 bp L 200 150 100 C/C T/T C/T