Genome-Wide Association Studies
Xiaole Shirley Liu
Stat 115/215
Association Studies
• Association between genetic markers and
phenotype
• Especially, find disease genes, SNP / haplotype
markers, for susceptibility prediction and
diagnosis
• Influences individual decisions on life styles,
prevention, screening, and treatment
2
3
Mike Snyder’s iPOP Reveals Diabetes
4
Warfarin and CYP2C9:
SNPs in Pharmacogenomics
• Warfarin anticoagulant drug; CYP2C9 gene
metabolizes warfarin.
• A patient requiring low dosage warfarin
compared to normal population, has an odd
ratio of 6.21 for having 1 variant allele
• Subgroup of patients who are poor
metabolisers of warfarin are potentially at
higher risk of bleeding
Aithal et al., 1999, Lancet.
Genome-Wide Association Studies
• Two strategies:
– Family-based association studies
– Population-based case-control association
studies
• Quality Control
–
–
–
–
6
Unusual similarity between individual
Wrong sex
Trio has non-Mendelian inheritance
Genotyping quality
Quality Control: SNP calls
Good calls!
Bad calls!
Family-based Association Studies
TDT: Transmission Disequilibrium Test
• Look at allele transmission in unrelated families
and one affected child in each
Aa
92
2.11
A a
92
~ 2 , 1 df
ZTDT
2
ZTDT
• Could also compare
allele frequency
between affected vs
unaffected children
in the same family
8
Like coin toss
Case Control Studies
• SNP/haplotype marker frequency in sample
of affected cases compared to that in age
/sex /population-matched sample of
unaffected controls
• Size matters
9
Visscher, AJHG 2012
From Genotyping to Allele Counts
10
Test Significant Associations
• Expected:
– (24 + 278) * (24 + 86) / (24 + 278 + 86 + 296) = 49
– (278+296) * (86+296) / (24 + 278 + 86 + 296) = 321
2
•
i, j
(eij oij )2
eij
2 = 27.5, 1df, p < 0.001
• Multiple hypotheses testing?
11
GWAS Pvalues
GWAS Pvalues for Type II Diabetes
• Bonferroni correction: most common, typically p
< 10-7 or 10-8
• Split samples to improve power
McCarthy et al, Nat Rev Genetics, 2008
14
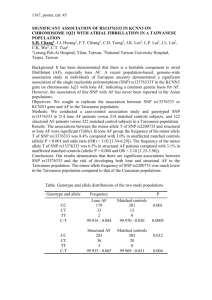
Association of Alleles and Genotypes of
rs1333049 (‘3049) with Myocardial Infarction
C
N (%)
G
N (%)
2,132 (55.4)
1,716 (44.6)
Controls 2,783 (47.4)
3,089 (52.6)
Cases
2
(1df)
P-value
55.1
1.2 x 10-13
Allelic Odds Ratio = 1.38
• OR = 1, no disease association
• OR > 1, allele increase risk of disease
• OR < 1, allele decrease risk of disease
Samani N et al, N Engl J Med 2007; 357:443-453.
Manolio et al., Clin Invest 2008
Pitfalls of Association Studies
• Not very predictive
17
Pitfalls of Association Studies
•
•
•
•
•
•
18
•
•
Not very predictive
Explain little heritability
Poor reproducibility
Poor penetrance (fraction of people with the
marker who show the trait) and expressivity
(severity of the effect)
Focus on common variation
Difficult when several genes affecting a
quantitative trait
Many associated variants are not causal
No available intervention for many disease risks
Reproducibility of Association Studies
• Most reported associations have not been
consistently reproduced
• Hirschhorn et al, Genetics in Medicine, 2002,
review of association studies
– 603 associations of polymorphisms and disease
– 166 studied in at least three populations
– Only 6 seen in > 75% studies
19
Cause for Inconsistency
• What explains the lack of reproducibility?
• False positives
– Multiple hypothesis testing
– Ethnic admixture / stratification
• False negatives
– Lack of power for weak effects
• Population differences
– Variable LD with causal SNP
– Population-specific modifiers
20
Population Stratification
• Population stratification
●
●
21
– e.g. some SNP unique to ethnic group
– Need to make sure sample groups match
– Hidden environmental structure
Two populations have different disease frequency,
and different allele frequency.
Association picks up they are different
populations!
Balding, Nature Reviews Genetics 2010
Genotyping Principal Components (PCs)
Can Model Population Stratification
• Li et al., Science 2008
Causes for Inconsistency
• A sizable fraction (but less than half) of
reported associations are likely correct
• Genetic effects are generally modest
– Beware the winner’s curse (auction theory)
– In association studies, first positive report is
equivalent to the winning bid
• Large study sizes are
needed to detect these
reliably
23
Should we Believe
Association Study Results?
• Initial skepticism is warranted
• Replication, especially with low p values, is
encouraging
• Large sample sizes are crucial
• E.g. PPARg
Pro12Ala &
Diabetes
24
Replication, Replication, Replication
• Meta-analysis of multiple studies to
increase GWAS power
• Combine data from different platforms /
studies
• Impute unmeasured or missing genotypes
based on LD (e.g. HapMap haplotypes or
1000 Genomes)
• Analyze all studies together to increase
GWAS power
25
Missing Heritability?
Visccher, AJHG 2011
Detection Power of GWAS
27
Acknowledgement
• Tim Niu
• Kenneth Kidd, Judith Kidd and Glenys
Thomson
• Joel Hirschhorn
• Greg Gibson & Spencer Muse
• Jim Stankovich
• Teri Manolio
28