Geology PowerPoint Presentation
advertisement

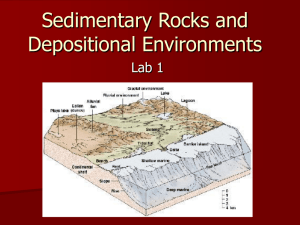
Ohio Rocks! Lynda Price The Wilderness Center This Rocks! Sedimentary Igneous Metamorphic Sedimentary Rocks Weathering Erosion Deposition Sediments cemented by pressure over time. Sandstone Limestone Shale Igneous Rocks Cooling magma or lava forms Igneous rock. Granite Pumice Metamorphic Rocks Changed by heat and pressure. Slate Gneiss Geologic Time 1 million days = 2,740 years 1 million hours = 114 years Precambrian •Basement rocks •13,000 – 2,500 feet deep. •Igneous and metamorphic rocks Ohio earthquakes are caused from faults in these rocks. Mississippian Pennsylvanian •Cambrian rocks not exposed. •Oil and gas from abundant marine life. •Warm shallow sea •Limestone and shale •Ohio is world famous for its fossiliferous Ordovician rocks in the Cincinnati area. Cephalopods squids in a shell Crinoids – sea lilies Limestone Dolomite •Driveways, concrete •Building stone •Fertilizer •Toothpaste, lipstick Ocean mud Shale Claystone •Pottery •Bricks •Concrete •Antacids Mud •Dry land, then warm, shallow to deep seas •Reef building formed barriers, restricted water flow: salts accumulated. •Limestone, dolomite, shale, gypsum. Salt deposits under lake Erie. Gypsum Ocean brine •Drywall •Plaster of Paris •Bakery products Rock Salt Ocean salt •Snow and ice control •Seasoning •Water softening •Dry land at first, then warm shallow seas. (Deposited the Columbus & Delaware limestone.) •Seas became stagnant and “anoxic”. (Deposited the Ohio Shale.) The Ohio Shale: • Huron Shale Member • Chagrin Shale Member •Cleveland Shale Member Dunkleosteus •Muddy to sandy seas deposited shale and sandstone. •Appalachian Mts. begin to form as plates collide. Supercontinent Pangea begins to form. Berea sandstone economically important. Black Hand sandstone Hocking Hills & Mohican Sandstone Sand •Building stone •Glass •Golf sand traps •Furnace liners Hocking Hills State Park Flint Volcanic ash in streams •Ohio’s official gemstone •Spearpoints •Flintlock guns •Tropical forests and swamps. •Seas level rises and falls. •Appalachian Mts. continue to rise. Supercontinent Pangea complete. Marine rocks: shale, limestone, flint. Non-marine rocks: conglomerate, sandstone, shale, clay and coal. Coal Decayed plants •Electric power •Heating •Steel production Permian •Coastal plains swamp. •Sandstone, shale, coal. • Uplift and erosion • No dinosaur fossils in Ohio Clay Sand & Gravel Sand and Gravel •Road building •Concrete •Groundwater source Sedimentary Igneous & Metamorphic rocks Ohio Geology Lynda Price The Wilderness Center Clifton Gorge State Nature Preserve