Evidence for Former Depositional Environments
advertisement
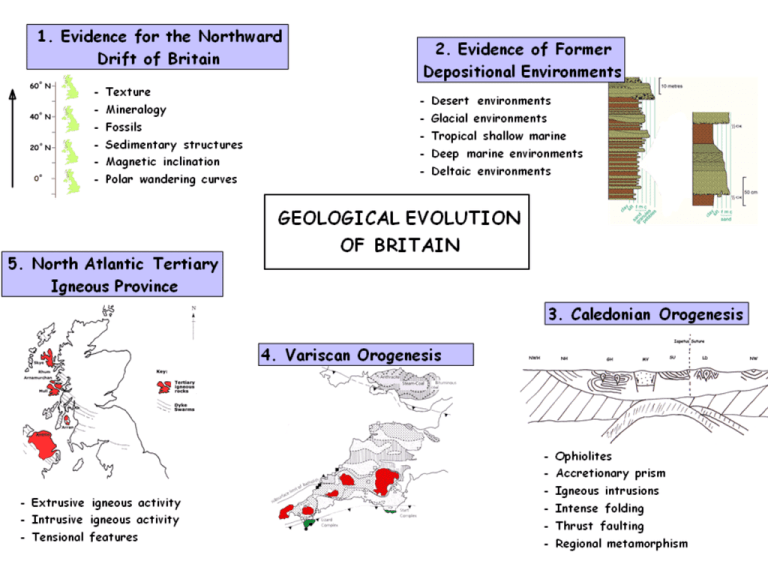
2. Evidence of Former Depositional Environments Deep Marine •Black Shales •Pelagic Muds/Oozes •Greywackes •Mature •Immature •Laminations •Graded Bedding ( some evidence of cross bedding & ripple marks) •Sole Marks •Graptolites •Slow build up of sediment apart from turbidites Carboniferous 360 – 290 MYA Carboniferous Limestone Brachiopods Crinoids Ammonoids Colonial coral Upper Carboniferous Delta top / swamp Fluvial channel fill Delta front sandstone Prodelta Offshore mudstone limestone Upper Carboniferous Delta top / swamp Fluvial channel fill Turbidity currents Delta front Prodelta Offshore Upper Carboniferous Millstone Grit (ssts) Medium-grained Arkose Quartz Feldspar Weak cross bedding Mudstones Shales Carboniferous Limestone Brachiopods Crinoids Ammonoids Colonial coral Suggest the environment of deposition of the sediments shown in Fig. 1c and give evidence for your conclusion. (5) Environment: Deltaic (1) Evidence: Coal swamp/rootlets/complete fossil plants (1) Coarsening up sequence (1) Cross-bedded sands (1) Marine sediments/bivalves (1) Marine to freshwater (1) Shallowing of water (1) limestone 290 Ma Coal Measures 315 Ma Millstone Grit 325 Ma Carboniferous Limestone 363 Ma shale & siltstone sandstone conglomerate coal Texture Crystalline, finegrained, chemical bioclastic Fragmental, finegrained, well sorted Fragmental, coarse sand, moderately sorted, sub-rounded, smooth surface Fragmental, coarsegrained, poorly sorted, sub-rounded, smooth surface Chemical Mineralogy CaCO3 clay & silt Quartz, feldspar rock fragments organic material Structures Bedding Tectonic joints cross bedding coarsening upwards imbrication Seat earth (fossil soils) Fossils Goniatites Corals Crinoids Brachiopods Marine bivalves Freshwater bivalves Texture Fragmental, coarse sand, moderately sorted, smooth surface, sub-rounded Mineralogy Quartz, feldspar Structures Cross-bedding Fossils Freshwater bivalves Texture Crystalline fine-grained, chemical, bioclastic Mineralogy CaCO3 Structures Bedding, tectonic joints Fossils Goniatites Corals Crinoids Brachiopods Giant lycopods (Lepidodendron) Tree ferns Amphibians, early reptiles Spiders, giant flying insects Devonian 409 – 360 MYA Sandstones & conglomerates Limestones & Marine fossils Devonian - 400 mya South of equator 10-20º Arid/desert climate – similar to SW USA (New Mexico/Texas) Old Red Sandstone (ORS) Continent Rapid erosion of Caledonian mountains (Caledonian orogeny) Rivers & lakes in basins between mountains Tropical ocean to south (Rheic Ocean) Desert sandstones – lack of fossils Alluvial sandstones – river deposits Limestones – brachiopods Shales – lake deposits, primitive fish, land plants, insects on land & first winged insects Alluvial Environments (meandering rivers) Lithology: Texture: Mineralogy: Structures: Fossils: Old Red Sandstone Deposits • conglomerates • well-sorted red sandstones • desiccation cracks & calcrete • cross bedding • repeated cycles • alluvial fan deposits formed at edge of Caledonian mountain area ORS sandstone, Orkney 1 cm Medium to fine grained red sandstone with cross bedding ORS conglomerate, Aberdeen Boulder sized clasts of quartzite, granite, rhyolite & andesite 50 cm Devonian Marine Deposits