AS MAPPING
advertisement
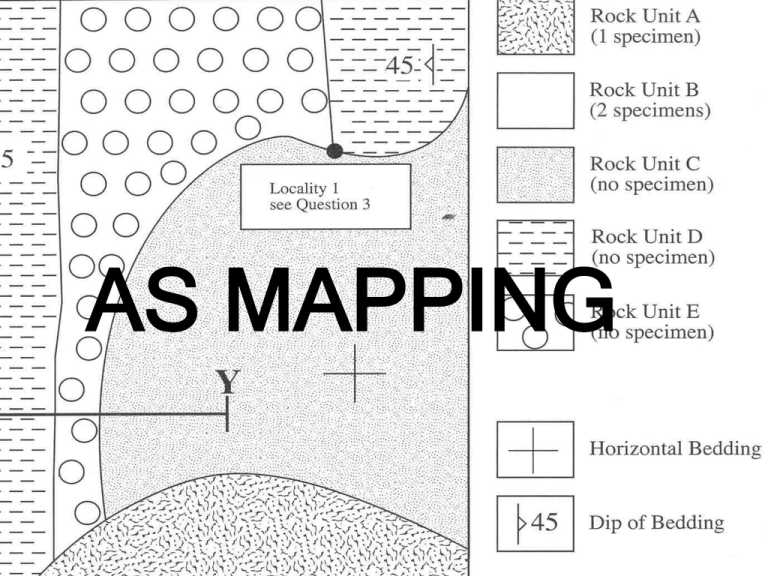
AS MAPPING You will be given a map which shows some simple geological structures and features to interpret. There will also be some questions which relate to the map and to the rock, mineral and fossil specimens. The map will have a key, a scale and a north arrow. The key will include the Rock Units shown on the map. Sometimes you are told what type of rocks each rock unit represents but not always. It is a good idea to write the letters of each rock unit on the map before you start using it. The key also tells you which rock units have a specimen available to study. What type of folds are these? What is the trend and the symmetry of these folds? Folds A B Folds A B There are two folds on this map. What type of folds are they? What is the trend and the symmetry of these folds? Unconformities mark times when erosion is dominant and no sediments are deposited. They mark a break in deposition because of uplift and mountain building. The rocks above overlay the rocks below UNCONFORMABLY and are often very different in dip and strike. Unconformities cut across other beds. D A Folds B C What type of fold is this? What is the trend and the symmetry of this fold? Give the geological history of this map. A Unconformi ties B D C Locate a fold and an unconformity on this map. Describe them both fully. Give the geological history of this area. A Unconformities B Where are the unconformities on these maps? How can you be sure that they are unconformities? Unconformities D B A C Locate two folds and an unconformity on this map. Describe them both fully. Give the geological history of this area. Locate a fold and an unconformity on this map. Describe them both fully. Igneous intrusions B A What type of igneous intrusions are shown on this map? What rocks could A and B be? If faults are shown by straight lines then they are vertical. If faults have a sinuous outcrop then they are at an angle to the horizontal and are probably reverse or thrust faults. What type B of faults are Faults these? What is the F2 A geological C history of E D this area? Faults granite What type of fault is F2? How do you know? Why does it appear to be in two sections? Faults The youngest rocks are always on the downthrow side of a fault. You need to know how old each rock is to find out the downthrow. Faults Strike-slip faults are vertical but the movement on them is lateral (sideways). If the far side moves to the right the sense of movement is dextral, if it moves to the left the movement is called sinistral. Which way has this strike-slip fault moved? What types of faults are F1 and F2? How can you tell? E Faults D A Which one occurred first? How do you know? What is the geological history of this area? B C Faults F2 What types of faults are F1 and F2? Which occurred first? How do you know? A B Which fault F1 or F2 is not vertical? How do you know? C Which fault F1 or F2 came first? How do you know? D What is the geological history of this area? E Answer the exam question about locality 1 on the map above. A A Using evidence from Map 2, give one reason why this is a dyke rather than a sill. What map evidence would you need to know to convince you that the feature formed by Rock B was a sill? C C Sills B Graphic logs Asymmetrical ripples Cross bedding Erosional base Give the evidence from the graphic log that shows that these rocks were laid down in a fluvial environment. Graphic logs Complete the log using the descriptions contained in Table 2. Complete this table about F2. Has the student got this geological history right? Fossil evaluation A student identified this fossil as being Fossil A. Was this correct? Fold wavelengths and amplitudes wavelength amplitude Evaluation of fold axes Are these statements true? • the fold trends are NS •the folds are symmetrical •the fold wavelength is 200m. What is the Geological D geological historyhistory of this area? A B G E F C Questions State three pieces of evidence, either from Map 3 or your fieldwork or knowledge, which confirm the presence of an unconformity. Draw and label on Map 3 the axial planes of two folds to the east of Fault F2. Rock unit B was deposited in tropical, shallow seas. What evidence from the photo and the graphic log would confirm this statement? THE END