6419A_09
advertisement

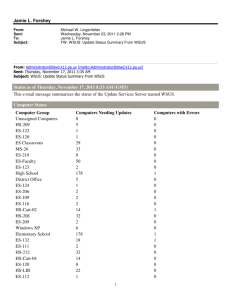
Module 9 Configuring Server Security Compliance Module Overview • Securing a Windows Infrastructure • Overview of EFS • Configuring an Audit Policy • Overview of Windows Server® Update Services (WSUS) • Managing WSUS Lesson 1: Securing a Windows Infrastructure • Discussion: Challenges of Securing a Windows® Infrastructure • Applying Defense-in-Depth to Increase Security • Core Server Security Practices Discussion: Challenges of Securing a Windows Infrastructure • Discuss consequences of not addressing security within your network environment. • Discuss challenges related to implementing and managing secure configuration of servers. • Discuss challenges related to protecting against malicious software threats and intrusions. • Discuss challenges implementing effective identity and access control. Applying Defense-in-Depth to Increase Security Defense-in-depth provides multiple layers of defense to protect a networking environment Data Application Host Internal Network Perimeter Physical Security Policies, Procedures, & Awareness ACLs, encryption, EFS Application hardening, antivirus OS hardening, authentication Network segments, IPsec Firewalls Guards, locks Security documents, user education Core Server Security Practices Apply the latest service pack and all available security updates Use the Security Configuration Wizard to scan and implement server security Use Group Policy and security templates to harden servers Restrict scope of access for service accounts Restrict who can log on locally to servers Restrict physical and network access to servers Lesson 2: Overview of EFS • What Is Encrypting File System? • What Is BitLocker Drive Encryption? • Troubleshooting EFS What Is Encrypting File System? Encrypting File System (EFS) is a system for encrypting files EFS: • File contents are protected by a symmetrical key • The symmetrical key is protected by asymmetrical encryption • Enabled in the properties of a file • Requires a user certificate • Can be used on shared files • Can be configured with a recovery agent in case user certificates are lost What Is BitLocker Drive Encryption? BitLocker is a system that encrypts the entire operating system drive and potentially data volumes BitLocker Drive Encryption: • Helps protect data on the operating system drive • Helps protect the operating system from modification • Access to the operating system drive is controlled by encryption keys Troubleshooting EFS Determine if the problem occurs when encrypting or decrypting files, and whether the files are local or remote Check the following items: • Unable to Encrypt • The volume is NTFS • User has Write access to file • Roaming user profiles generally required to encrypt remote files • Unable to Decrypt • File location is trusted for delegation • Roaming profile is available • User account cannot be delegated • Certificate or Private Key problems Lesson 3: Configuring an Audit Policy • What Is Auditing? • What Is an Audit Policy? • Types of Events to Audit • Troubleshooting Audit Policy What Is Auditing? • Auditing tracks user and operating system activities, and records selected events in security logs, such as: • What occurred? • Who did it? • When? • What was the result? • Enable auditing to: • Create a baseline • Detect threats and attacks • Determine damages • Prevent further damage • Audit access to objects, management of accounts, and users logging on and off What Is an Audit Policy? • An audit policy determines the security events that will be reported to the network administrator • Set up an audit policy to: • Track success or failure of events • Minimize unauthorized use of resources • Maintain a record of activity • Security events are stored in security logs Types of Events to Audit • Account Logon • Account Management • Directory Service Access • Directory Service Changes • Directory Service Replication • Detailed Directory Service Replication • Logon • Object Access • Policy Change • Privilege Use • Process Tracking • System Troubleshooting Audit Policy View Security Log in Event Viewer After you configure auditing, it may not work for the following reasons: • A site, a domain, or an organizational unit policy setting overrides the audit policy that you configured • A GPO that overrides the audit policy setting has a higher priority • The site, the domain, or the organizational unit policy setting that contains the audit policy setting has not replicated to other computers Object Access Auditing • Understand how inheritance affects file and folder auditing • Test an audit rule for a file or folder • Open and close the file or folder • View the security log to ensure Event ID 4663 is logged Demonstration: How to Configure Auditing In this demonstration, you will see how to: • Enable auditing for various events • Enable object access auditing Lesson 4: Overview of Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) • What Is Windows Server Update Services? • Obtaining Updates • Windows Server Update Services Process • WSUS Deployment Considerations • Server Requirements for WSUS • Installing WSUS • WSUS Group Policy Settings • Automatic Updates Configuration What Is Windows Server Update Services? Microsoft Update Web site Automatic Updates Server running Windows Server Update Services Test Clients LAN Internet Automatic Updates Obtaining Updates Windows Update WSUS WSUS WSUS Windows Server Update Services Process Phase 1: Assess • Set up a production environment that will support update management for both routine and emergency scenarios Assess Phase 4: Deploy Phase 2: Identify • Approve and schedule update installations • Review the process Deploy Update Management • Discover new updates Identify after the deployment is complete in a convenient manner • Determine whether updates are relevant to the production environment Evaluate and Plan Phase 3: Evaluate and Plan • Test updates in an environment that resembles, but is separate from, the production environment • Determine the tasks necessary to deploy updates into production, plan the update releases, build the releases, and then conduct acceptance testing of the releases WSUS Deployment Considerations Internet connectivity Number of WSUS servers Simple WSUS deployment WSUS server hierarchy Computer groups Update storage Server Requirements for WSUS Software requirements: • Windows Server 2003 SP1 or Windows Server 2008 • IIS 6.0 or later • Windows Installer 3.1 or later • Microsoft .NET Framework 2.0 • SQL Server 2005 SP1 or later (optional) • Microsoft Report Viewer Redistributable 2005 Installing WSUS Considerations for installing the WSUS Server: • Select Update Source • Select the software used to manage the WSUS database • Select the Web site that WSUS will use to point client computers to WSUS The WSUS Administration Console: • The WSUS 3.0 administration console can be used to manage any WSUS server that has a trust relationship with the administration console computer WSUS Group Policy Settings Group Policy can specify: • Which WSUS server to use • Whether update notifications are displayed • Frequency of checking for updates • Auto-restart behavior • WSUS computer group membership • Whether computers should wake up to apply updates Automatic Updates Configuration • Configure Automatic Updates by using Group Policy Computer Configuration/Administrative Templates/ Windows Components/Windows Update • Requires updated wuau.adm administrative template • Requires: • Windows Vista • Windows Server 2008 • Windows Server 2003 • Windows XP Professional SP2 • Windows 2000 Professional SP4, Windows 2000 Server/Advanced Server SP3 or SP4 Demonstration: Configuring WSUS In this demonstration, you will see how to: • Configure Automatic Update client settings using Group Policy Lesson 5: Managing WSUS • WSUS Administration • Managing Computer Groups • Approving Updates • Server Core Security Updates WSUS Administration Command-line tools for managing updates: • Wuauclt.exe – controls the Windows Update Agent • Wsusutil.exe – management of WSUS Managing Computer Groups • Computers are automatically added • Default computer groups • All Computers • Unassigned Computers • Client-side targeting Approving Updates • Approval options include: • Install • Decline • Unapprove • Removal • Automate approval is also supported Demonstration: Managing WSUS In this demonstration, you will see how to: • Add a computer to WSUS • Approve an update Server Core Security Updates To enable Windows Update on Server Core: • Cscript c:\Windows\system32\scregedit.wsf /au /4 To manually install updates onto Server Core: • Wsua.exe <update>.msu /quiet To manually remove updates from Server Core: • In <update>.xml, replace Install with Remove and save the file. • pkgmgr /n:<update>.xml Lab: Manage Server Security • Exercise 1: Configuring Windows Software Update Services • Exercise 2: Configure Auditing Logon information Virtual machine NYC-DC1, NYC-SVR1, NYC-CL2 User name Administrator Password Pa$$w0rd Estimated time: 60 minutes Lab Scenario • As the Windows Infrastructure Services Technology Specialist, you have been tasked with configuring and managing server and client security patch compliance as well as implementing an audit policy to track specific events occurring in AD DS. You must ensure systems maintain compliance with corporate standards. Lab Review • After installing the WSUS server software, a wizard appears to help you with the configuration of WSUS properties. How can you change any incorrectly assigned properties after the wizard has been completed? • When implementing directory service auditing, what criteria are relevant when choosing to implement success and or failure? Module Review and Takeaways • Review Questions • Best Practices