발표자료 style file
advertisement

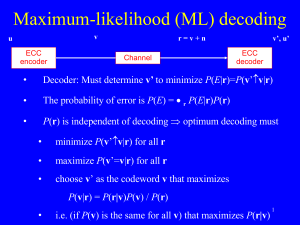
발표제목 발표제목 둘째 줄 2000년 11월 송홍엽 연세대학교 전기전자공학과 송홍엽 <유한체 이론 및 응용> 1/10 Table of Contents Introduction to Error Correction: 3-16 – Linear Binary [n,k,d] Code Binary Hamming Codes: 17-37 – Hamming Codes, Parity Check Matrix and Syndrome Decoding – Standard Array Decoding, Shortening and Extending Coding Gain of some BCH code and MPSK modem: 38-55 – Uncoded MPSK vs Coded MPSK – Coding Gain – etc 송홍엽 <유한체 이론 및 응용> 2/10 TYPES OF CODES Source Coding (Data Compression + Formatting) : remove as much redundancy as possible, subject to unique recovery at the receiver. Huffman code, LPC, CELP, JPEG, MPEG,... Channel Coding (Error Control Coding) : add some redundancy so as to detect and/or correct possible errors at the receiver. Hamming code, RS code, Convolution code, Turbo code Secrecy Coding (Encryption + Authentication) : convert the message in one format into another so that no unintended user may detect/understand/modify the content. DES, RSA,... 송홍엽 <유한체 이론 및 응용> 3/10 Digital Communication Systems Source Source Encoder Secrecy Encoder CRC Encoder Block/Conv Encoder Inter-lea ver Modulator (Writing) Channel Encoder Impairments Noise,Fading Channel (Storage Media) Channel Decoder Sink (User) 송홍엽 Source Decoder Secrecy Decoder CRC Decoder Block/Conv Decoder <유한체 이론 및 응용> Deinterleaver Demodulator (Reading) 4/10 Example of Channel Coding : Repetition code 0 0 1-p Binary Symmetric Channel p p 1 • 1-p 1 Message = (101) • Message Error Probability Without Coding : Puncoded ( E ) 1 (1 p) 3 • With Coding : 0 000, 1 111 Decoding rule : majority vote for every 3 bits • Message error probability :Pcoded ( E ) 1 (1 q ) 3 • where 송홍엽 q p 3 p (1 p) 3 2 <유한체 이론 및 응용> 5/10 Example of Channel Coding : Repetition code (Performance) Comparison of MEP between Uncoded and Coded Systems 0.00 1.00 Message Error Probability -LOG10 (P(error)) 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 P(uncoded) P(coded) 6.00 7.00 8.00 9.00 1.00E+00 1.00E-01 1.00E-02 1.00E-03 1.00E-04 1.00E-05 Bit Error Probability p 송홍엽 <유한체 이론 및 응용> 6/10 Advantages of ECC Principle (Shannon, 1948) If you transmit information at a rate less than the channel capacity, then error-free transmission is possible by using some ECC. Practice 송홍엽 At a given Bit Error Rate, you can reduce the amount of power to be transmitted. <유한체 이론 및 응용> 7/10 송홍엽 <유한체 이론 및 응용> 8/10 송홍엽 <유한체 이론 및 응용> 9/10 송홍엽 <유한체 이론 및 응용> 10/10