Bad SSL 3
advertisement

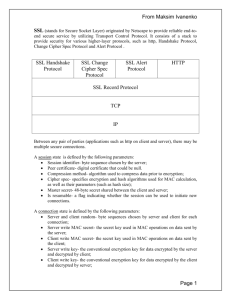
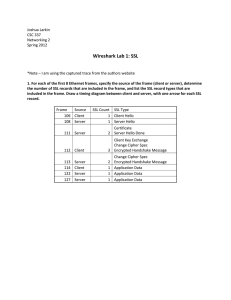
The Dog’s Biggest Bite Overview History Start Communication Protocol Weakness POODLE Issues History 1994 – Netscape Communications Design SSL Version Never Released Publicly 1995 – SSL 2.0 Release as Part of Netscape Navigator 1996 – V3.0 Redesign of Protocol Address 2.0 Vulnerabilities First Version to Authenticate Handshake Messages Prevents Attackers from Triggering Downgrade protocol versions 1999 – IETF Publishes TLS 1.0 Standard Start Communication Handshake Agree on Shared Secret Key Includes Cipher Algorithms Block Cipher Most Common Used If Both Cannot Agree On Protocol Downgrade Dance Start Communication Handshake Client Hello Information that the server needs to communicate with the client using SSL. Including SSL version number, cipher settings, sessionspecific data. Server Hello Information that the client needs to communicate with the server using SSL. Including SSL version number, cipher settings, sessionspecific data. Including Server’s Certificate (Public Key) Start Communication Authentication and Pre-Mater Secret Client authenticates the server certificate. (e.g. Common Name / Date / Issuer) Client (depending on the cipher) creates the pre-master secret for the session, Encrypts with the server's public key and sends the encrypted pre-master secret to the server Decryption and Master Secret Server uses its private key to decrypt the pre-master secret, Both Server and Client perform steps to generate the master secret with the agreed cipher. Start Communication Generate Session Keys Both the client and the server use the master secret to generate the session keys, which are symmetric keys used to encrypt and decrypt information exchanged during the SSL session Encryption with Session Keys Both client and server exchange messages to inform that future messages will be encrypted. Protocol Weakness Today Agreement on Process to Produce Authenticated Encrypted Data Not True When SSL was Created Today Encrypt-Then-Mac (Message Authentication Code) SSL uses Mac-Then-Encrypt POODLE POODLE –Padding Oracle On Downgraded Legacy Encryption Attacker Takes Advantage of Downgrade Dance Works by Using Padding Padding is Created by Block Cipher Attacker Gets 1 byte out of Every 256 Requests Attacker Can Retrieve n Bytes of Data in 256 X n Request Work as part of Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) POODLE Issues Turn Off SSL V3.0 Could Lock Out 1% - 5% of Users (XP /IE 6) Must Achive MITM Before Using Attack Vector Exploit Not as Bad as HeartBleed, Implementation Hard References https://www.dfranke.us/posts/2014-10-14-how-poodle- happened.html http://www.theregister.co.uk/2014/10/16/poodle_analy sis/ http://news.netcraft.com/archives/2014/10/15/googlespoodle-affects-oodles.html http://www.symantec.com/connect/blogs/how-doesssl-work-what-ssl-handshake http://security.stackexchange.com/questions/20803/h ow-does-ssl-tls-work