LI2013 (13) – Pragmatics (for students)
advertisement
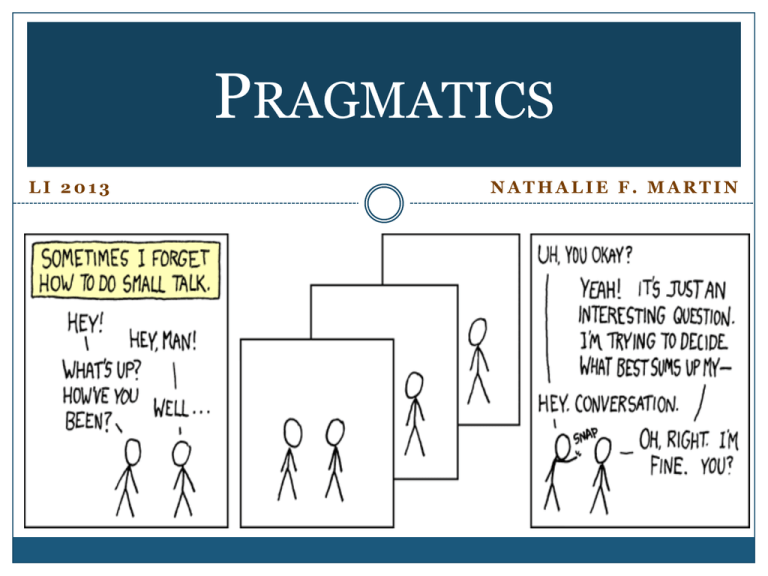
PRAGMATICS LI 2013 NATHALIE F. MARTIN So What Are You Saying? Question: Would you like a burger? Answer 1: No, thank you. Answer 2: I’m on a diet. Answer 3: My husband thinks I’m fat. Answer 4: I’m a vegan. The last three answers do not give a direct answer to the questions, but the answer is implied ! Another Utterance Question: “Would you like to go to the movies?” Answer 1: No, thank you. Answer 2: I don’t like to watch movies. Answer 3: I have homework. Answer 4: I have to walk my dog. So much is implied when we speak, right? SEMANTICS vs PRAGMATICS • Semantics: – meaning abstracted away from users • Pragmatics: – Pragmatics is a systematic way of explaining language use in context. – It seeks to explain aspects of meaning which cannot be found in the plain sense of words or structures, as explained by semantics. Ex: “It is cold in here” (Implicature: request to close the window) Semantics/pragmatics distinction: not always easy to draw PRESUPPOSITIONS What is the speaker possibly trying to say when he says: “John’s brother married that linguist.” What are the speakers Presuppositions: Speaker assumes that the listener knows that John has a brother (and hence not mentioned explicitly) that fact is presupposed common ground or old information (within discourse) ‘marrying’ and/or ‘whom he married’ is new information. PRESUPPOSITIONS 1. The police ordered the minors to stop drinking. The minors were drinking. 2. Please take me out to the ball game again. You have already taken me out to the ball game. 3. Gisèle wants more popcorn. Gisèle has already had popcorn. 4. The captain realized that the ship was in danger. It presupposes that it is true that the boat is sinking. IMPLICATURE “Have you stopped going to the gym?” Statements generate inferences beyond the semantic content of the sentences uttered. Implicature: “Implicature” refers to what is suggested in an utterance, even though not expressed nor strictly implied by the utterance. Tim Hawkins on Marriage http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iK2OakMoW_c Tim Hawkins on Marriage PRESUPPOSITIONS: I really like that dress. It reminds me of my old girlfriend’s. o Presuppositions? He had an old girlfriend. He like one of the dresses she used to wear. IMPLICATURES: Hey honey, have you gained some weight in your rear end? Where did you get those shoes? Implicature? Implicature: I think they’re pretty lame! I’m trying to watch the game! Implicature? DEICTICS [daɪktɪks] Deictic: understanding the meaning of certain words and phrases in an utterance requires contextual information Examples: as we, you, here, there, now, then, this, that, the former, or the latter, etc. Highly context sensitive; make direct reference to the context. 1. 2. 3. Personal deictic (Ex: Personal pronouns, Spatial deictic (Ex: Temporal deictic (Ex: ) ) ) DEICTICS The use of deictics requires knowledge of the setting of the utterance: “Do you like this book?” To answer, the addressee has to know where the speaker is or points/refers to “John is here.” To know where exactly John is, we have to know where the speaker is. DEICTICS The Son is on the right hand. I saw him standing there. Yesterday, all my troubles seemed so far away. These are the days that are of the harvest. After that time, I went to bed. Speech Act Theory JOHN L. AUSTIN Speech Act Theory Speech act theory (John L. Austin) broadly explains that utterances (or speech acts) have three parts or aspects: Locutionary act Illocutionary act Perlocutionary act /loʊkyuʃənɛri/ /ɪləkyuʃənɛri/ /pɜrləkyuʃənɛri/ The key word here is act! We do “things” when we speak! This theory seeks to break down the act of speaking ! John L. Austin's Speech Act Theory Locutionary acts: simply the speech that has taken place Illocutionary force: are the real actions which are performed by the utterance In other words : where saying equals doing. Ex: betting, pleading, declaration, welcoming, warning, etc. Perlocutionary force: are the effects of the utterance on the listener. John L. Austin's Performative Verbs a. I bet you five dollars that the Canadians win. b. I challenge you to a match. c. A dare you to step over this line. d. I move that we adjourn. e. I nominate John for president. f. I promise to improve. g. I resign! Exercise: Performance Sentences? I testify that she met the agent. b. I know that she met the agent. c. I suppose the Yankees will will. d. I bet her $2500 that Clinton would lose the election. e. I dismiss the class. f. I teach the class. g. We promise to leave early. h. We owe Revenue Canada 1, 000, 000. i. I bequeath $ 100, 000 to ABU. j. I swore I didn’t do it. k. I swear I didn’t didn’t do it. a. CONVERSATIONAL MAXIMS H. PAUL GRICE CONVERSATIONAL MAXIMS • Philosopher H. Paul Grice • Cooperative principle in communication: agreement by speaker and listener to cooperate in communication • Listener assumes (unless there is evidence to the contrary) that a speaker will have calculated his/her utterance along a number of principles (maxims): Ex: speaker tells the truth, tries to estimate what the audience knows, etc. CONVERSATIONAL IMPLICATURES • Conversational Maxims: not rules like phonological or syntactic rules, but rather conventions, initial assumptions the speaker starts out with • Maxims can be violated (intentionally or unintentionally) to convey certain implicatures – Speaker A: Why are you in such a bad mood? Aren’t you happy that we’ll all go see the movie about fish? I am sure you’ll like it. – Speaker B: Sure, I’ll love it. – Implicature: I am sure I will hate it. The Cooperative Principles: Maxims of Conversations (Grice, 1989) Name of Maxim Description of Maxim QUANTITY Say neither more nor less than the discourse requires Be relevant RELEVANCE MANNER QUALITY Be brief and orderly; avoid ambiguity and obscurity Do not lie; do not make unsupported claims OBEYED, VIOLATED or FLOUTED • Violating maxims (Grice’s term): speaker secretly breaks them (e.g., intentionally lying) • Flouting (flaʊt): overtly breaking the maxims for some linguistic effect (e.g., sarcasm, irony, entertainment…) To flout is to show disdain, scorn, or contempt; scoff or mock. Distinguishing factor: we must look at a speaker’s intention! Implicature Implicature “Implicature” refers to what is suggested in an utterance, even though not expressed nor strictly implied by the utterance. “Have you stopped going to the gym?” MAXIM OF QUALITY • Try to make your contribution one that is true. – Do not say what you believe is false – Do not say that for which you lack adequate evidence. • Example: – “My children are so well-behaved” –Truth: I am aware (and embarrassed) that they are not well-behaved We would know that it is : - Flouting (certain intonation) - Violating (if a secret lie) MAXIM OF QUANTITY • Make your contribution as informative as is required for the current purposes of the exchange (i.e., no more or less informative). • Example: – Speaker A: What did you have for lunch today? – Speaker B: I had cottage cheese. Flouted or Violated: if the speaker also had pizza and banana split. …Quantity continued • Example: – Situation: Child is allowed only 2 cookies per day. – Parent: Did you eat three cookies today? – Child: No. Flouted or violated: if the child had 4! • Example: – Speaker A: Is your daughter studying at university now? – Speaker B: She is going to classes and buying the books. Implicature: She is not studying much. MAXIM OF RELEVANCE • Make your contributions relevant. Examples: – Question: Are you … ? – In response to anything: Is the Pope Catholic? – Implicature: Your question is so obvious… – Speaker A: Can you tell me the time? – Speaker B: Yes. MAXIM OF RELEVANCE • Examples: – Speaker A: When can you hand your paper in? – Speaker B: It’s a beautiful day. – Implicature: I don’t want to answer your question. – Flouted: answer is not relevant, but hearer will catch the irrelevance; – Or speaker hopes that listener does not catch the irrelevance = violation. MAXIM OF MANNER • Constraints on language use : – Avoid ambiguity – Avoid obscurity – Be brief – Be orderly • Example: – Parent: Who broke the vase? – Son: It was one of your two children. – Implicature: I don’t want to answer this. …Manner continued • Examples: – This is my mother’s husband. – Respected: mother’s husband is not speaker’s father. – Implicature: Person is speaker’s father, but speaker is mad at him – Speaker A: Does your daughter play the piano? – Speaker B: She sits at the piano and pushes the keys and the keys make noise… – Implicature: She doesn’t play well. – This also violates the Maxim of Quantity PRACTIC PROBLEMS Violation of flouting? Secretly or overtly? Which maxim? Quality, quantity, relevance or manner? Example 1: – Question: How long did you watch TV today? – Answer: I watched for three hours. (When in fact it had been 5 hours.) Violated Maxim of Quality Example 2: – I love it when you make me wait for you outside in the cold weather. Flouting Maxim of Quality PRACTIC PROBLEMS Violation of flouting? Secretly or overtly? Which maxim? Quality, quantity, relevance or manner? Flouting/violation Example 3: Maxim of Relevance – Question: When can you pay me back what you owe me? – Answer: I wonder how the Canadians will do this year. Flouting Example 4: Maxim of Manner – Question: Can you pick the kids up at school this afternoon? – Answer: I have piano lessons at 3pm. Example 5: Violated Maxim of Quantity – Not all students came to the party – (When in fact none of the students came) The Art of Not « Really » Telling Lies What did you get me for Christmas? Truth: I got you a « Jars of Clay » CD. Possible answers: Implicature and conversational maxim: Violated or flouted? Did you get me a guitar case? Truth: No Possible answers: Implicature and conversational maxim: Violated or flouted? Silence Can Be Dangerous Context: Nathalie trying to open her heart / David trying to be attentive. Nathalie: I don’t think I pray nearly enough. David: … Nathalie: As a pastor’s wife, I should pray for you more. David: … Nathalie : Maybe I’m not spiritual enough for you. David: … Nathalie (almost in tears) : Do you really think that of me? IMPLICATURE and CONVERSATIONAL MAXIMS Hey honey, have you gained some weight in your rear end? Implicature: You should loose weight. Conversational maxim? Obeyed, violated or flouted:? Where did you get those shoes? Implicature: I think they’re pretty lame! Conversational maxim? Obeyed, violated or flouted? I’m trying to watch the game! Implicature: Please shut up! Conversational maxim? Obeyed, violated or flouted? CONVERSATIONAL MAXIMS Now that you have learned about conversational maxims, what would you say is behind these statements? - What’s up? How’ve you been? - I’m fine. You? Pragmatics Practice exercises Examples: 1. I’m a multimillionaire (Actually, I’m penniless.) Violated maxim: Quality Explanation: The speaker has failed to tell the truth. 2. A: When am I going to get back the money I lent you? B: Boy, it’s hot in here! Violated maxim: Relevance Explanation: B’s answer is not related to A’s question. 3. A: What should I do to get rid of this headache, Doctor? B: Take some medicine. Violated maxim: Quantity Explanation: B has not provided enough information. Exercises 1. Don’t be silly. I love working 80 hours a week Quality with no vacation. 2. A: Excuse me–how much is this screwdriver? B: $9.95. The saw is $39.50, and the power drill there on the table is $89.00. Quantity 3. A: What’s playing at the Rialto tonight? B: A film you haven’t seen. Relevance 4. Dr. Smith received his Ph.D in 1986, his B.A. in 1980, and his M.A. in 1982. Manner Speakers sometimes deliberately violate the rules of ordinary conversation to achieve certain ends Example: A: Would you like to go out with Andrea? B: Is the Pope Catholic? Violated maxim: Relevance Motivation: B is being humorous. By replying with a question whose answer is obvious, he is implying that the answer to A’s question is equally obvious: Yes! Exercises: 1. A: I’ll pay you back in full next week, I promise. B: Sure, and pigs will fly and fish will sing. Violated maxim: Relevance Implicature: B’s response implies sarcastically that he does not believe A. 2. A: What are the three most important things in real estate? B: Location, location, and location. Violated maxim: Quantity Implicature: To emphasize the overwhelming importance of location 3. A: So tell me, do you like what I did to my hair? B: Er…what’s on TV tonight? Violated maxim: Relevance Implicature: B does not like A’s hairstyle, so he changed the subject. 4. A: How can I develop a great body like yours? B: Choose your parents carefully. Violated maxim: Quality Implicature: Indirectly saying that it is impossible, because it’s all in the genes









