An Internet Architecture for Efficient, Accurate, and
advertisement

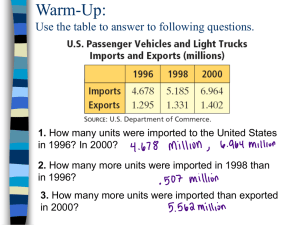
An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Hongbin Luo, Zhe Chen, Jianbo Cui, Hongke Zhang Beijing Jiaotong University The 17th IEEE Global Internet Symposium April 28, 2014, Toronto Roadmap 1 2 Motivation 2 Requirements and Implications 3 A Possible Internet Architecture 4 Performance Evaluation 5 Conclusion and Future Work An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 1. Motivation What is a traffic matrix (TM)? A TM describes the traffic volume (packets/ bytes) between an ingress and egress (IE) node pair in a network. The traffic matrices are critical inputs to many aspects of network functions such as traffic engineering, capacity provisioning, and anomaly detection. Therefore, network operators desire to obtain accurate evaluations of the traffic matrices of their networks. Under the current Internet architecture, however, it is extremely challenging to accurately, efficiently, and timely measure the TM between IE node pairs. 3 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 1. Motivation Why is it extremely challenging? First, the TM in many networks is not directly observable. Instead, it can only be estimated through link load measurements. Second, the collected large amount of per flow/packet information has to be transported to a centralized location for correlation. But Correlation: is time-consuming: so, TM estimation cannot be timely; relies on high-performance servers: TM is not efficient; relies on inputs from different nodes that have different observations: TM is not accurate. Third, the TM estimation has to be done at very high speed since an Internet service provider (ISP) may forward data packets at a speed of over one Terabits per second (Tbps). 4 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 1. Motivation In addition, the current Internet faces other serious issues (such as poor security and scalability) that cannot be remedied by incremental changes. Therefore, in recent years there are increasing efforts in developing “clean-slate” redesigns of the Internet architecture, aiming at rectifying one or more of these problems through non-incremental changes. 5 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 1. Motivation So, the problem is: Could we design a future Internet architecture that makes it easy for network operators to accurately estimate the traffic matrices of their networks in an efficient and timely manner? 6 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University Roadmap 1 7 Motivation 2 Requirements and Implications 3 A Possible Internet Architecture 4 Performance Evaluation 5 Conclusion and Future Work An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 2. Requirements and Implications Requirements for TM estimation ① Accurate estimation: Novel technologies such as OpenFlow requires that the estimated traffic matrices are accurate since if otherwise, the controller may make wrong decisions when computing paths for flows. ② Timely estimation: Network managers can make the best use of network resources based on its state-ofthe-art network status only when the traffic matrices are estimated in real time. ③ efficient estimation: We desire that the traffic estimation is not dependent on computers with strong computation capability. 8 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 2. Requirements and Implications Implications of requirements ① Accurate estimation: Every byte/packet should be accounted. It is better to use the flow information observed at the ingress node to estimate the TM. ② Timely estimation: TM estimation should be performed during the packet forwarding process. ③ efficient estimation: TM estimation should be performed in a distributed manner, without requiring a centralized node for correlation. 9 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices The future Internet should make it possible for an ingress node to estimate the traffic matrices from it to the rest nodes during its packet forwarding process. Beijing Jiaotong University Roadmap 1 10 Motivation 2 Requirements and Implications 3 A Possible Internet Architecture 4 Performance Evaluation 5 Conclusion and Future Work An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 3. A Possible Internet Architecture We have proposed a future Internet architecture called CoLoR, whose basic idea is to couple service location with inter-domain routing, but to decouple them from forwarding. We have also built a prototype and demonstrate that CoLoR satisfies many requirements of the future Internet including being information-centric, encouraging innovation, and providing efficient support for mobility, multicast, multi-homing, and middle-boxes. Below we briefly introduce the basic ideas of CoLoR. 11 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 3. A Possible Internet Architecture Basic ideas: 12 I. Using four namespaces: Service identifiers (SIDs): used to name contents. They are flat, self-certifying. Node identifiers (NIDs): used to identify the identity of network nodes. They are flat, selfcertifying and 128 bits long. Intra-domain routing locators: used for intradomain routing. Every domain can choose its preferred intra-domain routing architecture and routing locators. Path identifiers (PIDs): used for inter-domain routing. Two domains can negotiate a set of PIDs, as long as the PIDs are unique in each domain. PIDs are not advertised throughout the Internet, but are Beijing Jiaotong University An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices local to the two domains. 3. A Possible Internet Architecture Basic ideas: II. Using name-based routing for service location. III.Inter-domain routing for data packet forwarding is determined during the service location process. IV. Intra-domain routing may or may not be determined during the service location process. We leave this for domains’ local policy. V. End-to-end data packet forwarding is based on loose source routing. While some of the ideas are borrowed from existing literature, we believe that: one can see further by standing on the shoulders of giants. 13 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 3. A Possible Internet Architecture Network topology D6 R7 R6 R8 R5 D3 D5 R2 R4 R1 D1 14 R10 R9 R11 R2 D2 As the current Internet, CoLoR assumes that the future Internet will still centered around domains. R12 D4 Domains have the AS-level provider/ customer/peer relationship. An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 3. A Possible Internet Architecture Intra-domain routing D6 Domain 3 uses MPLS for intra-domain routing. R7 R6 R8 Domain 1 uses IPv6 for intradomain routing. Domain 4 uses OpenFlow for intra-domain routing. R5 D3 D5 R2 R4 R1 D1 R10 R9 R11 R2 D2 R12 D4 A domain can freely choose its preferred intra-domain routing architecture, without considering other domains. 15 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 3. A Possible Internet Architecture Inter-domain routing P7 R4 D2 P6 R2 D1 P5 R5 D6 D6 R7 P5 P1 R6 R8 R5 D3 D5 R2 R4 P6 R1 D1 R10 R9 P7 R11 R2 D2 R12 P4 Interdomain routing relies on paths negotiate d by two neighbor domains. D4 Nodes in a domain maintains the end point of every path that connects the domain to a neighboring domain. 16 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 3. A Possible Internet Architecture Service registration RM6 Every domain has a logical resource manager. D6 R7 P5 The service registration process is similar to that in DONA. R6 R8 RM5 R5 D3 RM3 D5 R2 Content sources register SIDs to their local RMs, which registers the SID to their peers or provider RMs. 17 P1 R4 P6 R1 RM1 D1 R2 R10 R9 P7 R11 R12 RM2 D2 A An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices P4 D4 RM4 Beijing Jiaotong University 3. A Possible Internet Architecture Service location and inter-domain routing RM6 D6 R7 Users send requests to their local RMs when they want a content represented by an SID. P5 (iv) R6 R8 RM5 RM3 D5 R2 RMs forward requests to either the closest copy of the content, or their provider RMs. P1 R5 D3 P6 (v) RM1 D1 R2 R10 R9 R4 R1 (iii) P7 R11 R12 RM2 D2 A (ii) P4 (i) D4 C RM4 (vi) 18 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 3. A Possible Internet Architecture Service location and routing (vi) SID1 C P4 P1 P5 P6 (v) SID1 C P4 P1 P5 P6 RM6 D6 R7 SID1 C P4 P1 (iii) SID1 C P4 P1 (ii) SID1 C P4 (iv) (i) SID1 (iv) R6 D3 R8 RM5 RM3 D5 R2 P6 (v) RM1 D1 R2 R10 R9 R4 R1 (iii) P1 R5 C Every time a RM forwards a request to a neighboring RM, it appends the path between the two domains onto the request. 19 P5 P5 P7 R11 R12 RM2 D2 A (ii) P4 (i) D4 C RM4 (vi) An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 3. A Possible Internet Architecture Packet forwarding (d) Intra-domain packet forwarding is based on the routing mechanism of each domain. Inter-domain packet forwarding is based on PIDs that are determined during the service location process. R1 D1 RM1 (a) A (a) IP1 IP2 (b) R5 IP1 D3 IP2 (c) R2 P6 P6 P5 P5 P1 RM3 R4 P4 C SID1 data (b) P6 P5 P1 P4 C SID1 data (c) MPLS LSP1 P5 P1 P4 C SID1 data P5 P1 P4 C SID1 data (d) Every time a border router receives an incoming packet, it strips out the outer most PID in the packet header. 20 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 3. A Possible Internet Architecture TM estimation in CoLoR P5 R1 D1 R5 IP1 RM1 D3 RM3 A P6 IP2 P5 P1 P4 C R2 SID1 R4 data P7 R4 D2 P6 R2 D1 P5 R5 D6 Every time an ingress border router receives a packet, it reads the outermost PID, and looks up its inter-domain routing table. This way, it knows the egress node of the packet. Accordingly, it simply adds the bytes of the packet onto the TM from the IR to the ER. 21 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University Roadmap 1 22 Motivation 2 Requirements and Implications 3 A Possible Internet Architecture 4 Performance Evaluation 5 Conclusion and Future Work An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 4. Performance evaluation We have built a prototype to show the accuracy of TM estimation in CoLoR and that in OpenFlow. D1 PID1 Domain 5 A B PID2 D2 RM/ controller D3 PID2 C D PID4 D4 We estimate the traffic matrices from node A to the other nodes B, C, and D, assuming that node D1 is the source and nodes D2, D3, and D4 are the destinations of packets. (c) the network topology of the prototype While the results are similar, we only report the estimated TM from node A to node C. 23 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 4. Performance evaluation The estimated TM from node A to node C The traffic matrix from node A to node C 4500 4000 The number of bytes 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 The real traffic matrix The traffic matrix esimated with CoLoR The traffic matrix estimated with OpenTM 500 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 time (second) 700 800 900 1000 Both CoLoR and OpenTM can accurately estimate the traffic matrices. the duration between two consecutive polls in OpenFlow is shorter than the default value for a switch to remove a flow entry from its flow table. 24 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 4. Performance evaluation The estimated TM from node A to node C The traffic matrix from node A to node C 4500 OpenTM cannot accurately estimate the traffic matrices. But CoLoR can. 4000 The number of bytes 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 The real traffic matrix the traffic matrix estimated with CoLoR the traffic matrix estimated with OpenTM 1000 500 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 time (seconds) 700 800 900 1000 the duration between two consecutive polls in OpenFlow is larger than the default value for a switch to remove a flow entry from its flow table. 25 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 6. Conclusions and Future Work Conclusions we present the requirements for TM estimation and the corresponding implications on the future Internet architecture. we present a future Internet architecture that makes it easy to accurately, efficiently, and timely estimate traffic matrices. we describe how to estimate traffic matrices of a network under the proposed Internet architecture. we present numerical results to demonstrate the performance of the proposed Internet architecture in estimating traffic matrix. 26 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University 6. Conclusions and Future Work Future Work While we have shown that CoLoR makes it possible to accurately, timely and efficiently estimate traffic matrices, an important question needs to be answered. How an ISP could benefit from accurate, timely and efficient estimation of traffic matrices? We will investigate this question in the future. 27 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University Thanks! 28 An Approach for Efficient, Accurate, and Timely Estimation of Traffic Matrices Beijing Jiaotong University