Lecture Notes
advertisement

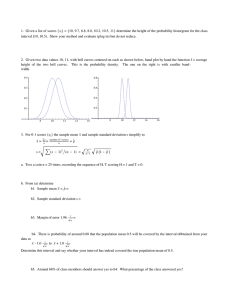
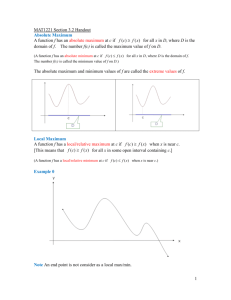
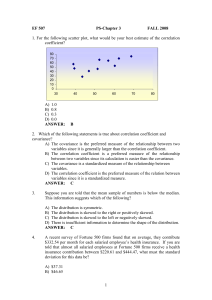
ME 322: Instrumentation Lecture 3 January 27, 2012 Professor Miles Greiner Normal Distribution • Population size N • Sample size n < N Normal Distribution • The probability the next sample is within: Lab 2: Cost Estimates • What cost is greater than 90% of all current and future measurements? Example Problem: based of lab Assume I measure the Quad and got a cost estimate of $963 and I know that the measurement process has led to a cost standard deviation of $323. How much money should I add to be 90% sure that I’ve budgeted enough? Uncertainty Take n samples of a population (n < N) Expect: 1) & S from different samples will not be equal. 2) as n increases, expect variation between samples to be smaller. Uncertainty un the population mean confidence interval. Confidence Level • Confidence Level P – Probability that the true µ is within the confidence interval. • How to estimate δ for a given P If N >30 Confidence Level If N >30 use student t Example 6.14 a We would like to determine the confidence interval of the mean of a batch of resistors made using a certain process. Based on 36 readings, the average resistance is 25 Ω and the sample standard deviation is 0.5 Ω. Example 6.14 a Example 6.16 A manufacture of VCR systems would like to estimate the mean failure time of a VCR brand with 95% confidence. Six systems are tested to failure, and the following data )in ours of playing time) are obtained: 1250, 1320, 1542, 1464, 1275, and 1383. If a 95% confidence interval of ± 120 h was found how many more must be tested to obtain a confidence interval of ± 50 h. Example 6.16 Example 6.16 Correlation Coefficient Correlation Coefficient