ppt Four Christian Views of Evolution
advertisement

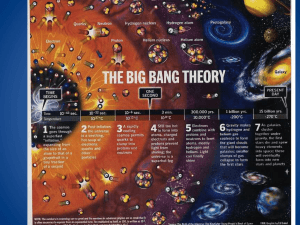
Science and Evolution: Four Christian Views JOHN OAKES, PhD Proyecto Esdras May 8, 2010 2010 ICEC Concordia University, Irvine CA June 11-13 International Christian Evidences Conference Featured Speaker: John Clayton www.evidenceforchristianity. org joakes01@san.rr.com Kevin Anderson Public Forum: Four Christian Views of Evolution John Clayton June 12 7:00 $12/$10 Students 10 Goodyear, Irvine CA Young Earth Creationism Progressive Creationism John Oakes Denis Lamoreax Intelligent Design Evolutionary Creationism Our Outline Science and Religion: The Limits of Science The History of Science and Christianity The Age of the Universe and the Age of the Earth Genesis 1 and Creation Evolution: The Evidence Four Christian Views of Evolution Science The use of experiment to test theories about the laws of nature. Science is about things which can be measured. Science Scientific knowledge is quantitative Scientific knowledge changes and improves over time Scientific knowledge is neither true nor false, but rather consistent with the observations and consistent with prior knowledge Religion Religion is a belief in something The belief is not necessarily substantiated by physical or material evidence Religious knowledge obtained through holy writings, authority, revelations Religious believers have faith or trust in such knowledge Religion Religious knowledge is qualitative not quantitative. Religious knowledge is not gotten through measurement In religion knowledge is taken as either true or false. Religious knowledge is neither progressive, nor tentative. Questions Science Can Answer When? What? Where? How many? By what means? Questions Science Cannot Answer: (That Religion Does Answer) Why am I here? Is that the right thing to do? How valuable am I? Does God exist? Does God act (theism)? Will that God respond if I pray? Do supernatural events (miracles) happen? In other words, Religion answers the questions people actually care about! A statement a scientist should not make (if he or she is well trained and is not manipulating you): Evolution is true. The Big Bang happened. Better statements: The theory of evolution is by far the best model we have to explain both the fossil evidence and the genetic evidence with regard to the origin of all species. The Big Bang model is in dramatic agreement will all known facts about the origin and history of the universe. Science seeks consistency, not “truth.” What is the simplest and most consistent explanation of the observation. Conclusions about Science and Religion Religion and science ask different kinds of questions and define words differently Religion and science are two very different world views but at times they address the identical information area If Christianity is true, then the Bible should not contradict what we know from science. Unanswered questions which seem to relate to science Consciousness (what is consciousness and why are we conscious?) Origins of life Origin of the universe. Why is there anything (as opposed to nothing) Origin of Species* (this is our topic) Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) “The Bible was written to tell us how to go to heaven, not how the heavens go” “In discussions of physical problems we ought to begin not from the authority of scriptural passages, but from the sense-experiences and necessary demonstrations.” Galileo on Revelation “For the Holy Bible and the phenomena of nature proceed alike from the divine Word, the former as the dictate of the Holy Spirit and the latter as the observant executor of God’s commands.” Is there such a thing as Natural Revelation/General Revelation? (as opposed to special revelation) In other words, can we gather genuine knowledge of God from looking at his creation? Sir Isaac Newton (1642-1727) “The Mechanical Universe” Introduced idea of deism (an uninvolved God) LaPlace (1749-1827) About God: “I have no need of that hypothesis” “It is mere rubbish to think at this point of the origin of life. One might as well think of the origin of matter.” Charles Darwin Might the origin if species be deistic—governed by natural processes? The Conservative Christian Reaction Scopes “monkey trial” 1925 Clarence Darrow and William Jennings Bryan 1940’s and afterward: Young Earth Creationism Movement Very Bad Science! Can Science and Religion peacefully coexist? The Language of God Head of Genome Project Head of National Institutes of Health (NIH) Reasons Collins believes in God 1. There is something instead of nothing. 2. The unreasonable effectiveness of mathematics. 3. The Big Bang. 4. Nature does not solve the problem of why. 5. Fine tuning of the universe. The “Goldilocks Paradox.” 6. The existence of moral law. 7. Let me add: The obvious inspiration of the Bible. The Age of the Universe and the Age of the Earth Bishop Ussher 1640: The universe was created on Sunday October 23, 4004 BC Cosmic Speedometer When a galaxy is receding, light waves travelling to us are red-shifted Hubble measured the spectrum of these galaxies and found the spectral lines to be red-shifted The faster the recession, the greater the red-shift Galaxies: islands of stars making up the universe Hubble constant graph: Distance vs. speed of regression Expansion of the Universe … ‘winding’ backwards, the universe must have had a beginning Image of Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation From COBE satellite red = slightly warmer The “smoking gun” of the Big Bang Tests of the Big Bang Theory Expansion of the universe Cosmic microwave background Relative abundances of hydrogen, deuterium, helium and lithium Obtaining the Age of the Universe Extrapolate the current expansion rate (Hubble constant) back to the Big Bang Look for the oldest stars (in globular clusters) 13.5 billion years 13.0 billion years old Best current estimate is 13.4 ± 0.4 billion years M10 Globular Cluster How Old is the Earth? James Hutton, 1787 Uniformitarianism “No vestige of a beginning, no concept of an end.” Deep Time Index fossils give the relative age of a rock Radiometric Dating Techniques mother/daughter isotope pair half-life U238 → Pb206 4.5 billion years U235 → Pb207 704 million years K40 → Ar40 1.25 billion years Th232 → Pb208 14.8 billion years Genesis Chapter One: Creation Young Earth Theory Earth is young and science supports this conclusion. Earth is young because God created it “with an appearance of age.” Day/Age Theory Gap Theory A huge “gap” of time between Genesis 1:1 and 1:2 Literary Theory It’s all just a myth Each view has its problems A Quick Summary of Genesis One: a. God pre-existed the universe b. God created the universe: “Let there be light” c. God created the earth d. God created life e. Last of all, God created mankind A More Detailed Summary of Genesis One From the Viewpoint of an Observer on the Earth: a. The earth created and is spinning: night and day. Day 1 b. Water covers earth, Very thick atmosphere forms. Day 2 c. The earth cools, land appears out of the water. Day 3 d. Life appears on the earth. Day 3 e. (Photosynthetic life dramatically changes the chemistry of the atmosphere from reducing to oxidizing.) f. Finally, the heavenly objects appeared in the sky Day 4 g. More advanced life forms; first in the water, later on the land Day 5 h. Even more advanced life forms. Last of all human beings Day 6 Where is the scientific error in this? Is Genesis 1:1 a Myth? Yes! It is a true myth. A myth is a simplified story, given to explain the gods (or God) to common people. Is the Metaphorical Day a Reasonable Interpretation? Pre-Science Theologians Who Said Yes. Philo 1st century Origen early 3rd century Augustine early 5th century Thomas Aquinas 13th century Evolution and the Bible What does the Bible say? God created all life in its various forms, but how did he do this? Remember, the Bible is not a science book. What does the physical evidence say? Fossil evidence Genetic/DNA evidence Is there “Irreducible Complexity?” What about human evolution? Finches discovered And drawn by Charles Darwin Evidence of Evolution? Evolution of whales over time? Evolution of horses? Morphological Evidence of Common Descent Human chromosome #2 and Great Ape chromosome #2p, 2q: evidence for common descent. More Genetic Evidence for Common Descent Pseudogenes Vitamin C Pseudogene in great apes and humans Retroposons, SINEs (short interspersed elements), etc. Viral insertions Bottom line, genetic evidence, at least in the big picture, strongly supports common descent. table 1 Chimpanzee Gene sequence that codes for protein Random DNA segment between genes 100% 98% Dog 99% 52% Mouse 99% 40% Chicken 75% 4% Fruitfly 60% ~0% Roundworm 35% ~0% Typical random point mutation rates are about 1x10-5 – 1x10-7 mutations/generation. 5 million years = 250,000 generations. Sufficient for random mutations to explain the change without the intervention of a guiding hand? But……….. The Cambrian Explosion “Punctuated Equilibrium?” Theistic Evolution Fossils from creatures which appeared in the “Cambrian Explosion” Life in the Cambrian Some Tentative Conclusions Evolution has happened. Microevolution has been observed. Fossil evidence strongly supports the idea of change over time, but that change often happens in surprisingly sudden bursts. The Cambrian explosion raises real questions. Genetic evidence gives rather strong support to the idea of common descent. Like it or not, this is true of humans as well. Statistical and other arguments give support for evolution being theistic, rather than deistic, but this is not a scientific argument. God invented evolution; let us give him credit for a great idea. Four Christian Views of Evolution Young Earth Creationism Scientific Young Earth Theological Young Earth Intelligent Design Theistic Evolution Evolutionary Creationism Scientific Young Earth Creationism A scientific hypothesis that the earth is young and, for all practical purposes, evolution has not happened. The scientific young earth view rejects cosmology, geology and evolution. In effect, it rejects science altogether. It requires rejecting science and general revelation. (Galileo and geocentrism) This is not scientific. It is anti-scientific. Why? There is literally no evidence the earth is young. Theological Young Earth Creationism A purely theological hypothesis that God created the earth “with an appearance of age.” Rejects cosmology, geology and evolution, but not science in general because the rejection is theological, not scientific. This view is NOT anti-scientific. How old was the wine Jesus created? Rejects general revelation? As a theological view, it is possible, but problematic. Is God tricking us? Young Earth Summary Scientific Young Earth Creationism is VERY bad science. Theological Young Earth Creationism is not bad science, but it raises difficult theological questions. Intelligent Design (ID)/Progressive Creationism Accepts Cosmology Accepts Geology Rejects Evolution? Rejects macroevolution. Rejects common descent. Skeptical of evolution. Argues for “irreducible complexity.” Uses God-of-the-gaps arguments Note: God-of-the-gaps arguments are NOT scientific (even if they are true!). Tends to confuse theological issues with scientific ones. Carries baggage from predestination/Calvinism? I agree with the theology of ID, but am hesitant about the science of ID. There is a sense in which it is not scientific. Theistic Evolution Accepts cosmology, geology and evolution as scientific hypothesis. Accepts common descent as a good scientific (note, scientific) hypothesis. Sees both free will and God’s sovereign will in history, in individuals and in nature. God works through evolution, but he directs the path, either by subtly directing it or by dramatic intervention. Although some scientific evidence and even statistical arguments support this conclusion it is a purely theological hypothesis. Theistic Evolution (cont.) God’s relationship with history is theistic, but with free will. God’s relationship with us is theistic, but with free will. God’s relationship with nature is theistic, but with free will. God gives us free will, in that choosing to reject God is not completely unreasonable. God uses nature to support our faith but not to demand it. Although the evidence supports evolution of human beings, Adam and Eve were special creations. John the Baptist: Out of these stones, God can raise up children of Abraham. The fish Jesus created had retroposons, pseudogenes and viral insertions. Evolutionary Creationism Accepts cosmology, geology and evolution. Accepts common descent as both a scientific and a theological hypothesis. Evolution was a purely natural, undirected process. God is the designer, who, in his incredible wisdom and foreknowledge, set the universe and evolution in motion. Hypothesizes a God-of-no-gaps. If God had to intervene in the free process of evolution, that would be to lessen God—a God who had to correct his mistakes. Evolutionary Creationism Adam and Eve are not real persons. They are symbolic. The human soul and spirit evolved, along with our intelligence and other abilities. Accepts the literary view of Genesis 1-3. The Bible has incorrect science because God “accommodates” our primitive understanding. God’s relationship with history is theistic, but with free will. God’s relationship with us is theistic, but with free will. God’s relationship with nature is deistic. God does not intervene. Good science, but questionable theology. Summary There is no view without any problems, either logical, scientific or theological. Obviously, I prefer the position described as Theological Evolution, but I may be wrong. This is not a salvation issue. We should be tolerant of divergent views on unimportant doctrines. (Titus 3:9) All agree that we are “fearfully and wonderfully made.” that all God’s works are wonderful (Psalm 139:14)