RCM Methods and Procedures
advertisement

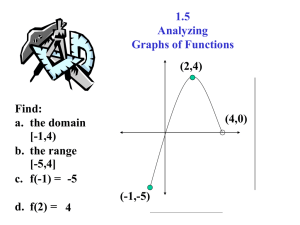
The P-F Interval According to NAVAIR 00-25-403 RCM Guideline NAVAIR P-F Interval The following describes NAVAIR [1] methods based on the classic CBM: 1. Determining the P-F Interval, and 2. Determining the Inspection Interval [1] NAVAIR 00-25-403 RCM Guideline OMDEC Inc Performance Session 4 Slide Number: 2 NAVAIR Methods for determining PF intervals: Laboratory testing (in conjunction with accelerated life testing (ALT)), Analytical methods Evaluation of in-service data - AE (Age Exploration), and engineering judgement based on inputs from operators and maintainer, (i.e. Classic RCM method) and Knowledge of the item’s design and of applications consisting of similar components. Note: NAVAIR does not provide details about the above methods in its 00-25-403 guide. OMDEC Inc Performance Session 4 Slide Number: 3 PF used only for starting Inspection Interval The PM task interval is determined by using some fraction of the PF interval. This fraction will depend on the consequences of failure and the effectiveness of the proposed task. I = PF/n Where: I = Inspection interval PF = potential failure to functional failure interval n = number of inspections in the PF interval OMDEC Inc Performance Session 4 Slide Number: 4 Determining n n = ln (Pacc) / ln (1-θ) Where: θ = Probability of detecting a potential failure with one occurrence of the proposed On Condition task, assuming the potential failure exists Pacc = Acceptable probability of failure Note: θ can only be determined practically in a LRCM program that tracks CBM hits and misses. OMDEC Inc Performance Session 4 Slide Number: 5 Error in the 00-25-403 Guide The next slide illustrates an error by NAVAIR regarding the P-F interval. It is a commonly held misconception … ON CONDITION TASK Task Development Functional Failure: A Functional Capability B POTENTIAL FAILURE DEFINED POTENTIAL FAILURE CONDITION DEFINED FUNCTIONAL FAILURE CONDITION C OPERATING AGE I I I FUNCTIONAL FAILURE Inspection Interval TASK INTERVAL PRACTICAL? PF Interval OMDEC Inc Performance Session 4 Slide Number: 7 ON CONDITION TASK Implies that functional capability will drop off as the system Task Development Functional Failure: approaches a potential failure state (point B). In fact, in most cases, especially in complex systems, the equipment's functions remain fully operational at the potential failure point A Functional Capability B POTENTIAL FAILURE DEFINED POTENTIAL FAILURE CONDITION DEFINED FUNCTIONAL FAILURE CONDITION C OPERATING AGE I I I FUNCTIONAL FAILURE Inspection Interval TASK INTERVAL PRACTICAL? PF Interval OMDEC Inc Performance Session 4 Slide Number: 8 ON CONDITION TASK Task Development Functional Failure: In the original on-condition model by Nowlan and Heap, and in Moubray's book "RCM II", the vertical axis is correctly labelled "Condition“ or “Failure Resistence” A Functional Capability B POTENTIAL FAILURE Condition DEFINED POTENTIAL FAILURE CONDITION DEFINED FUNCTIONAL FAILURE CONDITION C OPERATING AGE I I I FUNCTIONAL FAILURE Inspection Interval TASK INTERVAL PRACTICAL? PF Interval OMDEC Inc Performance Session 4 Slide Number: 9 Conclusion The P-F Interval is a good, but subjective, first approximation developed during an RCM analysis in the absence of data based on the recollection by the analysts of potential and functional failures that have occurred. Age exploration techniques (e.g. EXAKT and LRCM) during the In-Service (IS) phase of operation should be used to confirm inspection frequencies and refine predictive models for the continuous improvement in Remaining Useful Life Estimation (RULE). OMDEC Inc Performance Session 4 Slide Number: 10