2(b+c) Alcohol Chemistry
advertisement

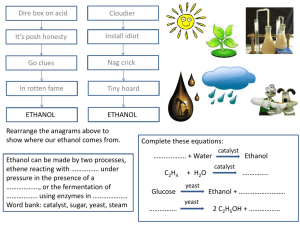
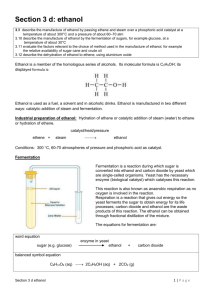
Alcohol Chemistry Uses: Alcoholic drinks (ethanol) Solvents Fuels Introduction Are a family of organic compounds containing the –OH (hydroxyl) functional group Draw the FSF and write molecular formulae for: 1. Methanol 2. 2-methylpropan-1-ol 3. 2-methylbutan-2-ol Naming practice H H C H H H H H H H H C C C C C C C H H O H C HH H H H H H C H H 3 - ethyl, 4 - methylheptan - 4 - ol A homologous series A family of compounds with the same general formula, similar chemical properties and a graduation in physical properties ALCOHOL: Any compound containing the -OH group ALKanols: Subset based on alkanes Alcohol H The chemical name for alcohol is ETHANOL: Ethanol is NOT a carbohydrate. Alcoholic drinks are made by fermenting sugar (glucose): H C H H C OH H Drink Carbohydrate % alcohol Beer Barley 3-6 Cider Apples 7 – 10 Wine Grapes 10 – 14 Whisky Barley 35 – 45 Vodka Potatoes 35 - 45 Fermentation Alcohol is made from sugar The process is called FERMENTATION: Glucose Alcohol + Carbon dioxide An ENZYME is needed to make this reaction happen - Zymase YEAST (a living organism) contains the enzyme which is needed Making Ethanol (C6H10O5)n starch C6H12O6 glucose Enzymes released during germination Enzyme zymase in yeast C2H5OH + CO2 ethanol Enzyme maltase in yeast C12H22O11 maltose FERMENTATION Practical Burning £5 note Practical demo Alcohol Rocket Collect a copy of “That’s the Limit” booklet That’s the Limit 1 How much beer contains the equivalent alcohol to one glass of wine? How much beer contains the equivalent alcohol to a single whiskey? Pint for pint, which contains more alcohol, beer or cider? What are the recommended weekly units of drink for men and women? Which organ is chiefly responsible for removing alcohol from the body? List 3 factors which affect how you are affected by alcohol. That’s the Limit 2 How long would it take your body to remove the alcohol consumed by 4 pints of beer? What is the legal driving limit in terms of units of alcohol? If you started drinking at 8pm, and consumed on average 2 pints every hour until 12pm, how long would it take you to be below the legal limit for driving? Explain what causes a hang-over. State 3 long-term effects of excessive alcohol consumption. Alcoholic Drinks Drink Carbohydrate % alcohol Beer Barley 3-6 Cider Apples 7 – 10 Wine Grapes 10 – 14 Whisky Barley 35 – 45 Vodka Potatoes 35 - 45 •At alcohol concentrations above 15 %, the yeast are poisoned and the enzymes do not work. •Fermentation therefore stops. Distillation To produce drinks with a high alcohol concentration, DISTILLATION must be carried out. cold water out mixture from fermentation cold water in 'anti-bumping' glass beads distilled ethanol Alternative method? Fermentation is too expensive to produce ethanol on an industrial scale Catalytic hydration of ethene is method used Ethene + water C2H4 + H2O H3PO4 catalyst 300oC & 70 atmospheres Ethanol C2H5OH H H H H C H C H H C OH + H C H OH H The reverse process mineral wool soaked in ethanol aluminium oxide catalyst rolled in mineral wool ethene This is called DEHYDRATION Chemistry of dehydration + Ethanol water Ethene H H H O H C C C C H H H H H H H H C C C C H H H H H NAME? + H H H H C C C C H H H H H NAME? H H O Practice Draw the FSF for the product(s) of hydration of the following alkenes: 3-methylpent-1-ene 2-methylbut-1-ene 2-methylbut-2-ene Which of the following compounds will produce isomers on dehydration? Hexan-3-ol Heptan-3-ol 2-methylbutan-1-ol