Stoichiometry Lecture Notes
advertisement

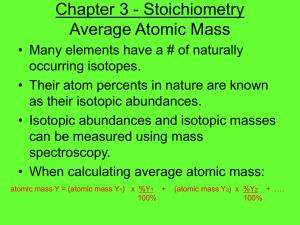
Chapter 3 - Stoichiometry Average Atomic Mass • Many elements have a # of naturally occurring isotopes. • Their atom percents in nature are known as their isotopic abundances. • Isotopic abundances and isotopic masses can be measured using mass spectroscopy. • When calculating average atomic mass: atomic mass Y = (atomic mass Y1) x %Y1 + 100% (atomic mass Y2) x %Y2 + …. 100% Determining Average Atomic Mass • Silver (Ag; Z = 47) has 46 known isotopes, but only two occur naturally, 107Ag and 109Ag. Given the following mass spectrometric data, calculate the atomic mass of Ag: • Atomic mass of Ag = 55.42 amu + 52.45 amu = 107.87 amu Avg. Atomic Mass Example Problem • Bromine consists of two isotopes: Bromine-79 (78.92 amu) and Bromine-81 (80.92 amu). What is the abundance of the heavier isotope? • 79.90 = 78.92 (100-x) + 80.92 (x) 100 100 or • 79.90 = .7892 (100-x) + .8092 (x) x = 49% of Br-81 The Mole • The mole represents 6.022 x 1023 items – Atoms, formula units, molecules • The MM, in grams/mole, is equal to the sum of the masses of the atoms in the formula. – i.e. MM of H2O = ? • Mole-gram conversions: m = MM x n • Mole-liters conversions: 22.4 L = 1 mole – This may only be used at STP Information Contained in the Chemical Formula of Glucose, C6H12O6 (MM = 180.16 g/mol) Mole Conversions - Example • Acetylsalicylic acid, C9H8O4, is the active ingredient in aspirin. a) What is the mass (g) of 0.509 mol of acetylsalicylic acid? b) What is the mass of H in this sample? c) How many moles of acetylsalicylic acid are in a onegram sample of aspirin that contains 91.6% by mass of acetylsalicylic acid? • a) 91.7 g C9H8O4 b) 4.10g H c) 5.08 x 10-3 mol Percent Composition • This allows us to determine the mass percents of the elements present in a compound. • Calculate the % composition of all elements in water: – Hydrogen - 11.19% – Oxygen - 88.81% % Composition Example • Metallic iron is most often extracted from hematite ore, which consists of iron (III) oxide mixed with impurities such as silicon dioxide. a) What are the mass percents of iron and oxygen in iron (III) oxide? b) How many grams of iron can be extracted from one kilogram of iron (III) oxide? c) How many metric tons of hematite ore, 66.4% iron (III) oxide, must be processed to produce one kilogram of iron? • (a)69.94% Fe, 30.06% O (b) 699.4g Fe (c)2.14 x 10-3 metric tons % Composition Example 2 • Hexachlorophene, a compound made up of atoms of carbon, hydrogen, chlorine, and oxygen. Combustion of a 1.000gsample yields 1.407g of carbon dioxide, 0.134 g of water, & 0.523 g of chlorine gas. What are the mass percents of all the elements that make up hexachlorophene? – 38.40% C, 1.50% H, 52.3% Cl, 7.80% O Empirical Formula • The empirical formula of a compound is the simplest ratio possible for 2 or more elements. – CH4 C2H6 – CH5N C2H10N2 – To solve for the empirical formula you are generally given the %composition or masses of the elements in the compound from combustion analysis. Combustion Analysis Empirical Formula - Example • Determine the empirical formula for a compound that gives the following percentages on analysis: • 71.65% Cl, 24.27% C, 4.07% H • ClCH2 Steps to an Empirical Formula Molecular Formula • This is basically multiples of the empirical. • You need to know the molar mass of the sample and its empirical formula to find. • In the last example we determined the empirical formula to be ClCH2, what if you were told this sample had a molar mass of 98.96 g/mol, how would you find the molecular formula? • Cl2C2H4 Empirical & Molecular Formula Example 1 • A white powder is analyzed and found to contain 43.64% phosphorous and 56.36% oxygen by mass. The compound has a molar mass of 283.88 g/mol. What are the compounds empirical and molecular formulas? • Empirical = P2O5 Molecular = P4O10 Empirical & Molecular Formula Example 2 • The compound that gives vinegar a sour taste is acetic acid, which contains the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. – A)Using combustion analysis, if a 5.000 g sample of acetic acid yields 7.33 g of carbon dioxide and 3.00 g of water, determine the empirical formula. – B) The MM of acetic acid, as determined with a mass spectrometer, is 60 g/mol. Determine the molecular formula for acetic acid. Chemical Equations • Reactants & products in a chemical equations represent what is happening in a chemical reaction. • Coefficients are used to balance these equations. • States of matter are not required on the AP Chemistry exam however any aqueous solution must be written as ions in aqueous solution. Balancing Chemical Equations » (a) A characteristic reaction of Group 1A(1) elements: chunks of sodium react violently with water to form hydrogen gas and sodium hydroxide solution. » (b) The destruction of marble statuary by acid rain: aqueous nitric acid reacts with calcium carbonate to form carbon dioxide, water, and aqueous calcium nitrate. » (c) Halogen compounds exchanging bonding partners: phosphorus trifluoride is prepared by the reaction of phosphorus trichloride and hydrogen fluoride; hydrogen chloride is the other product. The reaction involves gases only. » (d) Explosive decomposition of dynamite: liquid nitroglycerine (C3H5N3O9) explodes to produce a mixture of gases—carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrogen, and oxygen Stoichiometric Calculations • The coefficients in a balanced equation give you a molar ratio of the reactants and products. This ratio is used to convert from one substance to another in a balanced chemical equation. • Solid lithium hydroxide is use in space vehicles to remove exhaled carbon dioxide from the living environment by forming solid lithium carbonate and liquid water. What mass of gaseous carbon dioxide can be absorbed by 1.00 kg of lithium hydroxide? – 9.20 x 102 g of CO2 Stoichiometric Calculation - Example • Baking soda is often used as an antacid. It neutralizes excess HCl acid secreted by the stomach: NaHCO3(s) + HCl(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(aq) Milk of Magnesia, which is an aqueous suspension of magnesium hydroxide, is also used as an antacid: Mg(OH)2(s) + 2HCl(aq) 2H2O(l) + MgCl2(aq) Which is the more effective antacid per gram, the baking soda or milk of magnesia? -Baking soda neutralizes 1.19 x10-2 mol HCl while milk of magnesia neutralizes 3.42 x10-2 mol HCl. So milk of magnesia is more effective. The Limiting Reactant The Limiting Reactant • This reactant limits the amount of product produced because it runs out first: – Nitrogen gas can be prepared by passing gaseous ammonia over solid copper (II) oxide at high temperatures. The other products of the reaction are solid copper and water vapor. If a sample containing 18.1 g of ammonia is reacted with 90.4 g of copper (II) oxide, how many grams of nitrogen will be formed? • 10.6 g of N2 Percent Yield • The actual yield of product is generally given as a percentage calculated from the following formula: % Yield = actual yield x 100 theoretical yield % Yield Example • Silicon carbide (SiC) is an important ceramic material that is made by allowing sand (silicon dioxide, SiO2) to react with powdered carbon at high temperature. Carbon monoxide is also formed. When 100.0 kg of sand is processed, 51.4 kg of SiC is recovered. What is the percent yield? Sources • (Silberberg, Martin S.. Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change, 5th Edition. McGraw-Hill, 012009. 3.7.5). MC #1 How many grams of calcium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2, contains 24 grams of oxygen atoms? (A) 164 grams (B) 96 grams (C) 62 grams (D) 50. grams (E) 41 grams MC #2 The simplest formula for an oxide of nitrogen that is 36.8 percent nitrogen by weight is (A) N2O (B) NO (C) NO2 (D) N2O3 (E) N2O5 MC #3 When a hydrate of Na2CO3 is heated until all the water is removed, it loses 54.3 percent of its mass. The formula of the hydrate is (A) Na2CO3 . 10 H2O (B) Na2CO3 . 7 H2O (C) Na2CO3 . 5 H2O (D) Na2CO3 . 3 H2O (E) Na2CO3 . H2O MC #4 In which of the following compounds is the mass ratio of chromium to oxygen closest to 1.6 to 1.0? (A) CrO3 (B) CrO2 (C) CrO (D) Cr20 (E) Cr2O3 MC #5 When hafnium metal is heated in an atmosphere of chlorine gas, the product of the reaction is found to contain 62.2 percent Hf by mass and 37.4 percent Cl by mass. What is the empirical formula for this compound? (A) HfCl (B) HfCl2 (C) HfCl3 (D) HfCl4 (E) Hf2Cl3 FRQ #1 The molecular formula of a hydrocarbon is to be determined by analyzing its combustion products. • (a) The hydrocarbon burns completely, producing 7.2 grams of water and 7.2 liters of CO2 at standard conditions. What is the empirical formula of the hydrocarbon? • (b) Calculate the mass in grams of O2 required for the complete combustion of the sample of the hydrocarbon described in (a). • (c) With a molar mass of 56.2 g/mol, what is the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon? FRQ #2 CH4(g) + 2 Cl2(g) CH2Cl2 (g) + 2 HCl(g) • Methane gas reacts with chlorine gas to form dichloromethane and hydrogen chloride, as represented by the equation above. (a) A 25.0 g sample of methane is placed in a reaction vessel containing 2.58 mol of Cl2(g). (i) Identify the limiting reactant when the methane and chlorine gases are combined. Justify your answer with a calculation. (ii) Calculate the total number of moles of CH2Cl2(g) in the container after the limiting reactant has been totally consumed. FRQ #3 Answer the following questions about acetylsalicylic acid, the active ingredient in aspirin. • (a) The amount of acetylsalicylic acid in a single aspirin tablet is 325 mg, yet the tablet has a mass of 2.00 g. Calculate the mass percent of acetylsalicylic acid in the tablet. • (b) The elements contained in acetylsalicylic acid are hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen. The combustion of 3.000 g of the pure compound yields 1.200 g of water and 6.602 g of carbon dioxide. Calculate the mass, in g, of each element in the 3.000 g sample.