ppt
advertisement

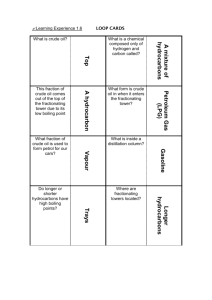
Fun easy Mole All about pts with Conversion Crude Oil nothing to Vocabulary s& and do about Formulas Petroleum Chem Misc. 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 Question 1 - 10 • What is the formula to convert from MOLES to GRAMS: • Moles Grams Answer 1 – 10 • # moles X (molar mass/1 mole) = mass (g) Question 1 - 20 • What is the formula to convert from GRAMS to MOLES • Grams moles Answer 1 – 20 • Mass (g) X (1mole/molar mass) = # of moles Question 1 - 30 • What is the mass of one mole of water? Answer 1 – 30 • 18 grams! • Work: 2(2) + 16 = 18 grams Question 1 - 40 • How many moles of propane C3H8 are in 250.00g of propane? Answer 1 – 40 • 5.7 moles – Work: 250g X (1 mol/44 g) = 5.7 moles Question 1 - 50 • Calculate the molar mass for (NH4)2SO4 Answer 1 – 50 • 132.1 g/mol Question 2 - 10 • Ms. Musta named her newborn……? Answer 2 – 10 • Exyn Question 2 - 20 • Ms. Y’s full last name (must pronounce it correctly) is……. Answer 2 – 20 • Ms. Yackanin Question 2 - 30 • Your new sub will be starting next week. Her name is…. Answer 2 – 30 • Ms. Bell! Question 2 - 40 • Where can you find any and all resources to do well on this test? Answer 2 – 40 • On Ms. Musta’s website! Question 2 - 50 • Where (what school) and what grade did Ms. Yackanin teach last semester? Answer 2 – 50 • Mount Elden Middle School • 8th grade Question 3 - 10 • What is a mole?? • Does a mole account for a large or small amount? Answer 3 – 10 • It is a counting unit for chemistry. • It is a large (huge!) amount Question 3 - 20 • What are hydrocarbons? Answer 3 – 20 • Molecular compounds that contain the elements HYDROGEN and CARBON only Question 3 - 30 • What is an isomer? Answer 3 – 30 • It is a compound with the same MOLECULAR structure as another but with a DIFFERENT structure. – Example: Question 3 - 40 • A catalyst does what? • A basic example of a catalyst is when we introduce an ________ into a reaction. Answer 3 – 40 • Changes the rate of the reaction • An enzyme Question 3 - 50 • Combustion is? Answer 3 – 50 • A special type of oxidation that hydrocarbons go through Question 4 - 10 • Is petroleum a renewable or nonrenewable resources? • Crude oil is the same thing as: – Normal oil and gases – Fossils – Petroleum – Coal – Gasoline Answer 4 – 10 • Nonrenewable • Petroleum Question 4 - 20 Why is crude oil superheated in the refinery process? Answer 4 – 20 The hydrocarbons in the crude oil can be separated based on their boiling point. Question 4 - 30 • When superheated (to boiling point), small hydrocarbon would have a __________ boiling point where as a larger hydrocarbon would have _________ boiling point. • Low • High Answer 4 – 30 • Small hydrocarbon is characterized by a low boiling point • Large hydrocarbon is characterized by a high boiling point Question 4 - 40 • We learned that petroleum in the refining process produces several distinctive mixtures called ______________ ? – Hint: We learned about 7 of those last week Answer 4 – 40 • Fraction Question 4 - 50 • A petroleum is defined as what? Answer 4 – 50 • A collection of hydrocarbons of similar length found in the crude oil Question 5 - 10 • What does the hydrotreating process remove from the hydrocarbon fractions? Answer 5 – 10 • It removes impurities: – Examples are sulfur, metals, and nitrogen Question 5 - 20 • In naming organic compounds, an alkane is what?? Answer 5 – 20 • Compounds with a single bond between carbon atoms Question 5 - 30 • In naming organic compounds, what is an alkene? Answer 5 – 30 • Compounds with atleast one double bond between carbon atoms Question 5 - 40 • What do we mean that a hydrocarbon can go through combustion? • Why do hydrocarbons make good fuels? Answer 5 – 40 • We are burning it • They produce a lot of energy when combusted Question 5 - 50 • How do we know if a compound is organic or inorganic? • Is H2O organic or inorganic? Answer 5 – 50 • It contains a carbon atom • Inorganic