Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Fourth Edition Chapter 11
advertisement

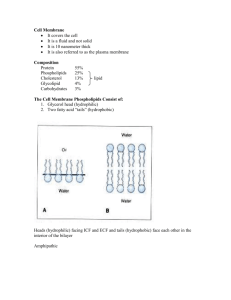
David L. Nelson and Michael M. Cox Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry Fourth Edition Chapter 11: Biological Membranes and Transport Copyright © 2004 by W. H. Freeman & Company 1 Chapter Outline • The composition and architecture of membranes • Membrane dynamics • Solute transport across membranes 2 The composition and architecture of membranes • Proteins • Polar lipids • Carbohydrates (glycoproteins, glycolipids) 3 Different types of membrane have different protein/lipid proportions 4 Membrane lipids varies for different organelles from the same cell 5 6 7 Types of integral proteins 8 9 10 Fluidity of biological membranes • Sat’d FA • Unsat’d FA • Cholesterol • Temperature Decide the membrane fluidity. 11 12 13 FRAP (flourescence recovery after photobleaching) 14 15 16 17 18 Type of transporter • Carrier (carrier, pump) : binding site binds to ligand; can go against concentration gradient • Channel : must from high low, gate is present 19 Type of transport system • Simple diffusion • Facilitated diffusion • Active transport – Primary: need pump, energy from ATP or light – Secondary: need carrier, energy from ion gradient • Ion channel: from high low 20 Need protein carrier? NO YES Simple diffusion Saturable with substrate? NO Ion channels Produces concentration gradient? NO Facilitated transport ATP, light, substrate oxidation Primary active transport YES YES Energy source? Ion gradient Secondary active transport 21 22 23 24 GLUT1 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 P-type ATPase • Na+-K+ ATPase • Ca2+ ATPase Maintaining the differences in the ionic composition of the cytosol and the extracellular medium 33 34 ABC transports 35 36 Aquaporins 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44